Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1248–1271) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Shared decision making (SDM) is outlined as the first overarching principle of the treat to target guidelines for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The quality of SDM varies across patient populations with many patients reporting poor communication around SDM. We sought to measure baseline patient-reported SDM in the usual care phase of an RCT designed to measure the impact of a multicomponent intervention to improve SDM among U.S. Veterans with RA and their clinicians. We also evaluated whether SDM correlated with baseline disease activity during this study phase.
Methods: Eligible Veterans with RA and moderate or high disease activity were invited to participate in this stepped-wedge, cluster-randomized trial at 4 U.S. Veterans Health Administration (VA) rheumatology clinics. SDM was assessed during a usual care phase of the trial using two brief, validated patient-reported measures (3-item CollaboRATE; 4-item SURE, yes/no response to: “feeling uncertain,” “feeling informed,” “feeling clear about values,” and “feeling supported in decision-making”). Questionnaires were completed in person on the day of a routine visit along with patient-reported disease activity scores (RAPID3). Participants were also queried on demographics and health literacy. Medications were collected from the medical record. Summary statistics with mean (standard deviation, SD), median, or percentages used for demographics, health literacy, medications, SDM measures, and disease activity. T-tests were used to compare disease activity between SURE scores dichotomized as ≥ 4 vs. < 4 (no decisional conflict v presence of decisional conflict).
Results: 213 adults with RA across 4 sites contributed data during the usual care phases of the study (October 2022-September 2024). Nearly 80% were receiving a conventional synthetic DMARD, 57% a biologic DMARD, and 5% a targeted synthetic DMARD. 75% were male, mean (SD) age 69 (10), 64% white, 23% Black or African American, and 21% had limited health literacy (Table 1). 75% of participants ranked SDM highly on the 3-item CollaboRATE measure (9 out of 9) reflecting top scores. 95% overall reported no decisional conflict by SURE (Table 2). RAPID3 scores did not vary by SDM, however participants with decisional conflict by the SURE measure had slightly higher RAPID3 scores [mean (SD) 16.8 (5.3)] compared with those without decisional conflict [mean (SD) 13.7 (5.2)] though these were not statistically different (Table 3).
Conclusion: One quarter of Veterans with RA and moderate to high disease activity reported suboptimal SDM, which is similar to prior studies among non-Veterans with RA reporting up to 30%, and 5% reported decisional conflict. Ceiling effects of SDM measures present challenges to efficiently and thoroughly measure SDM across many chronic conditions, as identified in this RA population. Future work will use mixed methods to evaluate the effect of a multicomponent intervention on improving SDM and RA disease activity, and whether effects vary by literacy level or other patient- or facility-level characteristics.
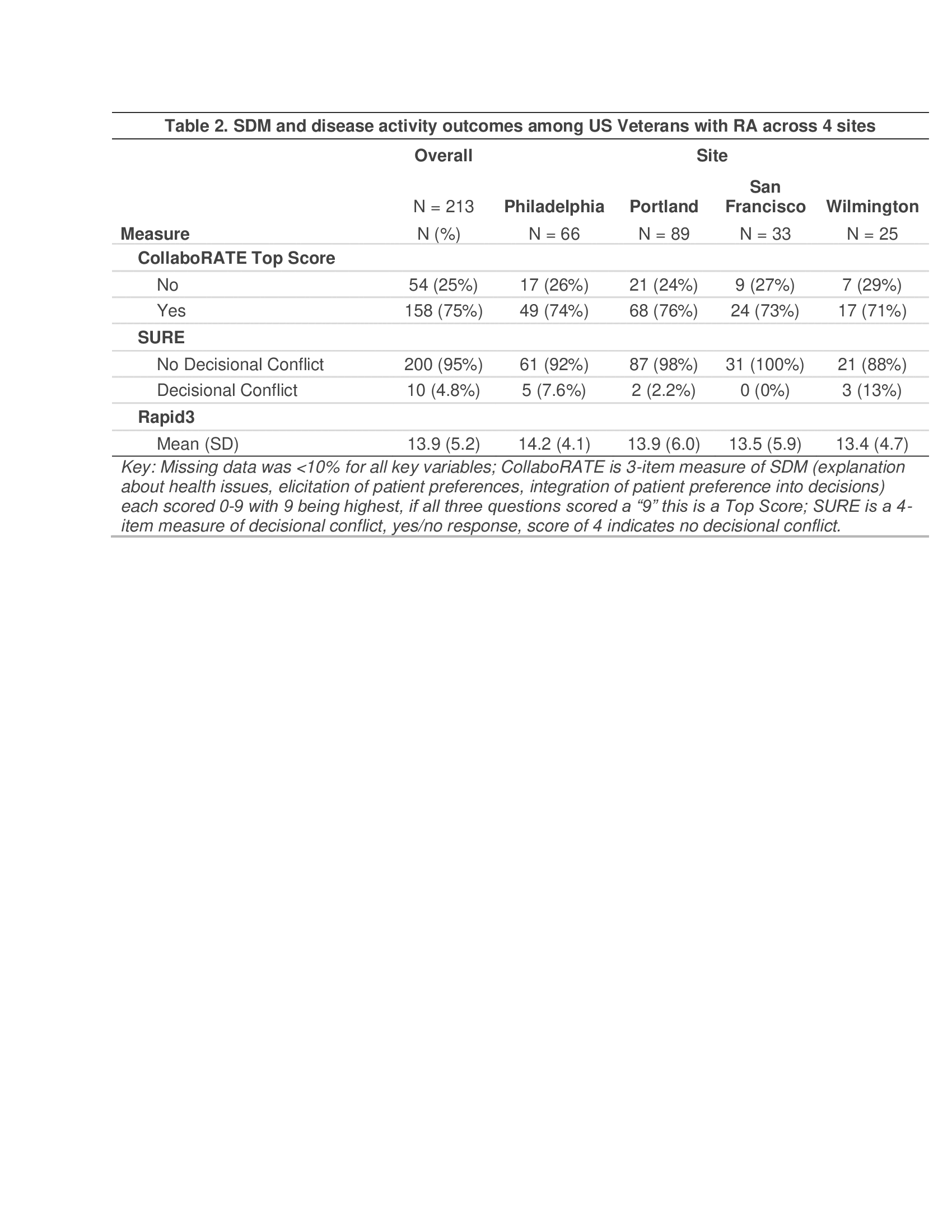 Table 1: Baseline characteristics of Veterans with RA enrolled during the usual care phase of an RCT of a multicomponent intervention to implement shared decision making (SDM)
Table 1: Baseline characteristics of Veterans with RA enrolled during the usual care phase of an RCT of a multicomponent intervention to implement shared decision making (SDM)
.gif) Table 2. SDM and disease activity outcomes among US Veterans with RA across 4 sites
Table 2. SDM and disease activity outcomes among US Veterans with RA across 4 sites
.gif) Table 3. RA Disease Activity by level of shared decision making and decisional conflict
Table 3. RA Disease Activity by level of shared decision making and decisional conflict
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Barton J, Baker J, Schmajuk g, Valiveti M, Bennett A, Morasco B, O'Neill A, Niederhausen M. Shared Decision Making in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Is RA disease activity associated with patient reported measures of shared decision making pre-SDM intervention? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/shared-decision-making-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-ra-disease-activity-associated-with-patient-reported-measures-of-shared-decision-making-pre-sdm-intervention/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/shared-decision-making-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-ra-disease-activity-associated-with-patient-reported-measures-of-shared-decision-making-pre-sdm-intervention/
