Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1306–1346) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The six-minute walk distance (6MWD) measures functional capacity in cardiopulmonary diseases, predicts mortality in interstitial lung disease (ILD), and is used as an endpoint in trials. In RA, 6MWD correlates with patient-reported outcomes and adverse cardiovascular events, yet few studies investigate 6MWD in RA-ILD.
Methods: We performed a cross-sectional analysis using baseline data from the Korean RA-ILD (KORAIL) cohort, a multi-center prospective study. RA was diagnosed based on the 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria, and ILD was confirmed by chest CT imaging. Participants were assessed for RA disease activity using the DAS28 and laboratory tests, including ESR and CRP. ILD status was evaluated by chest CT and pulmonary function tests, including forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO). The expected lower limit of the six-minute walk distance (eLL-6MWD) was calculated based on age, sex, height, and weight. Associations of 6MWD or having a 6MWD below the expected lower limit (eLL-6MWD) with predictors were analyzed using linear or logistic regression, while their associations with progression or mortality were analyzed using Cox regression, adjusting for age, sex, height, and weight.
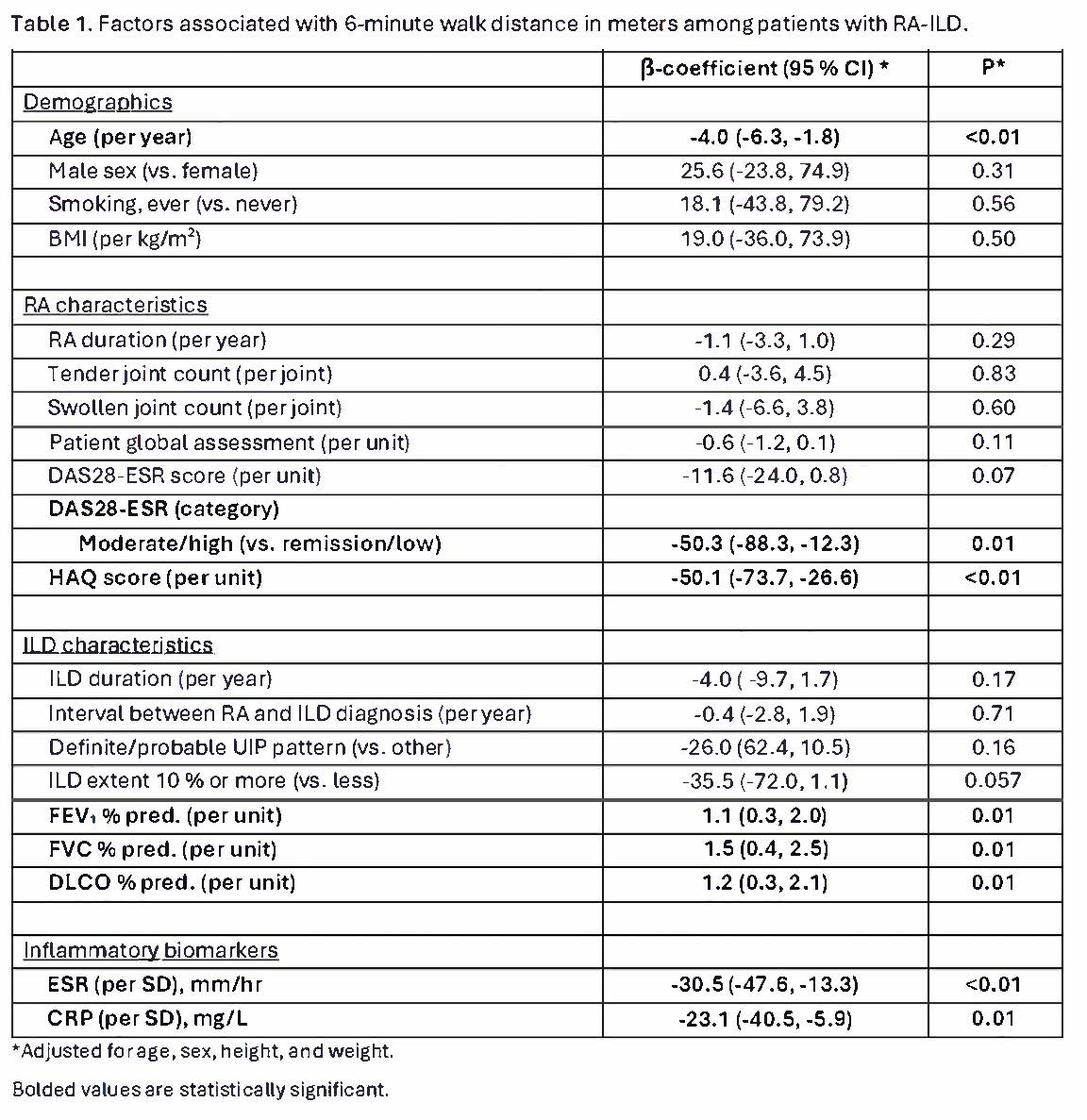
Results: We analyzed 141 patients with RA-ILD (mean age 66.7 years, 32.6% male, 61.7% with the usual interstitial pneumonia [UIP] pattern). The median RA duration was 6.0 years (interquartile range [IQR] 1.2 to 10.7), and the median ILD duration was 1.5 years (IQR 0.2 to 4.6). The mean DAS28-ESR score was 4.1 (standard deviation [SD] 1.4), with 70.7% of patients having moderate/high disease activity. ILD extent >10% on chest CT was present in 40.4%. The mean FVC% was 84.2 (SD 17.3), DLCO% was 71.3 (SD 19.4), and 6MWD was 339 meters (SD 113). Overall, 49.6% had a 6MWD below the eLL-6MWD. Participants with moderate or high disease activity demonstrated