Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0671–0710) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Background/Purpose Sjögren’s disease (SjD) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease characterized by lymphocytic infiltration and progressive, immune-mediated dysfunction of the exocrine glands. Immunoglobulin (Ig) G autoantibodies targeting Sjögren’s syndrome-related antigens (A/Ro and B/La ribonuclear complexes) and RF play a pivotal role in SjD development and are produced by B-cell activation. Current SjD therapies focus on symptom management, with limited efficacy in preventing glandular damage or suppressing systemic disease activity. Efgartigimod, an IgG1 antibody Fc fragment, selectively reduces IgG by blocking FcRn-mediated IgG recycling without impacting antibody production, albumin levels, or other parts of the immune system. By targeting disease-specific IgG autoantibodies, efgartigimod may reduce disease activity and symptoms in patients with SjD. We present the results of RHO, a phase 2, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, proof-of-concept study to explore the safety and efficacy of efgartigimod in adult participants with SjD (NCT05817669).
Methods: Anti-Ro/SSA positive patients meeting ACR/EULAR 2016 Sjogren’s syndrome criteria ≤7 years before screening, with EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Disease Activity Index (ESSDAI) ≥5 and residual salivary flow, were randomly allocated (2:1) to receive weekly intravenous efgartigimod or placebo for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of responders to the Composite of Relevant Endpoints for Sjögren’s Syndrome (CRESS; response on ≥3 out of 5 items) at week 24. Key secondary endpoints were proportion of responders to the candidate Sjögren’s Tool for Assessing Response (cSTAR), change from baseline in ESSDAI, Clinical ESSDAI (ClinESSDAI), EULAR Sjogren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI) scores, and safety.
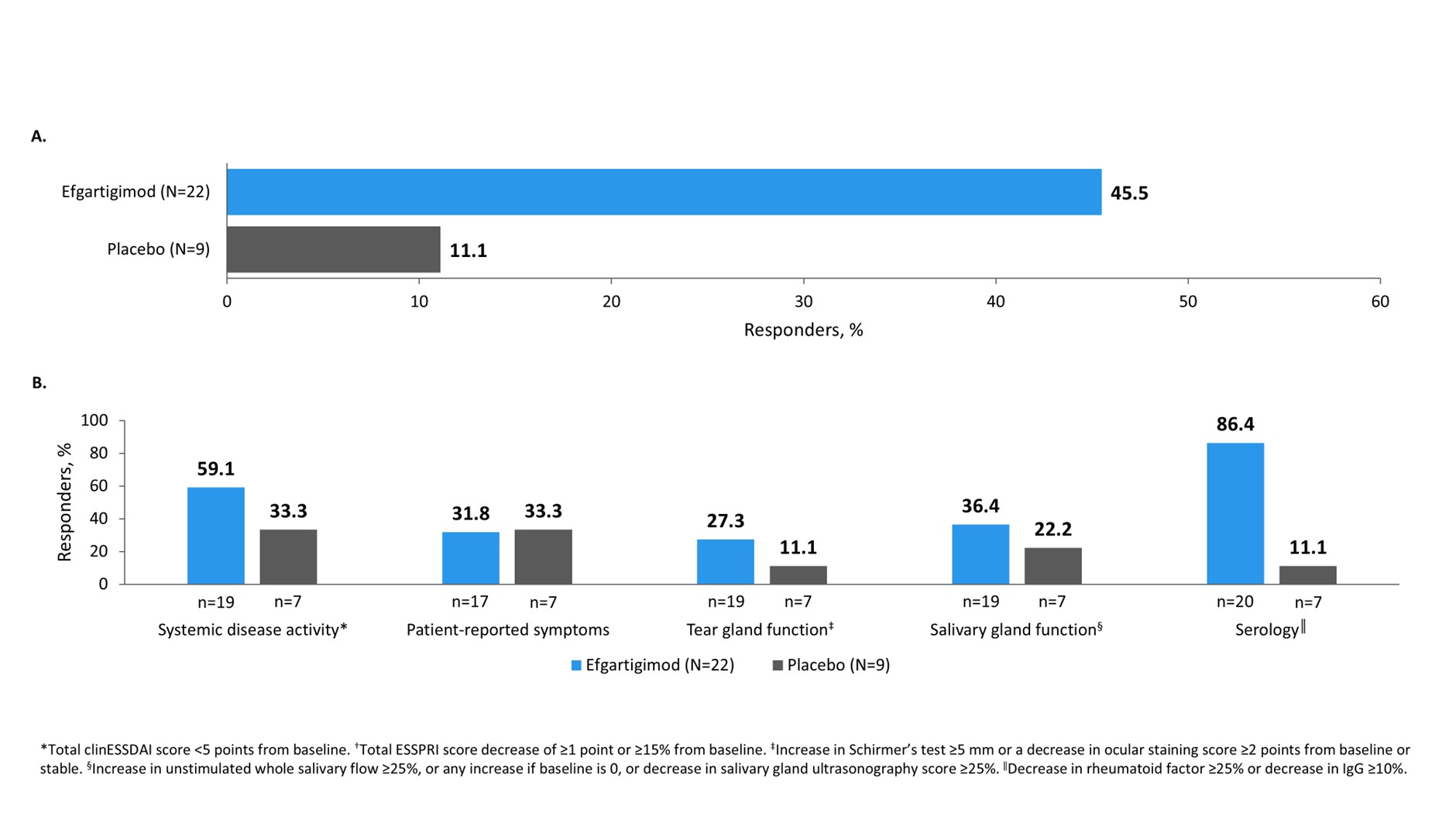
