Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1248–1271) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Many patients with uncontrolled gout (UG) experience symptoms despite being on urate-lowering therapy (ULT), often requiring support from informal caregivers. UG impacts patients and caregivers, yet research remains limited. This real-world study assessed the impact of UG on health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and activities of daily living (ADL) from the perspectives of patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals in the United States (US). Results presented here focus on patients and caregivers.
Methods: A cross-sectional web-based survey was conducted among patients with UG and caregivers of such patients. Patients included adults (≥18 years) diagnosed with UG (a history of severe gout, defined as ≥2 gout flares within the last 12 months or presence of ≥1 gout tophus; and either currently taking a ULT or previously treated with uricase therapy in the past 18 months). Caregivers were unpaid adults currently caring for an adult with UG. Data collected included demographics, clinical characteristics, treatment information, and patient-reported outcomes (Work Productivity and Activity Impairment [WPAI] and 12-item Short Form Survey version 2 [SF-12v2]). Data were summarized descriptively.
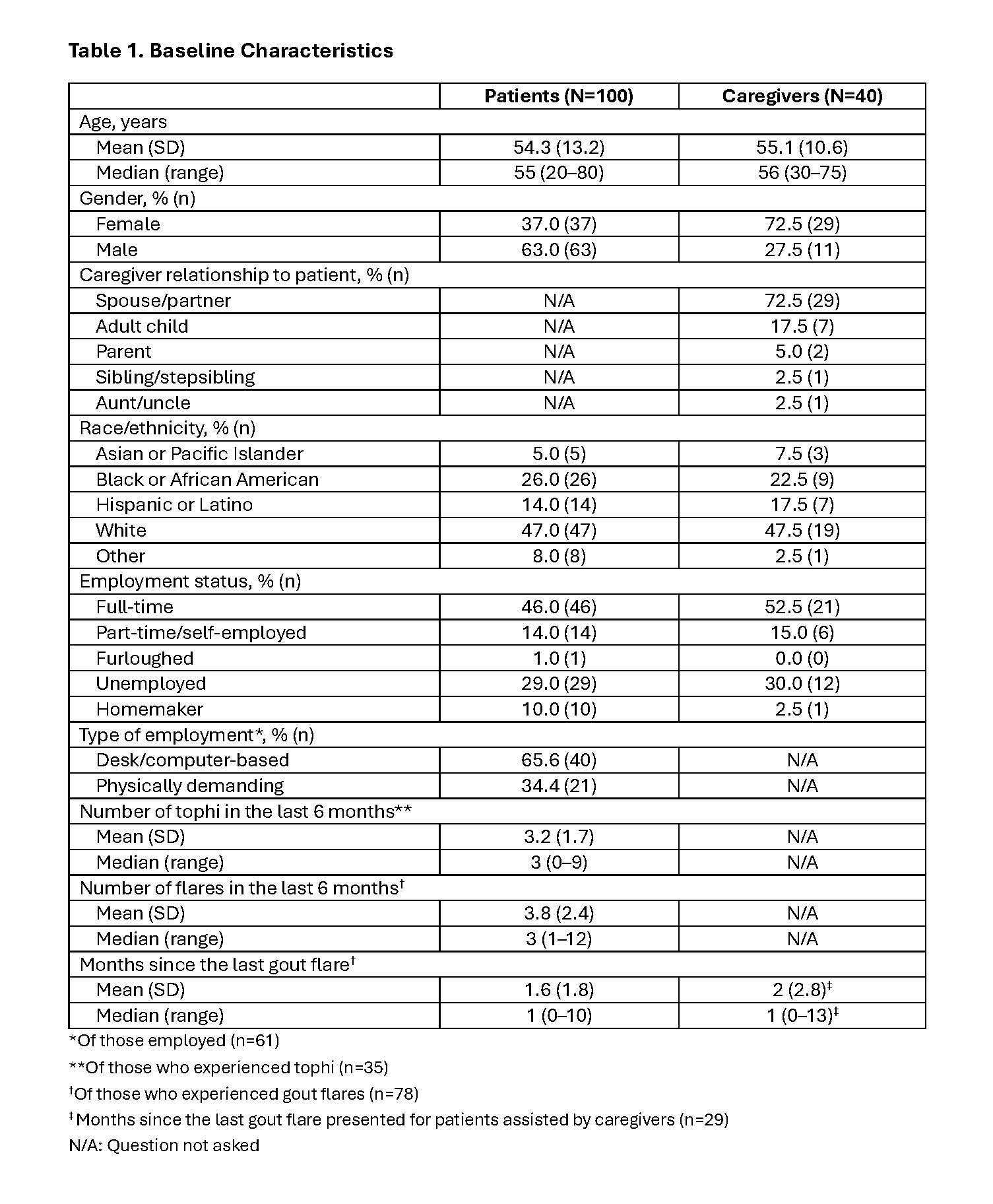
Results: A total of 100 patients (63% male, mean [SD] age 54.3 [13.2] years) and 40 caregivers (73% female, mean [SD] age 55.1 [10.6] years) completed the survey (Table 1). Patients were currently using the following ULT treatments: allopurinol (49%), pegloticase (26%), febuxostat (20%), and probenecid (4%). Despite ULT treatment, 35% experienced tophi and 78% reported gout flares. 72% of patients reported a recent serum urate level of ≥6 mg/dL. HRQOL as measured by the SF-12v2 is reported in Table 2. Patients had a mean physical component summary (PCS) score of 37.3 (SD: 6.3) and mental component summary (MCS) score of 42.7 (SD: 10.3), which were “well below”§ and “below” those of the general US population mean of 50 (SD: 10), respectively. The mean caregiver PCS score was 43.3 (SD: 11.7), which was “below” that of the general US population, and the MCS score was 45.2 (SD: 11.8). Common issues associated with caring for a patient with UG were stress (40%), inability to carry out a daily routine (35%) and/or work a job (35%), and feelings of being overwhelmed (35%). Over 90% of caregivers reported feeling some level of exhaustion. Overall activity impairment was 60% for patients and 41% for caregivers, measured by the WPAI. Employed patients and caregivers reported 53% and 36% overall work impairment, respectively. Employed patients missed an average of 6.8 (SD: 9.8) hours of work in the past 7 days due to UG, while employed caregivers missed an average of 2.7 (SD: 3.6) hours caring for a patient (Table 3).
Conclusion: This is the first study to present data on caregiver burden associated with UG, highlighting significant challenges and reduced HRQOL for caregivers and patients with UG. Both reported HRQOL below the general US population with the largest impact in physical health-related domains, likely due to clinical manifestations of UG for patients, and for caregivers, the physical demands of caring for a patient. Employed individuals also experienced notable work impairment demonstrating the multifaceted impacts of UG.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gaffo A, Desai B, Oladapo A, Kragh N, Zincavage R, Padilla B, Schlesinger N. Patient and Caregiver Perspectives on the Burden of Disease in Uncontrolled Gout: A Cross-Sectional Survey Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-and-caregiver-perspectives-on-the-burden-of-disease-in-uncontrolled-gout-a-cross-sectional-survey-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-and-caregiver-perspectives-on-the-burden-of-disease-in-uncontrolled-gout-a-cross-sectional-survey-study/

.jpg)
.jpg)