Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0593–0640) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Assessing disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is essential for effective treatment. SLEDAI-2K uses dichotomous items, while SLE-DAS incorporates both dichotomous and continuous variables. We intend to analyze the correlation between SLEDAI-2K and SLE-DAS in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus from central Spain, as well as to identify factors contributing to discordance in disease activity classification.
Methods: Retrospective assessment of 324 SLE patients followed up from 2010 to 2024 at Madrid’s Fundación Jiménez Díaz Hospital (Spain). Data were collected from the patients’ most recent visits and disease activity was evaluated using SLEDAI-2K and SLE-DAS, and discordant classifications between the tools were analyzed.
Results: The number of patients in each disease activity category was as follows: Remission (Clinical SLEDAI-2K =0, n=254 [78.4%] vs. clinical SLE-DAS =0, regardless of serology, and prednisone up to 5 mg/day, n=253 [78.3%]); Low activity (SLEDAI-2K 1-4 and prednisone dose ≤ 5 mg/day, n=42 [13.0%] vs. SLE-DAS >0 and ≤ 2.48 with prednisone dose ≤ 7.5 mg/day, n=14 [4.3%]); Mild activity (SLEDAI-2K 1-4 and prednisone dose > 5 mg/day or score 5-6, n=19 [5.9%] vs. SLE-DAS >0 and ≤ 2.48 with prednisone dose > 7.5 mg/day or score >2.48 and ≤7.64, n=46 [14.2%]); Moderate (SLEDAI-2K 7-12 n=7 [2.2%] vs. SLE-DAS >7.64 and ≤9.9 ,n=3 [0.9%]); Severe SLEDAI-2K > 12 (n=2 [0.6%] vs. SLE-DAS >9.9,n=7 [2.2%]). SLEDAI-2K and SLE-DAS showed strong correlation (ρ=0.970, p< 0.001), with high concordance (linearly weighted Kappa index=0.7715, p< 0.001). Forty-four patients were discordant in terms of disease activity categorization. Of these, 39 were discordant at only one level of disease activity. Notably, in 37 of the 44 cases, SLE-DAS classified patients as having a higher degree of disease activity compared to SLEDAI-2K. Patients with skin and hematological manifestations were more commonly discordant in terms of disease activity.
