Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1434–1466) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Spinal inflammation and structural progression are key features of radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA).1 Canada-Denmark (CANDEN) scoring enables anatomical-based assessments of MRI inflammatory and structural lesions by spinal compartment.2,3Bimekizumab (BKZ), a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits interleukin (IL)‑17F in addition to IL-17A, has shown sustained efficacy and safety to 2 years in patients (pts) with r-axSpA in the phase 3 study BE MOBILE 2 and its open-label extension (OLE), and to 5 years in a phase 2b study.4,5 Here, from BE MOBILE 2 and its OLE, we present the first 2-year evaluation of the effects of a biologic treatment (i.e., BKZ) on spinal MRI inflammatory and structural lesions in pts with r-axSpA using CANDEN scoring.
Methods: In BE MOBILE 2 (NCT03928743), pts with r-axSpA were randomized to subcutaneous BKZ 160 mg every 4 weeks (wks) or placebo (PBO); from Wk 16, all received BKZ. At Wk 52, eligible pts could enroll in the OLE (BE MOVING; NCT04436640).4Post hoc CANDEN scoring assessments were conducted in pts enrolled in the MRI sub-study who had evaluable spinal MRIs at all four timepoints: baseline, Wk 16, 52, and 104. All readers were blinded to timepoint. We report mean change from baseline (CfB) at Wk 16, 52, and 104 in total spinal inflammation score and subscores for inflammation in vertebral bodies (corners and non-corners), posterolateral elements, and facet joints, and total spinal structural lesions scores (fat, erosions, new bone formation). All data use observed case.
Results: 140/332 (42.2%) pts in BE MOBILE 2 had MRIs eligible for CANDEN scoring. 102 pts had CANDEN scores at baseline, Wk 16, 52, and 104 (PBO/BKZ: n=38; BKZ: n=64). Baseline characteristics of these pts were largely comparable between treatment arms and with the overall population. A greater reduction from baseline in total spinal inflammation was seen at Wk 16 with BKZ vs PBO. After switching to BKZ at Wk 16, PBO-randomized pts had an improvement from baseline comparable to BKZ-randomized patients at Wk 52, both of which were largely sustained at Wk 104 (Figure 1A). This was also observed for vertebral body (corners only) and posterolateral elements inflammation (Figure 1B, 1D). Data for vertebral body (non-corners only) and facet joint inflammation are shown in Figure 1C, 1E.At Wk 16, a greater increase from baseline in fat lesions was seen with BKZ vs PBO. BKZ-randomized pts had minimal change in fat lesions from Wk 16 to Wk 104. After switching to BKZ, PBO-randomized pts had an increase in fat lesions at Wk 52 and then minimal change at Wk 104 (Figure 2). Minimal changes were observed in new bone formation and erosion to Wk 104.
Conclusion: In pts with r-axSpA, comprehensive scoring of spinal inflammatory and structural lesions using CANDEN showed BKZ led to a rapid and sustained long-term reduction in individual components of spinal MRI inflammation, an initial increase in fat lesions with minimal subsequent change, and minimal changes in new bone formation and erosion over two years.References: 1. Navarro-Compán V. Lancet 2025;405:159–72; 2. Tu L. Front Immunol 2021;12:700260; 3. Krabbe S. RMD Open 2019;5:e001057; 4. Baraliakos X. Rheumatology 2025;keaf009; 5. Deodhar A. RMD Open 2025;11:e005081.
