Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Pain management in autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) increasingly includes NSAIDs, physical therapy, and self-management. However, the role of cannabis in ARD symptom relief remains unclear. We used natural language processing (NLP) on electronic health records (EHRs) to systematically characterize cannabis use patterns, motivations, and disparities in ARD patient
Methods: A retrospective analysis (2004–2024) included 5,051 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), systemic sclerosis (SSc), Sjögren’s syndrome (SjS), or ankylosing spondylitis (AS) from an academic health system. NLP models (ClinicalBERT) extracted cannabis documentation from 2,626,542 clinical notes, classifying cannabis use as current, past, or none and categorizing reasons as pain, sleep, anxiety, nausea, or appetite. Sociodemographic factors, comorbidities, medications, and healthcare utilization were compared between cannabis users and non-users.
Results: Clinical notes documenting current cannabis use rose from 0.1% (2017) to >1% (2024), a 900% relative increase. NLP classifiers performed well for cannabis documentation, current vs. past use (F1=0.85), and reasons for use (F1=0.86). Overall, 1,237 patients (24.5%) had current cannabis use documented. Higher usage was observed among Hispanic/Latino (30.1%) and Black (36.2%)patients. Pain was the primary reason overall (37.9%), notably higher among Black (54.5%) and Hispanic/Latino (43.2%) patients compared with White (38.5%) and Asian patients (21.6%). Women more frequently reported using cannabis for pain (39.4%) and sleep (16.4%) compared to men (33.0%, 11.6%, respectively). Older adults (≥66 years) most likely to report pain-related cannabis use (46.4%), whereas middle-aged adults (17.8%) and early middle-aged adults (16.1%) were more likely to use cannabis for sleep. Disease-specific differences showed pain-related use was highest among patients with RA (40.7%), SjS (38.3%), and SLE (37.0%), while sleep-related cannabis use was most frequently documented in patients with SLE (27.4%) and SjS (26.4%). Cannabis users had greater comorbidity burdens, more emergency visits, hospitalizations, and opioid prescriptions.
Conclusion: This study represents one of the largest and most comprehensive efforts to characterize cannabis use in ARDs using NLP and machine learning. This study demonstrates the feasibility of systematically identifying cannabis use patterns and motivations in ARD patients, highlighting opportunities for clinicians to initiate informed discussions with patients regarding cannabis as a symptom management strategy. Future research should investigate factors driving cannabis use, including specific ARD subphenotypes, disease activity and severity, treatment interactions, and the impact on overall disease management. Efforts to address disparities in medical cannabis access and rigorous studies evaluating safety and effectiveness will be essential for informing potential clinical guidance.
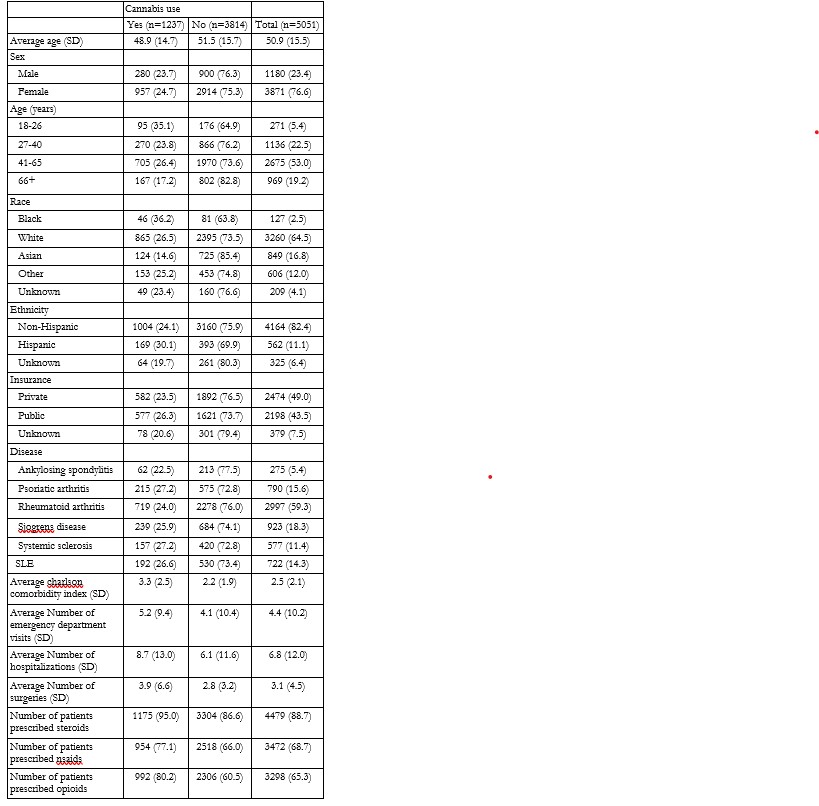 Characteristics of positive cannabis use patients compared to negative patients.
Characteristics of positive cannabis use patients compared to negative patients.
.jpg) Sociodemographic and Disease-Related Distribution of Reasons for Cannabis Use Among Patients with Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Among Cannabis Users, 2015-2024
Sociodemographic and Disease-Related Distribution of Reasons for Cannabis Use Among Patients with Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Among Cannabis Users, 2015-2024
*These proportions add up to more than >100% because individuals can mention any or all the uses in the clinic notes
.jpg) Annual Percentage of Notes Mentioning Current Cannabis Usage by Gender, Race, Ethnicity, Mean Age, and Disease Status, 2004-2024
Annual Percentage of Notes Mentioning Current Cannabis Usage by Gender, Race, Ethnicity, Mean Age, and Disease Status, 2004-2024
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Falasinnu T, Le N, Wang Y, Alagappan A, Weisman M, Irani A, Chaichian Y, Bozkurt S. Leveraging Natural Language Processing to Uncover Real-World Trends in Cannabis Use from Clinic Notes in Electronic Health Records [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leveraging-natural-language-processing-to-uncover-real-world-trends-in-cannabis-use-from-clinic-notes-in-electronic-health-records/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leveraging-natural-language-processing-to-uncover-real-world-trends-in-cannabis-use-from-clinic-notes-in-electronic-health-records/