Conclusion: SLEDAI-2K and SLE-DAS demonstrate a strong correlation and high reproducibility for assessing disease activity in the Spanish population. However, SLE-DAS offers additional information, particularly in patients with hematologic and skin involvement, enabling a more precise evaluation of disease activity in SLE patient.
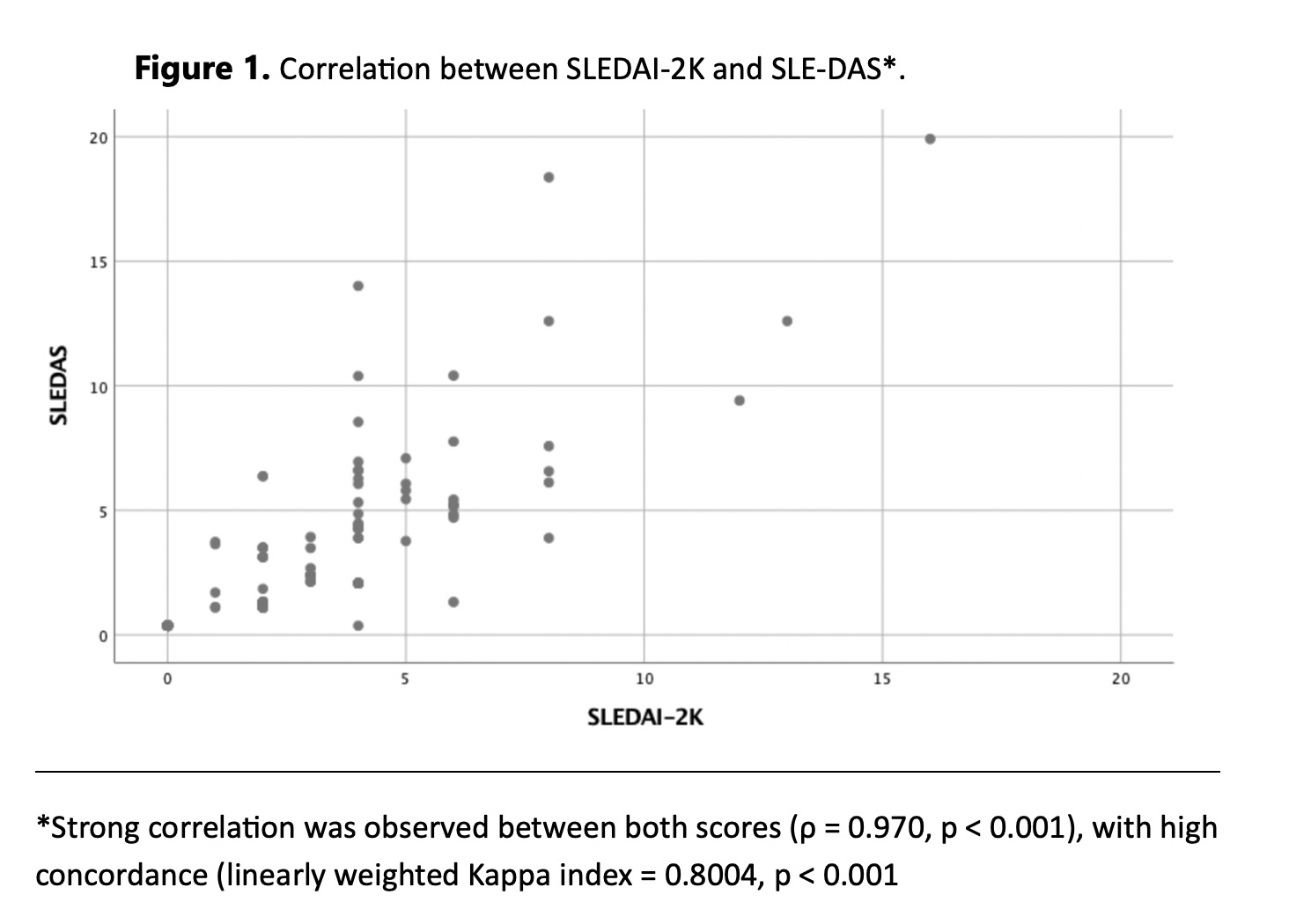 Figure 1. Correlation between SLEDAI-2K and SLE-DAS*.
Figure 1. Correlation between SLEDAI-2K and SLE-DAS*.
*Strong correlation was observed between both scores (ρ = 0.970, p < 0.001), with high concordance (linearly weighted Kappa index = 0.8004, p < 0.001
.jpg) Table 1. Clinical characteristics of 296 patients classified as having remission or low disease activity according to SLEDAI-2K, who were either concordant or discordant when assessed using SLEDAS.
Table 1. Clinical characteristics of 296 patients classified as having remission or low disease activity according to SLEDAI-2K, who were either concordant or discordant when assessed using SLEDAS.
.jpg) Table 2. Multivariate analysis to identify predictors of discordant evaluation of disease activity when SLEDAI-2K and SLE-DAS were applied.
Table 2. Multivariate analysis to identify predictors of discordant evaluation of disease activity when SLEDAI-2K and SLE-DAS were applied.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Heras Recuero E, Garcia Fernandez A, Gomez-Moreno C, Ferraz Amaro I, Llorca J, González-Gay M. Strong Correlation Between SLEDAI and SLE-DAS in the Spanish Population: Assessment of Discordant Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/strong-correlation-between-sledai-and-sle-das-in-the-spanish-population-assessment-of-discordant-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/strong-correlation-between-sledai-and-sle-das-in-the-spanish-population-assessment-of-discordant-patients/
