Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1553–1591) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) is an entity defined by clinical features of differentiated connective tissue diseases (dCTD), such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), systemic sclerosis (SSc), or idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) and the presence of autoantibodies directed toward ribonucleoprotein U1. Although juvenile onset MCTD (jMCTD) occurs in 7-23% of all MCTD cases, few studies have examined the course of jMCTD patients. The aim of the present study was to describe the characteristics, treatments, long-term outcomes of jMCTD, in comparison to adult onset MCTD patients.
Methods: We conducted a multicentric case-control, retrospective, observational, and longitudinal study in the French MCTD cohort. Adult and jMCTD patients were included if they fulfilled, at time of disease onset, at least one of the 4 sets of MCTD diagnosis criteria without fulfilling any current classification criteria for a dCTD. jMCTD patients were defined by an age < 18 years old (y.o) at disease onset. For each jMCTD, 3 adult controls were randomly matched for sex, date of inclusion and follow-up duration.
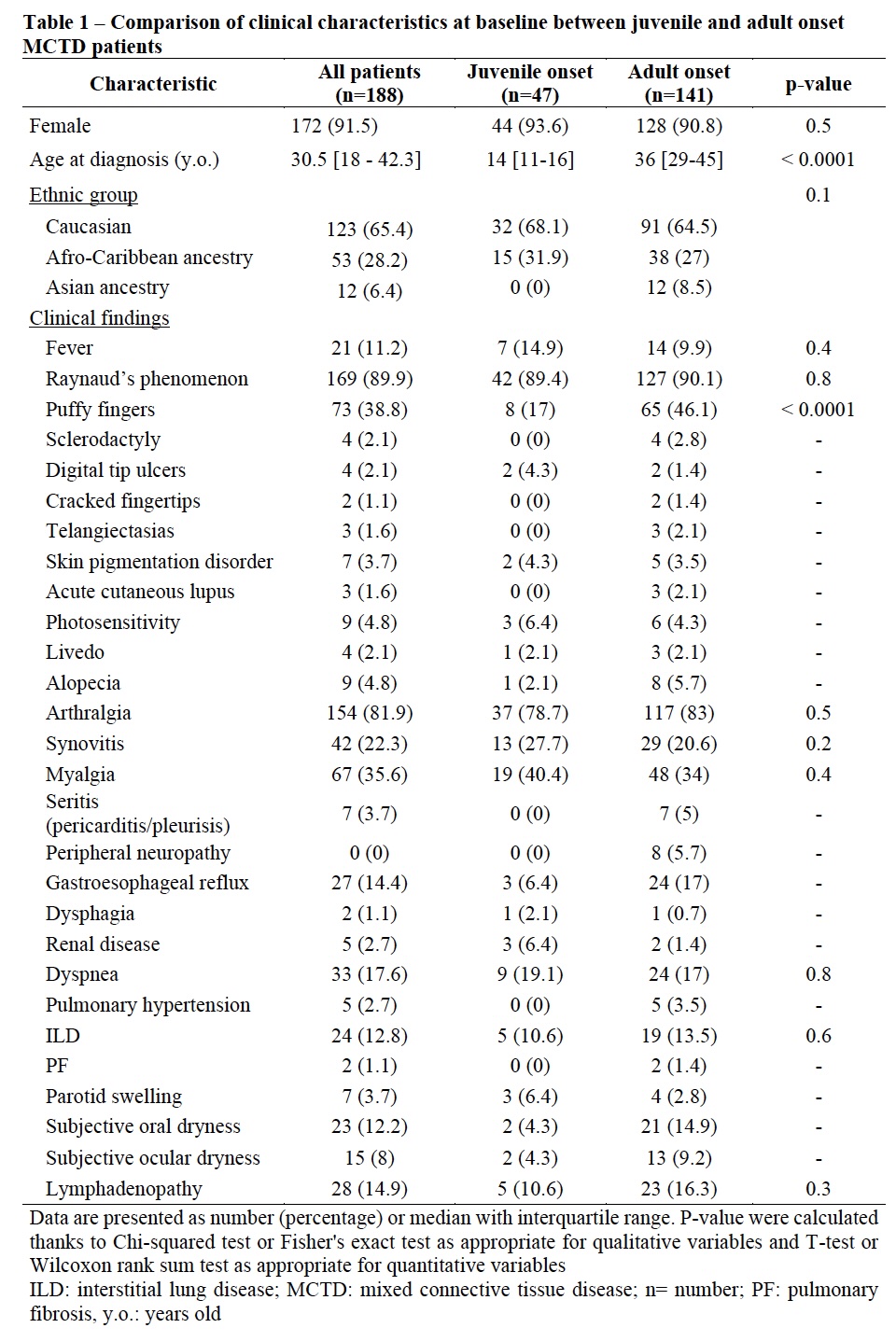
Results: Forty-seven jMCTD patients (44 (93.6%) girls with a median age of 14 [11-16] y.o) at disease onset were included. Forty-four (93.6%) patients met either Sharp or Kasukawa diagnostic criteria and 41 (87.2%) met both diagnostic criteria while none met other classification criteria without fulfilling Sharp or Kasukawa criteria (Figure 1). At diagnosis, jMCTD patients had less frequently puffy fingers (p < 0.0001) and higher creatine kinase level (p< 0.001) compared to adult-onset patients (Table 1). Among jMCTD, 26 (55.3%) had received hydroxychloroquine at MCTD diagnosis and 45 (95.7%) during follow-up. jMCTD patients were treated with higher dose of glucocorticoids (p=0.02) and more frequently with rituximab (p=0.01) than adults. After 118 [79-194] months follow-up, jMCTD patients had less frequently puffy fingers (p=0.003), oral dryness (p=0.02) but more renal disease (p=0.02) and were more often in remission than adult-onset patients (p=0.04). In addition, 2 (4.3%) jMCTD patients developed pulmonary hypertension (vs. 12, 8.5% in adults; p=0.5), 11 (23.4%) interstitial lung disease (vs. 45, 31.9%; p=0.3 in adults) and 1 (3.1%) died (vs. 7, 5% in adults). Seventeen (36.2%) jMCTD patients evolved toward a dCTD (vs. 43, 30.5% in adult-onset, p=0.5) (Table 2). During follow-up, occurrence of dyspnea (p=0.02), restrictive pattern (p=0.002) or altered DLCO on pulmonary function tests (p=0.005), lymphopenia (p=0.03), and hypergammaglobulinemia (p=0.05), were associated with absence of remission.
Conclusion: This works reports that jMCTD and adult-onset patients share the same phenotype. As for adult-onset patients, Sharp and Kasukawa criteria are sufficient to diagnose MCTD. It shows that jMCTD are treated with higher doses of GC and more frequently with rituximab than adult-onset patients. Importantly, jMCTD patients develop more frequently renal disease but more often reach remission, especially in the absence of respiratory function impairment, as compared to adult-onset patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chevalier K, Bader-Meunier B, Kone-Paut I, Torreau B, Michel M, Godeau B, AGARD C, Papo T, Sacré K, Seror R, Mariette X, Patrice C, Benhamou Y, Leclercq M, goujard C, Lambotte O, Bonnotte B, Samson M, Ackermann F, Schmidt J, Duhaut P, Kahn J, Hanslik T, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Terrier B, REGENT A, Dunogue b, Cohen P, Le Guern V, HACHULLA E, Mouthon L, Chaigne B. Clinical presentation, course, treatment and outcome of juvenile onset versus adult onset mixed connective tissue disease patients: a multicenter retrospective cohort. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-presentation-course-treatment-and-outcome-of-juvenile-onset-versus-adult-onset-mixed-connective-tissue-disease-patients-a-multicenter-retrospective-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-presentation-course-treatment-and-outcome-of-juvenile-onset-versus-adult-onset-mixed-connective-tissue-disease-patients-a-multicenter-retrospective-cohort/

.jpg)
.jpg)