shorter six-minute walk distances (6MWD) compared to those in remission or low disease activity (β -50.3) (Table 1). Higher HAQ scores were also associated with shorter 6MWD (β -50.1) and higher ESR and CRP levels (ESR: -30.5 per SD; CRP: β -23.1 per SD). Higher FEV1%, FVC%, and DLCO% were associated with longer 6MWD (FEV1%: β 1.1, FVC%: β 1.5, DLCO%: β 1.2). The odds of having a 6MWD below eLL-6MWD were higher among participants with moderate or high disease activity (odds ratio [OR] 3.00), higher HAQ score (OR 3.08 per unit), higher ESR (OR 1.96 per SD), and higher CRP (OR 1.67 per SD) (Figure 1).No significant associations were observed between 6MWD and ILD progression (hazard ratio [HR] 1.00 per meter, 95%CI 1.00 to 1.00) or all-cause mortality (HR 1.00 per meter, 95%CI 0.99 to 1.00), nor between 6MWD below eLL-6MWD and ILD progression (HR 1.23, 95%CI 0.68 to 2.22) or all-cause mortality (OR 1.85, 95%CI 0.71 to 4.81).
Conclusion: In RA-ILD, older age, moderate/high RA disease activity, worse HAQ, and increased ESR and CRP were associated with shorter 6MWD, while high FEV1%, FVC%, and DLCO% were associated with longer 6MWD. Collectively, these results suggest that the 6MWD test may provide a simple functional assessment that encompasses pulmonary function as well as RA-related disease activity and function.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chang S, Ha Y, Lee S, Paudel M, McDermott G, Zhang Q, Kim M, Lee J, Park C, Kim J, Ha J, CHUNG S, Kang E, Lee Y, Park Y, Choe J, Lee E, Sparks J. Six-Minute Walk Distance as a Functional Measure in Rheumatoid Arthritis-associated Interstitial Lung Disease Reflecting Both Lung and Joint Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/six-minute-walk-distance-as-a-functional-measure-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-reflecting-both-lung-and-joint-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/six-minute-walk-distance-as-a-functional-measure-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-reflecting-both-lung-and-joint-involvement/

.jpg)