Results: Of thirty-four patients randomized, three did not meet eligibility criteria and were removed from analyses. The study met its primary endpoint, with more responders to ≥3 of 5 CRESS items in the efgartigimod than placebo group at week 24 (45.5% [10/22] vs 11.1% [1/9]). Efgartigimod treatment resulted in a positive signal for 4 of 5 individual CRESS items compared with placebo (Figure), and an increased cSTAR response at week 24 (54.5% [12/22] participants compared with 33.3% [3/9] of placebo-treated participants). All participants showed improvements from baseline in disease activity (ESSDAI and ClinESSDAI scores), and no relevant changes in ESSPRI score. Efgartigimod rapidly reduced mean (SE) IgG and anti-Ro52 autoantibodies by 58.3% (2.4) and 63.8% (3.9), respectively, from Week 4, and mean (SE) C1Q immune complexes by 4.0 (1.3) μg Eq/mL, and mean (SE) RF by 19.6% (4.1) compared with 6.3% (3.0) by placebo at study end. Efgartigimod was well tolerated, with no new safety signals.
Conclusion: Proof-of-concept was demonstrated using efgartigimod in patients with SjD, which was generally well tolerated. The ongoing phase 3 UNITY trial (NCT06684847) will assess efficacy and safety of efgartigimod in patients with SjD with clinESSDAI ≥6 (moderate-to-severe systemic disease activity).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
peene i, Verstappen G, Deprez J, Kroese F, Arends S, Kelly A, Vandersarren L, Bowen E, Jacobs J, Meyvisch P, Elewaut D, Bootsma H. Treatment of Sjögren’s disease by blocking FcRn: clinical and translational data from RHO, a phase 2 randomized, placebo controlled, double-blind, proof-of-concept study with efgartigimod [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-sjogrens-disease-by-blocking-fcrn-clinical-and-translational-data-from-rho-a-phase-2-randomized-placebo-controlled-double-blind-proof-of-concept-study-with-efgartigimod/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-sjogrens-disease-by-blocking-fcrn-clinical-and-translational-data-from-rho-a-phase-2-randomized-placebo-controlled-double-blind-proof-of-concept-study-with-efgartigimod/