Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (2437–2469) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a severe extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Abatacept and rituximab are usually the recommended drugs. JAK inhibitors (JAKi) have demonstrated efficacy in RA, especially tofacitinib and baricitinib. Nonetheless, evidence on eficacy efficacy of other JAKi like Upadacitinib (UPA) in RA-ILD is scarce. Our objective was to assess a) the effectiveness and b) the safety of UPA in RA-ILD patients.
Methods: National multicenter study of RA-ILD patients on treatment with UPA. We analyzed from baseline the following outcomes: a) forced vital capacity (FVC), b) diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO), c) high resolution computed tomography (HRCT), d) dyspnea (modified Medical Research Council scale), e) arthritis activity (DAS28-ESR), and f) sparing effect of glucocorticosteroids.
Results: We studied 25 patients (16 women/9 men; mean age 61±9 years) from clinical practice on treatment with UPA. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in Table. All patients had received disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) before UPA [conventional DMARDs (n=23; 92%), anti-TNF (12; 48%), Tocilizumab (7;28%), Abatacept (11; 44%) and Rituximab (4;18%)]. Mean baseline values of FVC and DLCO (% predicted) were 88±16, and 68±23, respectively. Patients were followed-up for a median [IQR] of 12 [6-18] months. The evolution of FVC and DLCO remained stable during the first 12 months (Figure). At the end of the follow-up, available chest HRCT images improved/stabilized in all the patients. Stabilization or improvement of dyspnea was found in all the patients. Most patients [12 (67%)] showed articular remission or low activity. UPA was withdrawn in 5 (20%) patients due to ischemic heart disease (n=2), recurrent respiratory infections (n=1), zoster virus infection (n=1) and joint activity (n=1).
Conclusion: UPA may be useful and safe in controlling the course of both pulmonary and joint disease in RA-ILD patients, even in cases refractory to ABA and/or RTX.
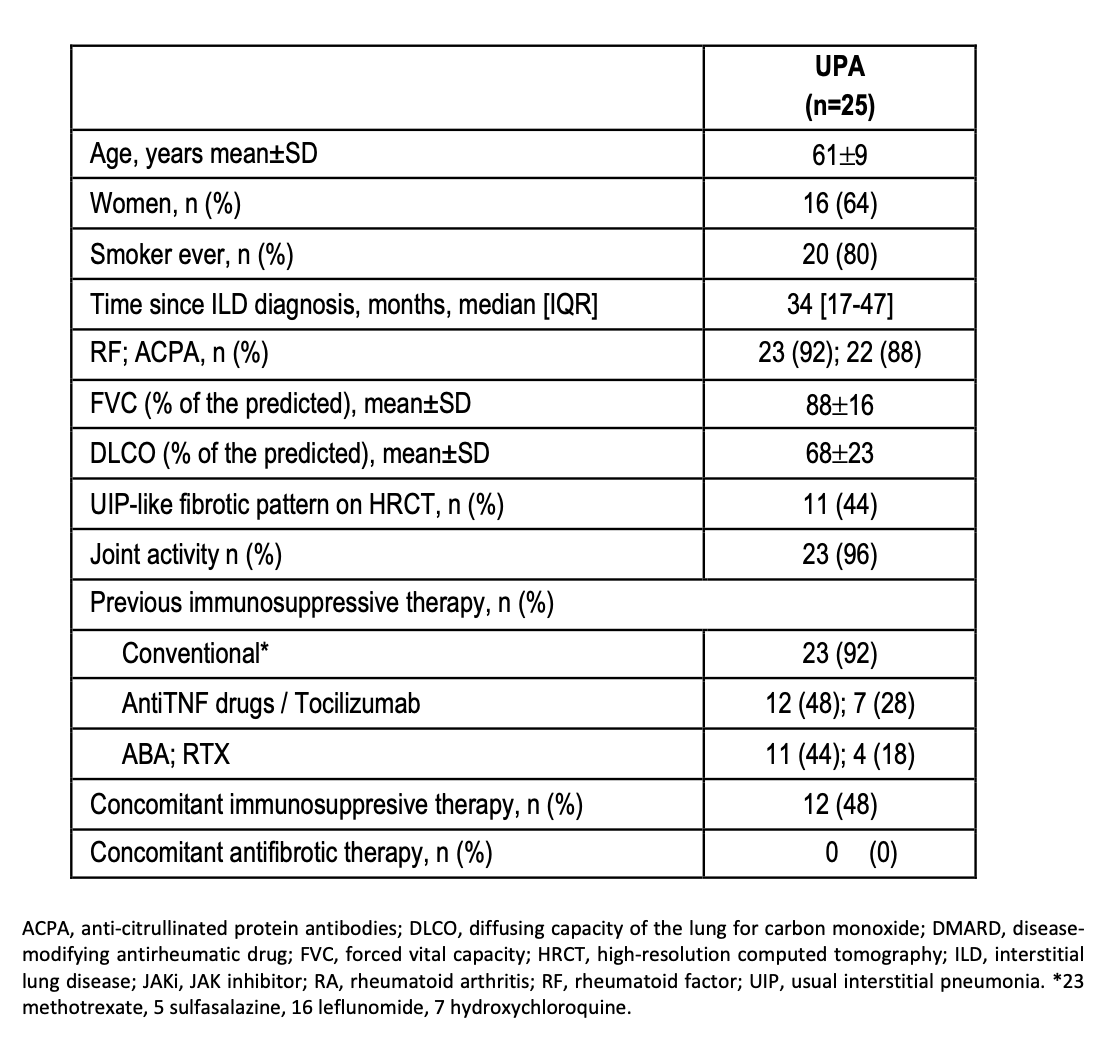 Table. Baseline characteristics of RA-ILD patients treated with UPA.
