Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-10:45AM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is the most common vasculitis in people over 50 years old and is a clinical diagnosis bolstered by non-specific inflammatory markers and variable pathologic findings on temporal artery biopsy (TAB). Patients with diseases that mimic GCA may undergo TAB during their workup, including those with atherosclerosis, infection, other autoimmune diseases, or simply older people with a new headache. Here we focus on the transcriptional differences in biopsy-positive GCA cases from clinically diverse controls at the level of the temporal artery.
Methods: We collected 46 TABs that were obtained during clinical care from 16 biopsy-positive GCA cases and 30 controls – polymyalgia rheumatica (3), rheumatoid arthritis (1), relapsing polychondritis (1), and granulomatosis with polyangiitis (2), infections (2), atherosclerosis (5), or an older person with new headache (16). Tissue was sequenced in bulk with RNAseq and analyzed for differential gene expression with edgeR with batch-effect correction with RUVseq and controlled for sex and age. Subsequent pathway enrichment was performed with Reactome and results were explored with data from the Human Aging Genomic Resource (HAGR) and the drug-gene interaction database (DGIdb).
Results: We found 2,279 genes to be significantly differentially expressed (DE) in biopsy-positive GCA cases compared to controls. Fifty-three pathways were enriched with an adjusted p-value < 0.05 (Fig. 1) and belonged largely to cytokine signaling (interleukin, interferon), neutrophil degranulation, cell-cell interaction (antigen presentation, integrin pathways, Fc receptor mediated signaling), and vascular activity (cell surface interactions at the vascular wall and hemostasis). Next, we found that 201 of our DE genes (8.8%) have been implicated in aging processes (HAGR). Among these is the secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) gene, also known as osteopontin, which had the largest expression fold change in cases vs controls (logFC: 6.23) in our data. SPP1 is expressed in several immune cells, including macrophages, and is an important mediator of immune cell recruitment, migration and adhesion, macrophage activation and polarization, stimulation of inflammatory cytokines and tissue fibrosis. SPP1 activates pathways of IL-6, IL-17, Jak/Stat, IFNγ, NFkB/ERK and granulomatous inflammation. In 2017, Prieto reported high osteopontin serum levels in GCA and suggested it as disease activity biomarker that is not suppressed by tocilizumab. Last, we found 705 of our genes linked to 5,824 established drugs in DGIdb, 1,564 of which are approved for use. Seventeen of these drugs were highly linked to our data (connected to 20+ genes). Fifteen drugs directly link to SPP1.
Conclusion: Our study recapitulates the roles of inflammation, aging and immune dysregulation in the pathophysiology of GCA that notably remain significant even with clinically diverse controls. We highlight several likely pathologic roles of SPP1 in GCA, a gene which has not yet featured prominently in the field of GCA but may well be a key disease activity biomarker and therapeutic target. Finally, our data have provided a rich source of candidate drugs currently on the market that may effectively treat GCA.
