Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical II (0879–0884)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:45AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Early detection and continuous monitoring of ILD are critical for timely intervention and improved clinical outcomes. In recent years, serum biomarkers have gained recognition as potential non-invasive tools for evaluating ILD onset, progression, and prognosis. However, their clinical utility in SSc-ILD remains incompletely understood. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of serum biomarkers—KL-6, IL-18, and IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP)—for assessing ILD progression and mortality in SSc patients.
Methods: This prospective cohort study followed 74 SSc patients for 24 months. Patients were stratified based on the presence or absence of ILD using high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT). Clinical assessments, pulmonary function tests (PFTs), and serum biomarker levels (KL-6, IL-18, and IL-18BP) were measured. ILD progression was defined by changes in forced vital capacity (FVC). Relationships between biomarkers, lung function, and ILD severity were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves determined optimal biomarker thresholds, while logistic regression identified predictors of ILD progression and mortality, accounting for potential confounders.
Results: Among the 74 patients, 38% had ILD at baseline, increasing to 54% over two years. The proportion of patients with lung involvement ≥20% rose from 26% to 43%. Serum KL-6 proved to be a strong biomarker for progressive ILD, with an annual increase of +14.18 serving as the threshold (AUC: 0.803, P = 0.002, sensitivity: 80%, specificity: 64%). For mortality, an annual KL-6 increase of +71.17 showed the highest predictive accuracy (AUC: 0.91, 95% CI: 0.84–0.99, P < 0.0001, sensitivity: 75%, specificity: 85%). DLCO decline (∆DLCO) also emerged as a mortality predictor, with a -17% annual decrease as the critical threshold (AUC: 0.20, P = 0.006). ∆KL-6 (OR: 3.21, 95% CI: 1.78–4.89, P = 0.03), ∆DLCO (OR: 1.98, 95% CI: 1.12–3.72, P = 0.03), ∆CRP (OR: 1.32, 95% CI: 1.13–3.24, P = 0.04), and anti-Scl70 antibodies (OR: 1.98, 95% CI: 1.04–3.24, P = 0.03) were independent predictors of progressive ILD, while ∆IL-18, ∆IL-18BP and ∆ESR exhibited limited predictive utility. Multivariate analysis confirmed that immunosuppressive therapy was protective against ILD progression (OR: 0.27, 95% CI: 0.16–0.92, P = 0.004).
Conclusion: Serum KL-6 is a reliable biomarker for predicting ILD progression and mortality in systemic sclerosis, with well-defined thresholds showing high sensitivity and specificity. ∆DLCO and anti-Scl70 antibodies were also independent predictors of ILD progression, while immunosuppressive therapy demonstrated a protective effect. These findings highlight the potential of KL-6 for non-invasive monitoring and risk stratification in SSc-ILD.
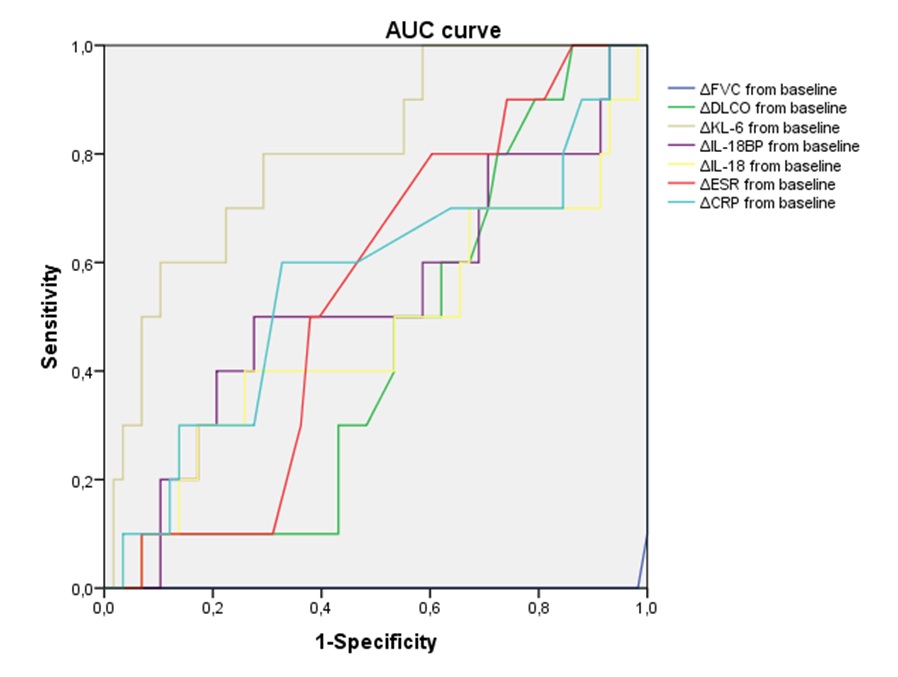 Comparison of the receiver operating characteristic curve of blood markers for predicting progressive ILD in patients with SSc; ROC curves: %FVC relative change from baseline; %DLCO relative change from baseline; KL-6 relative change from baseline; IL-18BP relative change from baseline; IL-18 relative change from baseline; ESR relative change from baseline; CRP relative change from baseline, AUC area under the curve.
Comparison of the receiver operating characteristic curve of blood markers for predicting progressive ILD in patients with SSc; ROC curves: %FVC relative change from baseline; %DLCO relative change from baseline; KL-6 relative change from baseline; IL-18BP relative change from baseline; IL-18 relative change from baseline; ESR relative change from baseline; CRP relative change from baseline, AUC area under the curve.
.jpg) Fig 2. Comparison of the receiver operating characteristic curve of blood markers for predicting mortality in patients with SSc; ROC curves: %FVC relative change from baseline; %DLCO relative change from baseline; KL-6 relative change from baseline; IL-18BP relative change from baseline; IL-18 relative change from baseline; ESR relative change from baseline; CRP relative change from baseline, AUC area under the curve.
Fig 2. Comparison of the receiver operating characteristic curve of blood markers for predicting mortality in patients with SSc; ROC curves: %FVC relative change from baseline; %DLCO relative change from baseline; KL-6 relative change from baseline; IL-18BP relative change from baseline; IL-18 relative change from baseline; ESR relative change from baseline; CRP relative change from baseline, AUC area under the curve.
.jpg) Logistic regression analysis for progressive ILD in SSc. FVC forced vital capacity, DLco difusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide, KL-6 Krebs von den Lungen-6, CRP C-reactive protein, ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate, Δ changes from baseline
Logistic regression analysis for progressive ILD in SSc. FVC forced vital capacity, DLco difusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide, KL-6 Krebs von den Lungen-6, CRP C-reactive protein, ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate, Δ changes from baseline
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sieiro c, Ordas Martínez J, Calleja Antolín S, Garcia Herrero J, De la Calle J, Retuerto M, Sierra L, Bollo de Miguel E, Díez Álvarez E. Serum KL-6 as a Predictive Biomarker for Interstitial Lung Disease Progression and Mortality in Systemic Sclerosis: A Prospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-kl-6-as-a-predictive-biomarker-for-interstitial-lung-disease-progression-and-mortality-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-prospective-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-kl-6-as-a-predictive-biomarker-for-interstitial-lung-disease-progression-and-mortality-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-prospective-cohort-study/
