Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The computed tomography (CT) syndesmophyte score (CTSS) has shown to be more sensitive in capturing spinal structural damage progression in axial SpA (axSpA), compared to the current gold standard, the modified Stoke Ankylosis Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) (de Koning A et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2018). Additionally, assessing facet joint ankylosis (FJA) on CT seems promising in further detecting progression (Stal R et al, Rheumatology 2020). We investigated whether a score combining syndesmophytes and FJA is more sensitive than CTSS for assessing spinal damage progression in axSpA.
Methods: Data from the Sensitive Imaging in Ankylosing Spondylitis cohort were used, including axSpA patients fulfilling the modified New York criteria and with ≥1 syndesmophyte. Conventional radiography (CR) and low-dose computed tomography (ldCT) of the spine were performed at baseline and 2 years (2Y) and scored by 3 (CR) or 2 (ldCT) central readers, blinded for time order. Syndesmophytes were assessed on CR and ldCT by the mSASSS and CTSS, respectively (Figure 1). The presence of FJA was evaluated on ldCT with the facet ankylosis score (FAS) on 19 facet joints (levels C5-T2 excluded due to poor visibility). The total mSASSS, CTSS and FAS were calculated per reader at each timepoint. Three versions of a combined score of syndesmophytes and FJA were proposed and computed by adding the CTSS and FAS while giving equal weight to both components (CT facet ankylosis syndesmophyte spine score A [CTFASSS-A]), 50% (CTFASSS-B) or 100% more weight to FAS (CTFASSS-C). Change scores were calculated per reader by subtracting the baseline from the 2Y score and then averaged across readers. The number of patients with positive and negative change as well as net change >0 and >0.5 were calculated for each score and compared. The total number of new or growing syndesmophytes and new FJA were calculated per reader and then averaged across readers.
Results: Forty-eight patients were included: mean (SD) age of 49 (9.7) years, 85% male, 81% HLA-B27+. Between baseline and 2Y, progression of spinal damage was observed as assessed by all scores: mean (SD) mSASSS 18.3 (14.3) vs 20.4 (15.1), CTSS 161.6 (127.1) vs 179.5 (132.3), FAS 8.2 (9.8) vs 9.4 (10.2). CTFASSS changed from 169.8 (134.5) (CTFASSS-A), 174.0 (138.4) (CTFASSS-B) and 178.1 (142.3) (CTFASSS-C) at baseline to 188.9 (140.0), 193.6 (143.9) and 198.3 (147.9) at 2Y, respectively.After 2Y, CTFASSS-A, CTFASSS-B and CTFASSS-C detected any net change in a higher percentage of patients compared to CTSS (96% vs 83%) and, most notably, to mSASSS (96% vs 46%) and FAS (96% vs 48%) (Table 1A). Moreover, considering all 48 patients, 472 new or growing syndesmophytes and 73 new FJA were detected on ldCT, denoting that the combined score captured 1.15 times more new bone formation than CTSS (545 vs 472 new lesions) (Table 1B).
Conclusion: A combined score assessing syndesmophytes and FJA captures more spinal structural damage progression in axSpA than assessing syndesmophytes alone. With respect to sensitivity to change, all CTFASSS proposals performed similarly, with the simple addition of CTSS and FAS (CTFASSS-A) being the most straightforward approach. However, further validation will define which is the best combination.
