Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0506–0521) Sjögren’s Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I: Etiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) affects 10-15% of Sjögren disease (SjD) patients, leading to increased morbidity and reduced survival. The true prevalence may be higher due to underdiagnosis, partly due to the lack of effective risk factor–based screening tools compared to other connective tissue diseases. Current guidelines recommend screening at-risk SjD patients using high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), but effective risk factor estimation tools are lacking, leaving it unclear which patients should be referred for HRCT in practice. The objective was to develop a decision support tool for estimating the risk of ILD in SjD patients, guiding HRCT referrals in clinical practice.
Methods: We included all SjD patients from three European expert rheumatology centers (Zurich, Oslo and Vienna) with available HRCT images of the chest. All HRCT images were reviewed by expert radiologists at each site for the presence of ILD. Available data included demographic, serological and laboratory data, clinical SjD manifestations, and other comorbidities. To create the decision support tool, we developed a nomogram based on a logistic regression model (with Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confident interval (CI)) to estimate patient-specific probabilities, translating multivariable relationships into a graphical tool for clinical application. Predictor variables were selected based on clinical relevance, statistical significance and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) of the final multivariable logistic model.
Results: We included 547 SjD patients with HRCT, of which 163 (29.8%) had ILD. Demographic and clinical characteristics are presented in Table 1. In multivariable regression, age (OR 1.01, 95%CI 1.01-1.07, p< 0.001), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (OR 1.03, 95%CI 1.01-1.04, p=0.003), and complement C3 (OR 0.13, 95%CI 0.05-0.35, p< 0.001) were significantly associated with the presence of ILD, adjusted for male sex, polyneuropathy, lymphoma, hypergammaglobulinemia and anti-La/SSB antibodies. The model was deemed acceptable (AUC 0.8). Based on this multivariable model, we built a nomogram which is a practical decision support tool estimating the probability of ILD in SjD patients, informing HRCT referrals based on individual risk.An example patient who is female, 50 years old, positive for anti-La/SSB, has hypergammaglobulinemia, an ESR of 40 mm/hour, and C3 of 0.8g/L has a total score of 15.5, which corresponds to a 50% predicted risk of having ILD.
Conclusion: We developed a nomogram-based decision support tool that effectively estimates the risk of ILD in SjD patients using key predictors such as age, sex, hypergammaglobulinemia, antibodies, extrapulmonary organ manifestation, ESR and complement C3 levels. This tool aids clinicians in making informed HRCT referral decisions, addressing potential underdiagnosis in at-risk SjD patients and improving early detection and outcomes. Future validation in broader populations is necessary to confirm its clinical utility.
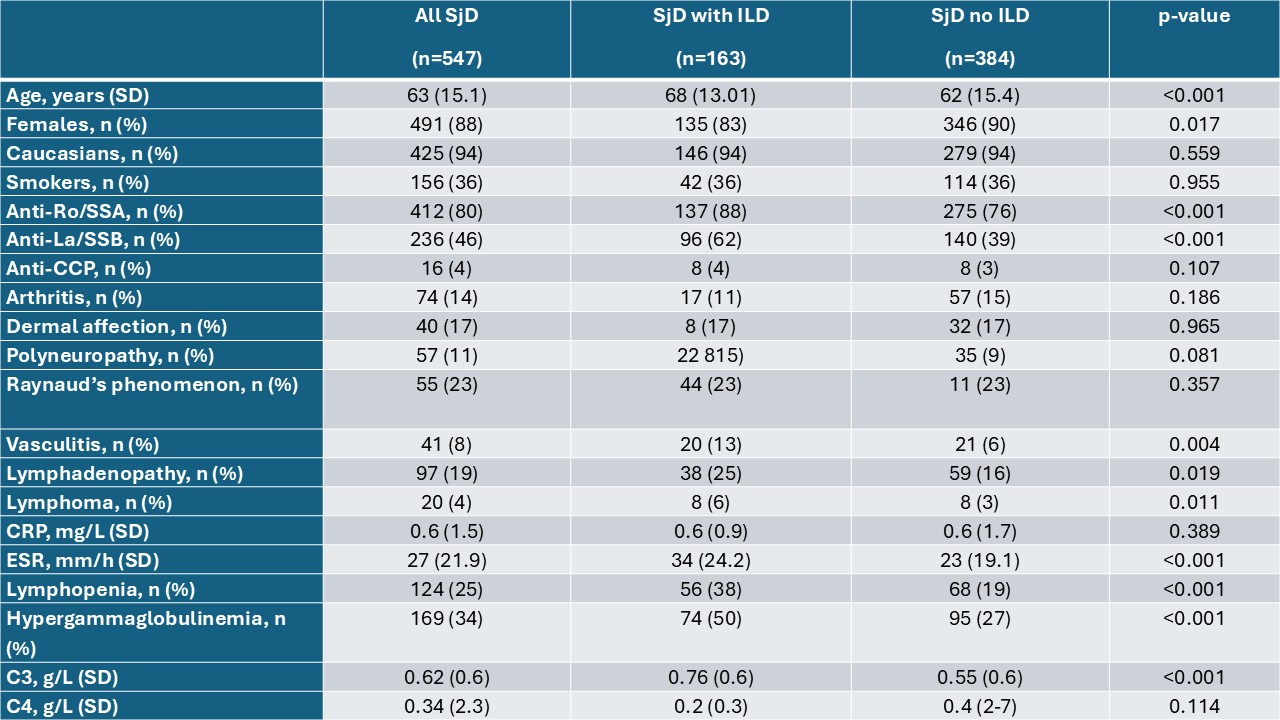 Table 1: Baseline characteristics of patients with SjD and HRCT scans segregated by the presence of ILD
Table 1: Baseline characteristics of patients with SjD and HRCT scans segregated by the presence of ILD
.jpg) Figure 1: Nomogram estimating the ILD probability in SjD patients, informing HRCT referrals based on individual risk
Figure 1: Nomogram estimating the ILD probability in SjD patients, informing HRCT referrals based on individual risk
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hoffmann-Vold A, Kastrati K, Sprecher M, Langballe E, Diep P, Fretheim H, Andersson H, Studenic P, Müller-Durovic B, Brunborg C, Bruni C, Clarenbach C, Frauenfelder T, Aaløkken T, Moe N, Prosch H, Radner H, Molberg Ø, Distler O. A risk estimation tool for clinical practice to improve early ILD detection in Sjögren Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-risk-estimation-tool-for-clinical-practice-to-improve-early-ild-detection-in-sjogren-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-risk-estimation-tool-for-clinical-practice-to-improve-early-ild-detection-in-sjogren-disease/
