Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1147–1190) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Individuals with psoriasis are at increased risk of developing heart disease. Echocardiographic parameters of impaired left atrial (LA) strain (Peak atrial contraction and longitudinal strain (PACS and PALS)) and volume index (LAVi) are associated with increased risk of heart disease. Whether cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers are associated with left atrial impairment in adults with psoriasis is unknown. The aim of this study was to assess whether plasma levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), high-sensitivity troponin I (hsTnI) and pro-brain natriuretic peptide (proBNP) were associated with LA structure and function in adults with psoriasis.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional analysis of a prospective cohort study of 1,010 participants with psoriasis who underwent echocardiographic examination and had blood samples analyzed from 2021-2024. Those without available measurements of hsCRP (n=27), TnI (n=5) or proBNP (n=17), LA strain (n=23) or LAVi (n=11) were excluded. The population was stratified according to hsCRP, hsTnI and proBNP tertiles, respectively. We used ANOVA, Pearson’s Chi2-test, Kruskal-Wallis test, linear regression and cubic spline models as appropriate to assess the associations between biomarkers, cardiac risk factors and measures of LA structure and function. Biomarkers were logarithmically transformed for the linear regression analyses. In multivariable analyses, models were adjusted for sex, age, package years, BMI >30, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, ischemic heart disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation and psoriasis treatment.
Results: We included 927 adults with psoriasis (mean age 54.0 years, 46.5 % women). In the entire cohort, median hsCRP was 1.1 mg/l (IQR 0.5-2.7), median hsTnI was 3.0 ng/l (IQR 1.2-6.0) and the median proBNP was 7.6 ng/l (4.2-14.3). The participants in the highest tertile groups of all three biomarkers were overall older, had more package years and a higher prevalence of hypertension. Furthermore, the highest hsCRP group >1.73 mg/l were predominantly women, had higher BMI and were less physically active. The highest TnI group >5 ng/l were predominantly men, had a higher prevalence of moderate-to-severe psoriasis, and cardiovascular disease was more prevalent. The proBNP-group >11.5 ng/l had more women and a higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease. In univariable analyses, higher levels of hsCRP were associated with lower PALS, while higher levels of TnI and proBNP were associated with lower PACS and PALS and higher LAVi. In multivariable analyses, higher levels of TnI and proBNP remained significantly associated with lower PACS and PALS and higher LAVi. (Figure)
Conclusion: In a sample of adults with psoriasis, higher levels of TnI and proBNP were associated with impaired LA structure and function. Given the known association between LA dysfunction and heart disease, these biomarkers may identify individuals with psoriasis at increased risk of cardiac disease.
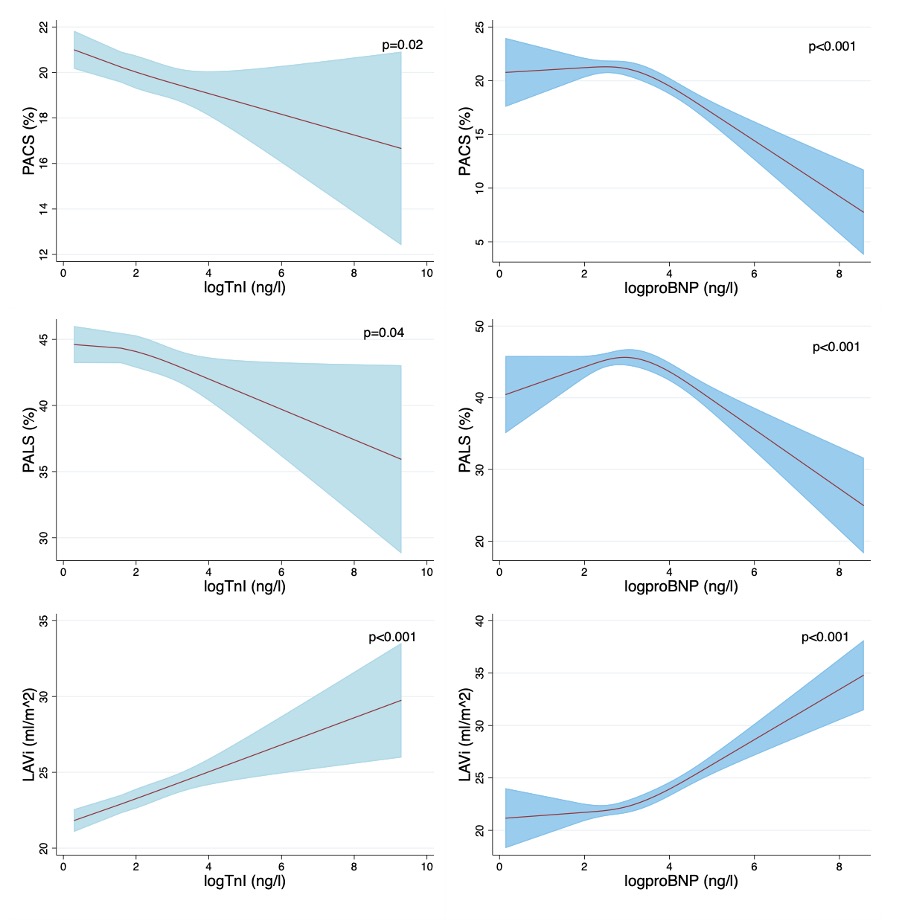 Cubic spline models analyzing the association between biomarkers and echocardiographic measures of left atrial strain and volume index.
Cubic spline models analyzing the association between biomarkers and echocardiographic measures of left atrial strain and volume index.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Borchsenius J, Dons M, Sengeløv M, Olsen F, Espersen C, Skaarup K, Lassen M, Johansen N, Davidovski F, Pareek M, Weber B, Zachariae C, Skov L, Biering-Sørensen T. Biomarkers Associated with Left Atrial Structure and Function in Individuals with Psoriasis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biomarkers-associated-with-left-atrial-structure-and-function-in-individuals-with-psoriasis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biomarkers-associated-with-left-atrial-structure-and-function-in-individuals-with-psoriasis/
