Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis (AAV) is an autoimmune disease causing small vessel inflammation. Underlying mechanisms of disease are unclear, but the human microbiota may be a contributor. One way that bacteria can affect the immune system is through small RNAs (sRNAs), which are found abundantly in human circulation. The purpose of this study is to determine if circulating bacterial sRNAs are altered in patients with AAV compared to those with and without other inflammatory autoimmune diseases.
Methods: Patients with AAV were recruited from Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) and Cleveland Clinic. Participants with other inflammatory diseases (rheumatoid arthritis [RA] and systemic lupus erythematosus [SLE], termed here as “inflammatory control”) and control participants were recruited from VUMC. Total RNA was extracted from plasma from all participants and libraries were constructed for next-generation sequencing. sRNAs not aligning to the human genome with up to one mismatch were aligned to bacterial genomes in RefSeq using the TIGER pipeline. sRNA sequences and sRNA counts of bacterial taxa were compared using DESeq2 and the Benjamini-Hochberg method to adjust for multiple comparisons with false discovery rate at 5%.
Results: The study included 31 AAV, 20 inflammatory control (2 RA,18 SLE) and 4 control participants (Table 1). Examining sRNA counts of bacterial taxa, sRNAs aligning to 79 orders (which is the most specific taxonomy to which sRNAs can be assigned with confidence due to the short length and conserved sequences) were altered in AAV versus control and inflammatory control participants (Figure 1). Over half of the orders came from the phyla Pseudomonadota and Actinomycetota. Examining the sRNA sequences, 23 bacterial sRNAs were altered after multiple comparison adjustment in AAV versus control and inflammatory control participants (Figure 2). Of the 23 sequences, 21 were aligned to the phylum Pseudomonadota and all were either tRNA-derived RNAs (tDR) or ribosomal RNA-derived RNAs (rDRs). Among the altered sRNAs were 4 sRNAs with the same base sequence of GGGGCUGUAGCUCAGCUGGGA (thus having the same regulatory seed region, GGGCUGU). These sRNAs were predicted to downregulate key genes involved in T-cell activation and inflammatory processes, including ICOS/ICOSL, CTLA4, NFATC2, CASP3.
Conclusion: The plasma bacterial sRNA composition is altered in patients with AAV compared to control and inflammatory control participants, and the majority of altered sRNAs were from the phylum Pseudomonadota. Among altered bacterial sRNAs were several with a similar base sequence which was predicted to downregulate multiple genes that dappen immune responses, particularly via T cells. Thus, these sRNAs could promote autoimmune inflammation. Future mechanistic studies will be needed to confirm these findings.
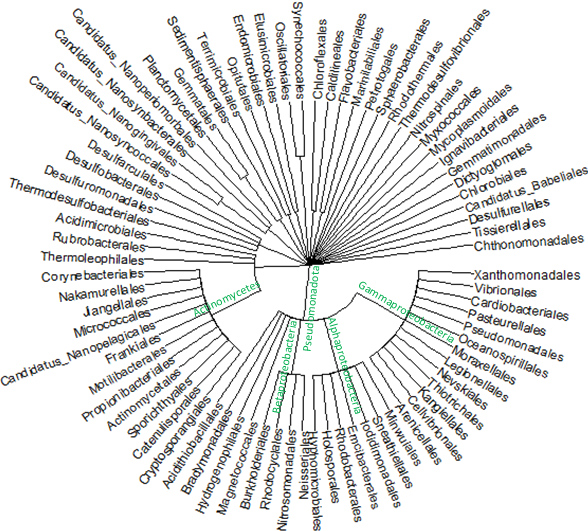 Table. Participant demographics
Table. Participant demographics
.jpg) Figure 1: Cladogram representing significantly altered phylum, class, and order level taxonomy of sRNA counts. Those order-level taxa counts with significant alteration (adjusted P value < 0.05) in both AAV versus control and versus inflammatory control participants were included.
Figure 1: Cladogram representing significantly altered phylum, class, and order level taxonomy of sRNA counts. Those order-level taxa counts with significant alteration (adjusted P value < 0.05) in both AAV versus control and versus inflammatory control participants were included.
.jpg) Figure 2: Volcano plots of altered plasma bacterial sRNAs in (A) AAV versus control and (B) AAV versus inflammatory control participants. Dots indicate one sRNA sequence with colored dots being those with a fold difference >1.5 and unadjusted p value < 0.05. (C) Venn diagram illustrating specific and common sRNA sequences altered in AAV versus controls and versus inflammatory controls after multiple comparison adjustment.
Figure 2: Volcano plots of altered plasma bacterial sRNAs in (A) AAV versus control and (B) AAV versus inflammatory control participants. Dots indicate one sRNA sequence with colored dots being those with a fold difference >1.5 and unadjusted p value < 0.05. (C) Venn diagram illustrating specific and common sRNA sequences altered in AAV versus controls and versus inflammatory controls after multiple comparison adjustment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xavier C, Byram K, Langford C, Ormseth M. Circulating Bacterial sRNAs are Altered in Patients with Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/circulating-bacterial-srnas-are-altered-in-patients-with-anti-neutrophil-cytoplasmic-antibody-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/circulating-bacterial-srnas-are-altered-in-patients-with-anti-neutrophil-cytoplasmic-antibody-associated-vasculitis/
