Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1553–1591) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The skin from patients with Very Early Diagnosis of Systemic Sclerosis (VEDOSS) already exhibits fibrotic alterations such as collagen deposition and perivascular infiltration (1), despite the absence of clinically detectable skin thickening. A distinct immune-mediated structural organization across the epidermis, sub-epidermal region, and dermis, is involved in both early and late stages of SSc [2] The sub-epidermal perivascular area, located between these layers, serves as a crucial immune-fibro-vascular niche that may play a role in early fibrotic remodeling useful for determining SSc progression and identifying novel therapeutic applications.Objectives: To identify key signaling and cell types involved in the sub-epidermal perivascular regions within Very Early Diagnosis of Systemic Sclerosis (VEDOSS) compared to those with established disease and healthy control using spatial transcriptomic analyses.
Methods: We employed digital spatial transcriptomics to map whole genome transcriptome expression in the area immediately surrounding CD34-stained vessels in the sub-epidermal regions. Differentially expressed genes (p < 0.05, log2FC >0) were analyzed to identify relevant canonical pathways and biological processes.
Results: Six skin biopsies from VEDOSS were compared with six biopsies from healthy individuals or patients with developed systemic sclerosis (SSc). Cell deconvolution revealed that the sub-epidermal region was dominated by diverse fibroblast subsets and vascular endothelial cells, with notable representation of immune populations such as T cells and macrophages. Disease-associated shifts included early depletion of secretory papillary fibroblasts in VEDOSS, enrichment of lymphatic endothelial cells, and progressive erythrocyte loss. Pathway Analysis of the sub-epidermal region in VEDOSS compared to healthy controls revealed significant upregulation of key stress and immune-related pathways. Notable among these were Cellular response to hypoxia, Oxidative Phosphorylation, Neutrophil Degranulation, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and pulmonary idiopathic fibrosis signaling pathway. Key genes significantly upregulated included cyclophilin A, CD47, ATP5MG, COX10, NDUFB9, S100A4, COL1A1, COL16A1, COL17A1, COL21A1, FN1, PIK3R2, PIK3C2B, PDGFRB, implying cellular remodeling and stromal transitions through associated signaling pathways involved in fibrosis.
Conclusion: We demonstrate that the sub-epidermal perivascular region is a transcriptionally dynamic niche in VEDOSS skin, where early immune, metabolic, and fibrotic reprogramming converges to initiate stromal remodeling before the onset of clinically detectable fibrosis and progression to SSc.References: [1] R[1] R. L. Ross et al., “Biological hallmarks of systemic sclerosis are present in the skin and serum of patients with Very Early Diagnosis of Systemic Sclerosis (VEDOSS),” Rheumatology, p. keae698, Dec. 2024, doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae698.[2] Z. Li et al., “Mapping spatially-resolved transcriptomes in systemic sclerosis,” bioRxiv, p. 2025.01.14.632962, Jan. 2025, doi: 10.1101/2025.01.14.632962.
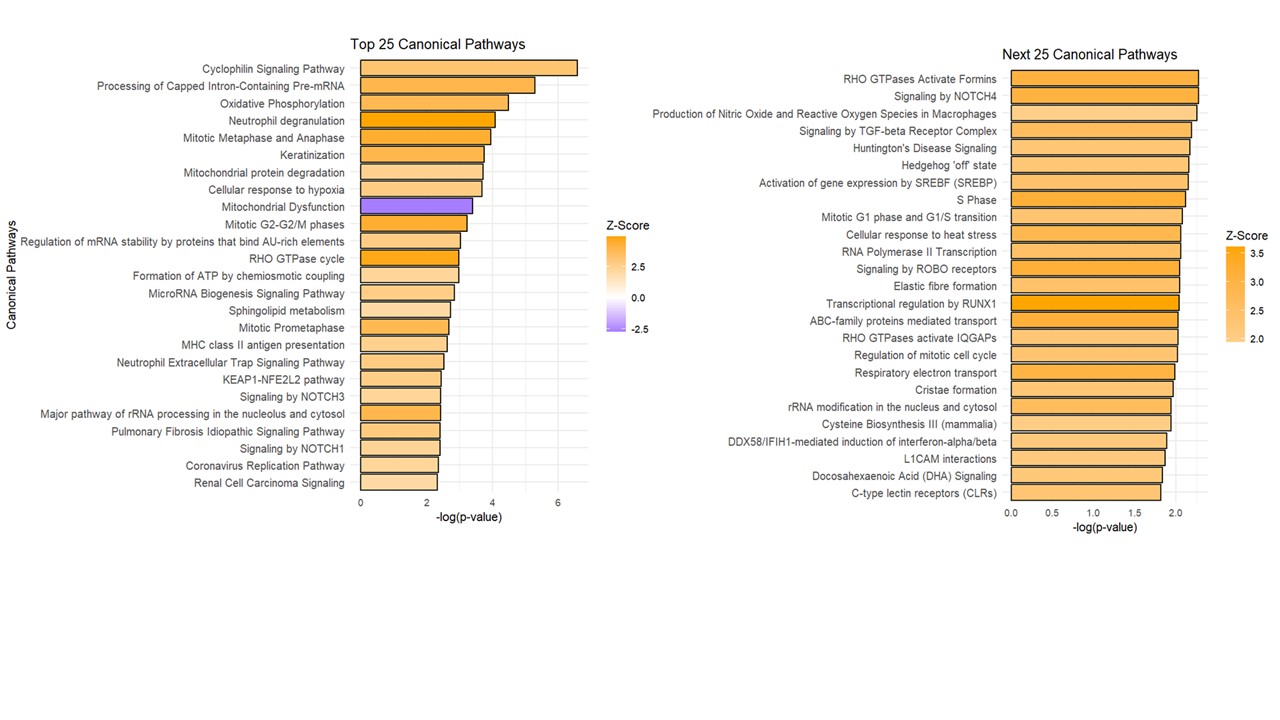 Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the subepidermal region of interest (ROI), comparing VEDOSS with healthy controls. Pathways with an absolute z-score > 2 and p-value < 0.001 were considered significantly activated (z ≥ 2) or inhibited (z ≤ –2). Orange are predicted activated pathways and blue predicted inhibited.
Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the subepidermal region of interest (ROI), comparing VEDOSS with healthy controls. Pathways with an absolute z-score > 2 and p-value < 0.001 were considered significantly activated (z ≥ 2) or inhibited (z ≤ –2). Orange are predicted activated pathways and blue predicted inhibited.
.jpg) Representative examples of subepidermal regions of interest (ROIs) selected from the 54 ROIs analyzed.
Representative examples of subepidermal regions of interest (ROIs) selected from the 54 ROIs analyzed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bamigbola I, Vadakekolathu J, Di Donato S, Kakkar V, Ross R, El-Sherbiny Y, Del Galdo F. Spatial Transcriptomics of Perivascular Subepidermal Regions in Very Early Systemic Sclerosis Unveils Cellular and Mitochondrial Stress-Driven Innate Immune Signatures that Initiate Stromal Remodeling [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spatial-transcriptomics-of-perivascular-subepidermal-regions-in-very-early-systemic-sclerosis-unveils-cellular-and-mitochondrial-stress-driven-innate-immune-signatures-that-initiate-stromal-remodeling/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spatial-transcriptomics-of-perivascular-subepidermal-regions-in-very-early-systemic-sclerosis-unveils-cellular-and-mitochondrial-stress-driven-innate-immune-signatures-that-initiate-stromal-remodeling/
