Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:30PM-1:45PM
Background/Purpose: Existing cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk stratification strategies underperform in RA. Lung disease is an established CVD risk factor, and RA-interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) clinically affects 1 in 10 RA patients. As RA-ILD is not captured by current CVD risk calculators, we evaluated RA-ILD as a risk factor for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and heart failure (HF) in RA, and assessed the performance of the Predicting Risk of cardiovascular disease EVENTs (PREVENT) calculator in RA-ILD.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of patients with RA and RA-ILD using national Veterans Administration (VA) data (2000-2021). RA patients were identified using ≥2 diagnostic codes, a rheumatologist diagnosis, plus a positive autoantibody or DMARD dispense. RA-ILD was defined at baseline and in follow up, using a validated RA-ILD administrative algorithm (PPV >80%). Cohort entry was the date the RA algorithm was fulfilled or the date of RA-ILD diagnosis (if ILD developed in follow up). Overall CVD, MACE (myocardial infarction, stroke), and HF were identified in VA, Medicare, and National Death Index data. Those with pre-existing MACE or HF were excluded. Cox regression was used to estimate the risk of CVD related to RA-ILD status, adjusted for age, sex, race, BMI, smoking status, CVD risk factors, rurality, and healthcare utilization. PREVENT variables were queried in the 12 months prior to cohort entry. Estimated 10-year risk of overall CVD, MACE and HF was calculated and PREVENT categories (low/borderline, intermediate, high risk) were described. Calibration (standardized incidence ratios [SIR = observed:predicted event rate]) and discrimination (Harrell’s C statistic, sensitivity using cutoff of 7.5%) of PREVENT were compared between those with and without RA-ILD.
Results: We studied 69,915 RA patients (mean age 63, 87% male). Patients with RA-ILD (Nf3,620) were more frequently smokers, seropositive, with more traditional CVD risk factors and healthcare utilization. Over 613,200 person-years, 17,713 overall CVD events occurred. The incidence of all CVD outcomes was higher in RA-ILD, as were unadjusted hazards for overall CVD (HR 1.93 [1.81-2.07]), MACE (1.49 [1.37-1.63]), and HF (2.46 [2.26-2.68], Table 1). In adjusted models, the risk of overall CVD (aHR 1.19 [1.11, 1.28]) and HF (1.44 [1.31, 1.58]) persisted, while MACE risk was null in RA-ILD vs. RA without ILD (0.98 [0.90, 1.07], Table 1). A greater percentage of patients with RA-ILD were categorized as high risk (overall CVD: 36.3% vs 19.1%; Table 2) using PREVENT, which demonstrated improved calibration (overall CVD SIR 1.49 vs. 2.07) and sensitivity (93.1 vs. 82.6%) in RA-ILD vs. RA without ILD (Table 3). Harrel’s C was similar regardless of RA-ILD.
Conclusion: RA-ILD was associated with higher CVD risk in RA, driven by increased HF risk, possibly due to the effect of pulmonary hypertension and chronic hypoxia on cardiac function. Reflecting a high comorbidity burden, RA-ILD patients were more frequently categorized as high risk by PREVENT, which may in turn improve calibration of PREVENT in RA-ILD. Whether early identification and management of RA-ILD may help mitigate the elevated HF risk observed in RA requires continued research.
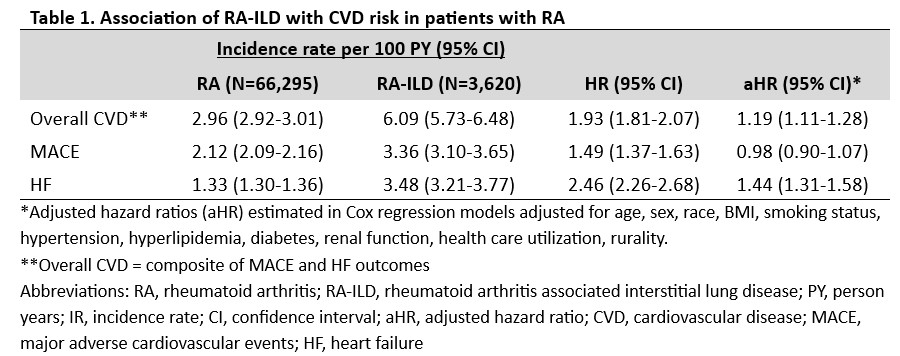 Table 1. Association of RA-ILD with CVD risk in patients with RA
Table 1. Association of RA-ILD with CVD risk in patients with RA
.jpg) Tabe 2. Baseline 10-year CVD risk in RA and RA-ILD according to PREVENT calculator
Tabe 2. Baseline 10-year CVD risk in RA and RA-ILD according to PREVENT calculator
.jpg) Table 3. Performance of the PREVENT CVD risk calculator in RA-ILD vs. RA without ILD
Table 3. Performance of the PREVENT CVD risk calculator in RA-ILD vs. RA without ILD
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khan O, Frideres H, Roul P, Cannon G, Kunkel G, Sauer B, Baker J, Mikuls T, England B, Johnson T. Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Risk Calculator Performance in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-disease-risk-and-risk-calculator-performance-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-disease-risk-and-risk-calculator-performance-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/