Table. Baseline characteristics of RA-ILD patients treated with UPA.
.jpg) Figure. Evolution of pulmonary function tests (mean % of the predicted FVC and DLCO) in RA-ILD patients with UPA therapy at baseline and 12 months.
Figure. Evolution of pulmonary function tests (mean % of the predicted FVC and DLCO) in RA-ILD patients with UPA therapy at baseline and 12 months.
Disclosures: A. Serrano-Combarro: None; B. Atienza-mateo: None; L. del Olmo Perez: None; S. García-Perez: None; G. Gonzalez Mozo de Rosales: None; J. Rosas Gómez de Salazar: None; a. Urruticoechea-Arana: None; A. García-Valle: None; J. Loarce: None; P. García-Escudero: None; B. Flores Robles: None; R. Melero-González: None; A. Garcia: None; M. Martín López: None; P. López Viejo: None; M. Perez Gaan: None; N. Vegas Revenga: None; A. Garcia-Aparicio: AbbVie/Abbott, 6, AstraZeneca, 6, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 1, 2, 6, UCB, 6; M. Bernabeu Gonzalvez: None; J. Moreno Morales: None; R. Blanco: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, 5, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, Merck/MSD, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, Roche, 2, 5, 6.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Serrano-Combarro A, Atienza-mateo B, del Olmo Perez L, García-Perez S, Gonzalez Mozo de Rosales G, Rosas Gómez de Salazar J, Urruticoechea-Arana a, García-Valle A, Loarce J, García-Escudero P, Flores Robles B, Melero-González R, Garcia A, Martín López M, López Viejo P, Perez Gaan M, Vegas Revenga N, Garcia-Aparicio A, Bernabeu Gonzalvez M, Moreno Morales J, Blanco R. Upadacitinib in the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis – Interstitial Lung Disease. National multicenter study of 25 patients in clinical practice. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/upadacitinib-treatment-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-national-multicenter-study-25-patients-clinical-practice/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/upadacitinib-treatment-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-national-multicenter-study-25-patients-clinical-practice/
