Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1088–1122) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Approvals for immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have expanded, and triple therapy combining anti-PD-1, anti-CTLA-4, and anti-LAG3 have been evaluated with encouraging results. But they lead to increasing toxicities, called immune-related adverse events (irAEs). IrAEs have been considered one organ at a time but in reality, comprise a range of systemic inflammatory syndromes targeting multiple organs. A global toxicity score called Organ, Severity, and total Toxicity (OST) has been developed. Patients experiencing irAEs have been shown to have longer survival compared with patients without irAE. But most studies did not correctly account for the immortal time bias. The objective of this study was to quantify the OST in patients with rheumatologic irAE and determine the impact of OST on oncologic outcomes, taking into account the immortal time bias.
Methods: The inclusion criteria were ICI treatment for any cancer leading to a rheumatologic irAE. We calculated the OST score to assess the cumulative toxicity burden at 6 and 9 months after ICI initiation. The OST score was composed of 3 parameters: number of organs (O), number of ≥ CTCAE G3 irAEs (S), and the sum of all CTCAE grades (T). Patients were divided into low and high-toxicity groups for each O, S, and T categories: high – O≥3, S≥1, T≥4 attributing 1 point each to calculate a composite OST score (cOST). To account for immortal time bias, landmark analysis methods were used at 2 time points: 6 and 9 months. Patients were included if they had experienced rheumatologic iRAE and were alive before the time points. Kaplan Meier (univariate) analysis was performed to compare patients according to the cOST score with 2 thresholds at the landmark timepoint.
Results: Out of 109 patients 74 patients were included in the landmark analysis. They mostly presented with polymyalgia rheumatica (53%), then peripheral polyarthritis (26%). Of these patients, 49 (66%) had a cOST=0 at 6 months after the ICI initiation, whereas 25 patients (34%) had a cOST >0. In the landmark analysis starting at 6 months, there was no significant difference in progression-free survival (PFS) according to cOST (p = 0.7) Fig 1A. The median of progression-free survival was 20 months in the cOST=0 group, and 30 months in the cOST >0 group. Likewise, there was no significative difference in overall survival (OS) between patients with cOST > 0 vs cOST=0 at 6 months of ICI initiation (p = 0.4) Fig 1B. The median of overall survival was 68 months in the cOST=0 group and was not reached in the cOST > 0 group. The same analysis performed with landmark at 9 months of ICI initiation returned similar results. When using a different threshold comparing a cOST score of 0-1 with cOST score of 2-3, there was also no significant difference in PFS or OS. There was no major misbalance between cOST groups regarding factors that might influence PFS or OS (table 1). Adjusted analysis will be presented during the meeting.
Conclusion: Patients with articular irAE tend to have a mostly low global inflammatory burden when assessed with this global score that is cOST. There were no significant differences in survival (PFS and OS) in patients with high or low global burden of checkpoint inhibitors toxicity, in this cohort of patients with rheumatic irAEs.
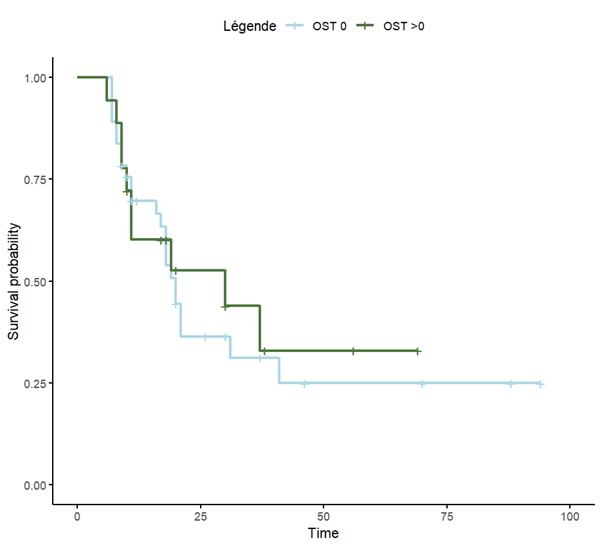 Figure 1 A Progression Free Survival (in months) depending on the cOST group calculated at 6 months from ICI initiation
Figure 1 A Progression Free Survival (in months) depending on the cOST group calculated at 6 months from ICI initiation
.jpg) Figure 1 B Overall survival (in months) depending on the cOST group calculated at 6 months from ICI initiation
Figure 1 B Overall survival (in months) depending on the cOST group calculated at 6 months from ICI initiation
.jpg) Patients characteristics according to their cOST group.
Patients characteristics according to their cOST group.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
quelain J, Mourre E, Henry J, Belkir R, Cope A, Sarker D, Wu Y, Kapiris M, Marabelle A, Robert C, Seror R, Mariette X, Bitoun S. Evaluation Of The Global Toxicity Burden In Patients Treated With Checkpoint Inhibitors Addressed For a Rheumatologic Toxicity And Its Impact On Oncological Outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-global-toxicity-burden-in-patients-treated-with-checkpoint-inhibitors-addressed-for-a-rheumatologic-toxicity-and-its-impact-on-oncological-outcomes/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-global-toxicity-burden-in-patients-treated-with-checkpoint-inhibitors-addressed-for-a-rheumatologic-toxicity-and-its-impact-on-oncological-outcomes/
