Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1088–1122) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a proinflammatory cytokine involved in B cell differentiation and antibody production through the JAK/STAT pathway. In clinical practice, hypogammaglobulinemia (HGG) has been observed in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRDs) treated with IL-6 receptor inhibitors (IL6Ri) (Vílchez-Oya et al., 2020), but this potential adverse effect remains insufficiently studied. We aimed to evaluate the impact of IL6Ri and Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) on humoral immunity through an ambispective approach.
Methods: We first conducted a retrospective chart review of adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), giant cell arteritis (GCA), or spondyloarthritis (SpA) treated with IL6Ri or JAKi. The primary endpoint was HGG (IgG < 750 mg/dL), also collecting cases of severe HGG (IgG < 450 mg/dL) and severe infections. Subsequently, we initiated a prospective observational study including patients with IRDs initiating IL6Ri or JAKi. Serum immunoglobulin levels and lymphocyte populations were assessed at baseline, 3 and 6 months. Statistical analyses included Student’s t-test or Wilcoxon test for paired comparisons, and Fisher’s exact test for categorical data.
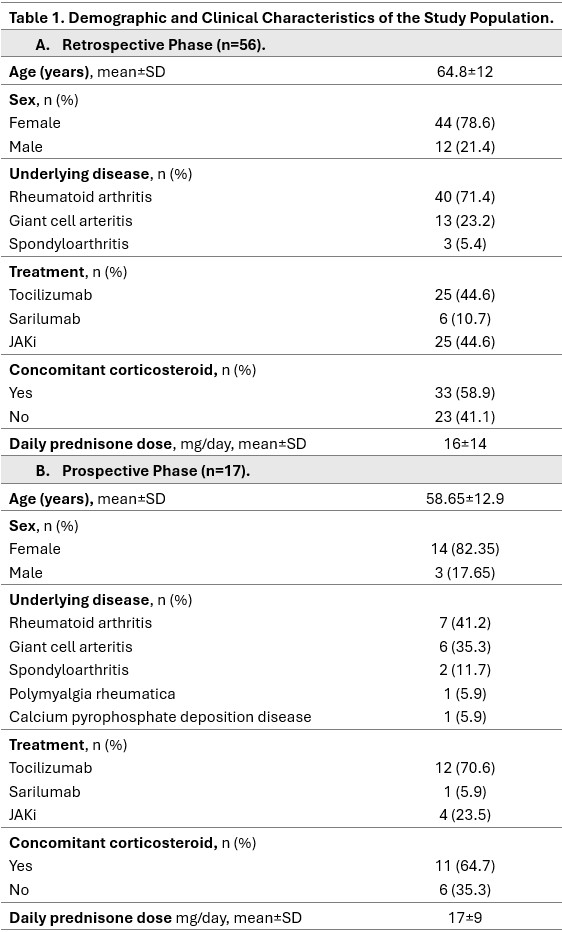
Results: In the retrospective cohort (n=56) (Table 1), HGG was observed in 20 patients: 35.7% (95% CI 24–49%); 41.9% with IL6Ri (95% CI 26-59%) and 28% with JAKi (95% CI 14-48%). Among these patients, 7 had baseline HGG, three of them had prior rituximab treatment. Severe HGG occurred in 5 patients (25%), with one requiring immunoglobulin replacement. Eight cases had low IgA levels, and six had low IgM. Lymphocyte counts remained within normal limits in all cases. Five patients with HGG developed severe infections, with no associated mortality. In the prospective cohort (n=17) (Table 1), IgG levels decreased significantly at 3 months (mean difference −50.7 mg/dL, p=0.018), primarily driven by a reduction in IgG4. However, no significant differences in IgG levels were observed at 6 months. Significant decreases in IgA and IgM levels were observed at 3 months, but only IgA persisted at 6 months (Figure 1). Four patients had baseline HGG, none had prior rituximab exposure. At 3 months, 6 patients (35.3%) had HGG (one severe), that was persistent in all cases at 6 months. Both the relative proportion and the absolute count of CD19+ B lymphocytes were reduced; however, the reduction was statistically significant only for the relative proportion at both 3 months (p=0.01) and 6 months (p=0.014) (Figure 2). No significant changes were observed in T lymphocytes.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that HGG in patients with IRDs treated with IL6Ri or JAKi is frequent. However, the determination of immunoglobulins in these patients is not integrated into clinical practice. These therapies may impact in immunoglobulin production and B cell function. Further studies are warranted to better assess this potentially harmful association.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Perea E, Avilés A, RodrÍguez-Alvear C, Vela P, Jovaní V, Martínez A, Bernabeu Gonzalvez M, Calabuig I, Jiménez-Portillo A, Bermúdez A, Gomez-Sabater S, Caño R, Marco F, Andrés M. Impact of IL-6 Receptor and JAK Inhibitors on Humoral Immunity in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: An Ambispective Study. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-il-6-receptor-and-jak-inhibitors-on-humoral-immunity-in-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-an-ambispective-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-il-6-receptor-and-jak-inhibitors-on-humoral-immunity-in-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-an-ambispective-study/

.jpg)
.jpg)