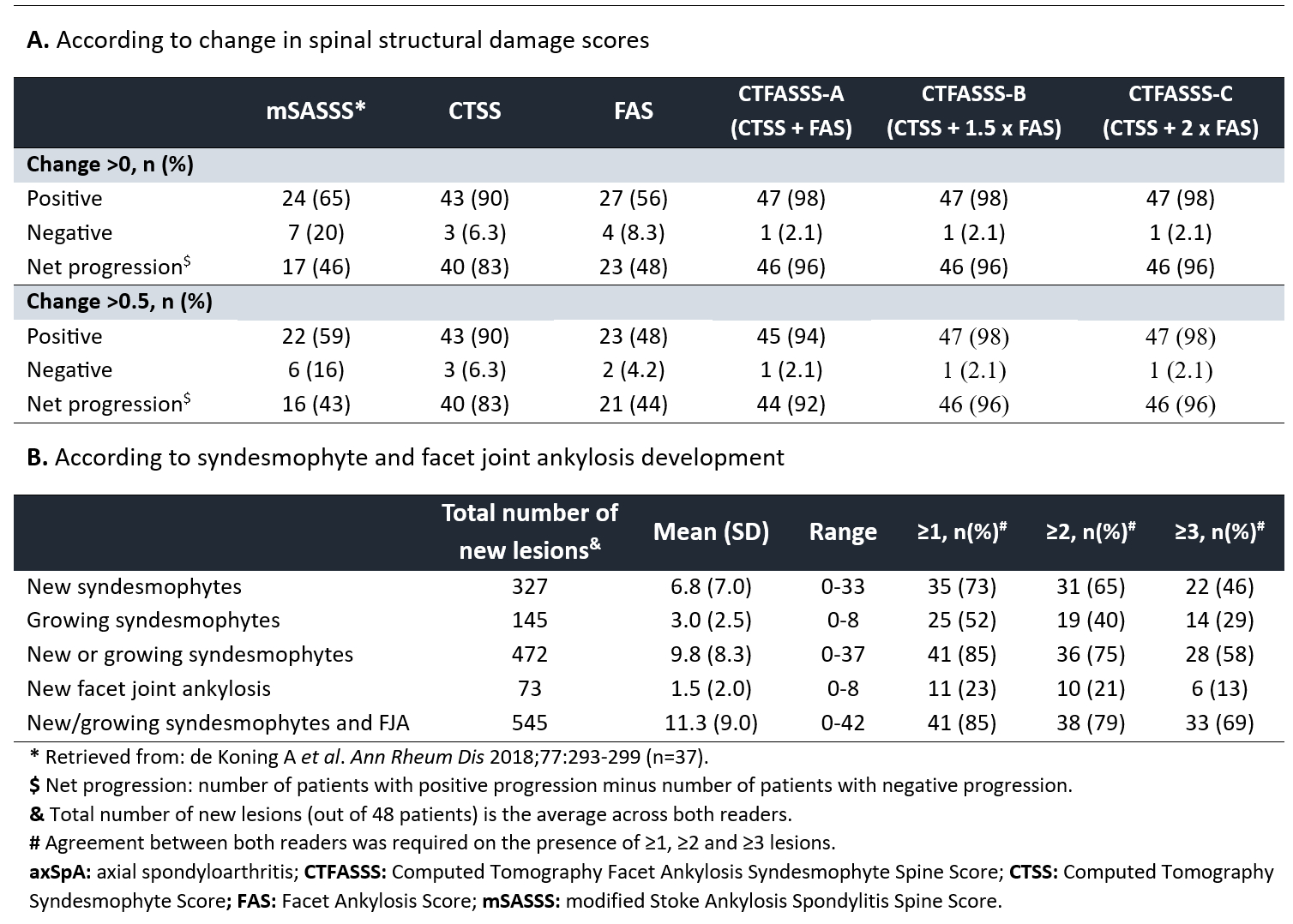 Figure 1. Schematic representation to guide the calculation of the mSASSS (A), CTSS (B), FAS (C) and CTFASSS (D)
Figure 1. Schematic representation to guide the calculation of the mSASSS (A), CTSS (B), FAS (C) and CTFASSS (D)
.jpg) Table 1. Number of axSpA patients with spinal structural damage progression on low-dose computed tomography (n=48)
Table 1. Number of axSpA patients with spinal structural damage progression on low-dose computed tomography (n=48)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bento da Silva A, van Gaalen F, Landewé R, de Hooge M, Marques M, van Lunteren M, de Bruin L, Ayan G, Baraliakos X, Reijnierse M, Braun J, Van Der Heijde D, Ramiro S. A Combined Score of Syndesmophytes and Facet Joint Ankylosis Improves Sensitivity to Spinal Structural Damage Progression in Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-combined-score-of-syndesmophytes-and-facet-joint-ankylosis-improves-sensitivity-to-spinal-structural-damage-progression-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-combined-score-of-syndesmophytes-and-facet-joint-ankylosis-improves-sensitivity-to-spinal-structural-damage-progression-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/