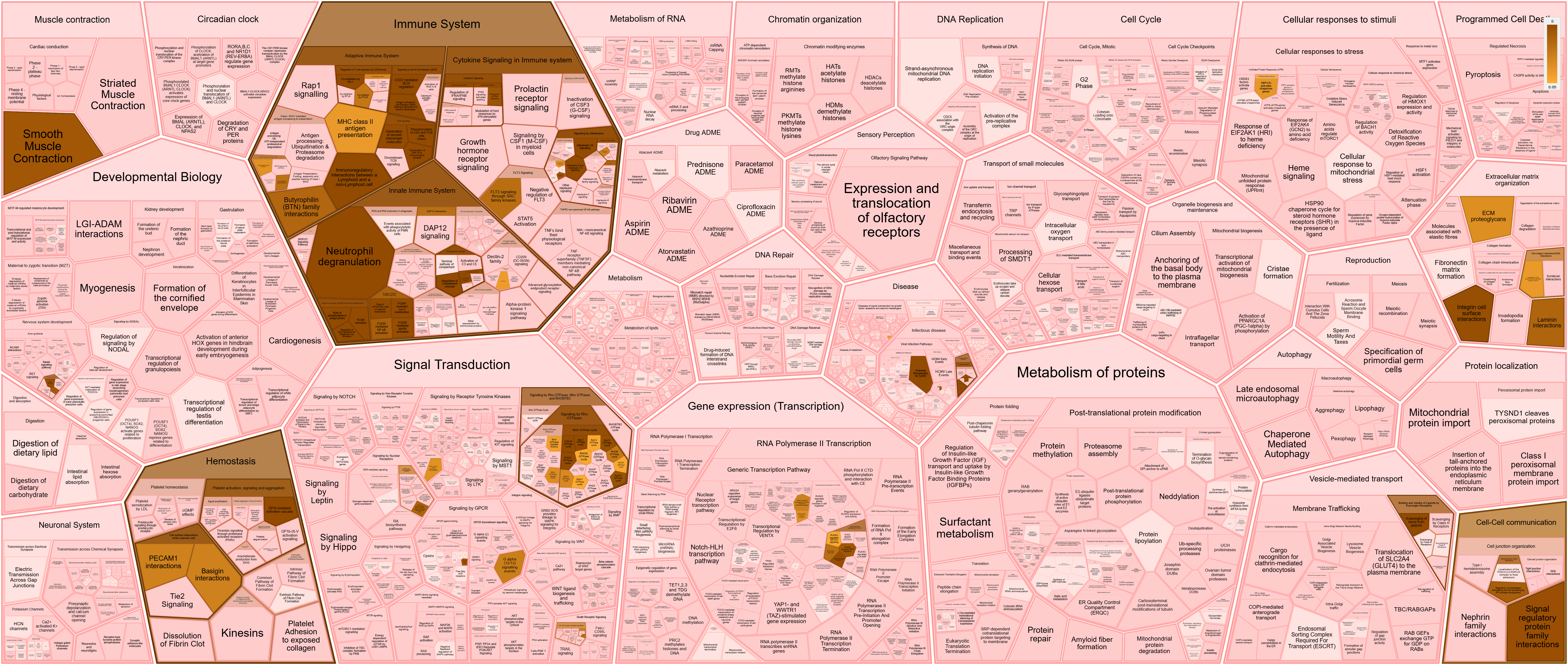 Fifty-three (53) pathways are significantly enriched with an false discovery rate (FDR) p-value < 0.05 and belong largely to cytokine signaling (interleukin, interferon), neutrophil degranulation, cell-cell interaction (antigen presentation, integrin pathways, Fc receptor mediated signaling), and vascular activity (cell surface interactions at the vascular wall and hemostasis). Darker color corresponds with greater statistical significance (lower FDR p-value). Analysis and rendering performed at Reactome.org.
Fifty-three (53) pathways are significantly enriched with an false discovery rate (FDR) p-value < 0.05 and belong largely to cytokine signaling (interleukin, interferon), neutrophil degranulation, cell-cell interaction (antigen presentation, integrin pathways, Fc receptor mediated signaling), and vascular activity (cell surface interactions at the vascular wall and hemostasis). Darker color corresponds with greater statistical significance (lower FDR p-value). Analysis and rendering performed at Reactome.org.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lindquist I, Eskew A, Choi D, Wilson D, Salomao D, Stiefel H, Albert D, Vakil-Gilani K, Ghetie D, Rosenbaum J, Friedman M. Transcriptomic insights into GCA compared to clinically diverse controls: Inflammation, Aging, Therapeutic Targets and the role of SPP1 in the temporal artery [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcriptomic-insights-into-gca-compared-to-clinically-diverse-controls-inflammation-aging-therapeutic-targets-and-the-role-of-spp1-in-the-temporal-artery/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcriptomic-insights-into-gca-compared-to-clinically-diverse-controls-inflammation-aging-therapeutic-targets-and-the-role-of-spp1-in-the-temporal-artery/