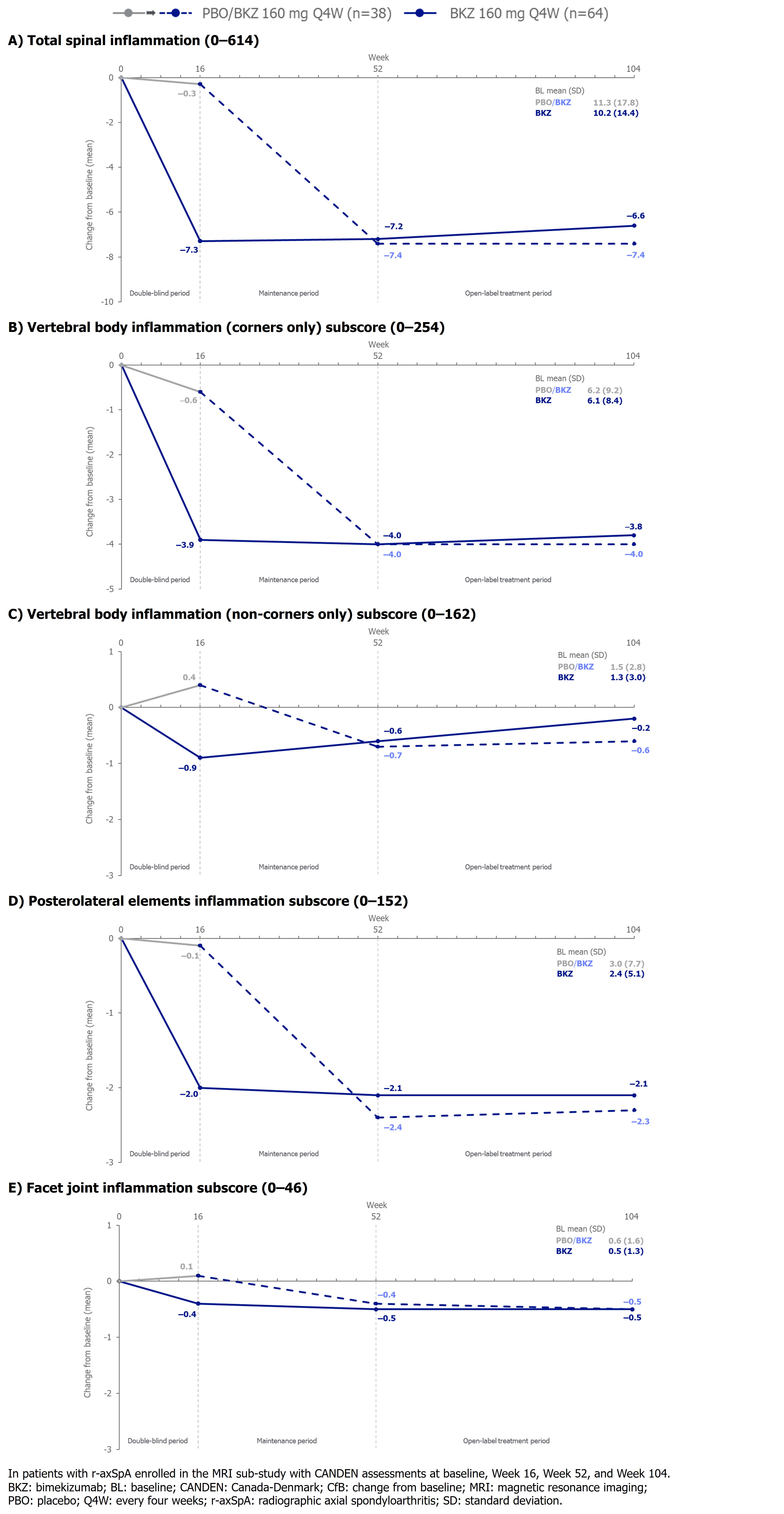 Figure 1. Change from baseline in CANDEN total inflammation score and subscores to Week 104 (observed case)
Figure 1. Change from baseline in CANDEN total inflammation score and subscores to Week 104 (observed case)
.jpg) Figure 2. Change from baseline in CANDEN total fat lesion score to Week 104 (observed case)
Figure 2. Change from baseline in CANDEN total fat lesion score to Week 104 (observed case)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, Lambert R, Navarro-Compan V, Baraliakos X, Coarse J, de Peyrecave N, Ostergaard M. Impact of Bimekizumab on Spinal MRI Inflammation and Structural Lesions in Patients with Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: 2-Year CANDEN Scoring Results from a Phase 3 Study and Its Open-Label Extension [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-bimekizumab-on-spinal-mri-inflammation-and-structural-lesions-in-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-2-year-canden-scoring-results-from-a-phase-3-study-and-its-open-label-ext/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-bimekizumab-on-spinal-mri-inflammation-and-structural-lesions-in-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-2-year-canden-scoring-results-from-a-phase-3-study-and-its-open-label-ext/
