Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Regulatory T cells (Tregs) modulate inflammation, maintain self-tolerance, and promote tissue repair, and thus hold promise as a versatile therapeutic tool. Autologous polyclonal Tregs have a favorable safety profile but equivocal efficacy in autoimmune disorders. Engineered Tregs offer a novel approach by introduction of a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific for tissue- or disease-associated antigens. SBT777101 is an autologous Treg product transduced with a CAR specific for citrullinated proteins (Cit-P), which are present in the inflamed synovium of participants with rheumatoid arthritis (RA, Figure 1). Unlike cytotoxic CAR-T therapies, SBT777101 may restore balance to the immune system without cell destruction. Potential mechanisms of action include bystander suppression of antigen presenting cells and effector T cells, IL2 consumption, and immunomodulatory cytokine production to promote immune homeostasis and tissue repair.REGULATE-RA is an ongoing first-in-human, phase 1 study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of autologous CAR-Treg therapy targeting Cit-P in patients with refractory RA. Exploratory endpoints include the assessment and characterization of SBT777101’s pharmacokinetic (PK) profile, pharmacodynamic (PD) parameters, mechanism of action (MOA), and preliminary efficacy.
Methods: The study includes RA participants aged 18-70 with moderate-to-severe active disease (DAS28-CRP≥3.2). Participants must have demonstrated an inadequate response to, or intolerance of, at least 3 biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs with differing MOA. SBT777101 is prepared by transduction of autologous Tregs with a Cit-P-specific CAR and is administered in a 3+3 dose-escalation design (figure 2). Participants are monitored for adverse events and clinical response over a 48-week study period. PK, PD, and MOA are evaluated in peripheral blood and, where available, synovial biopsies. All participants are encouraged to enter a 15-year long-term follow-up study for safety evaluation.
Results: Prior to patient enrollment, a manufacturing process for SBT777101 was established and shown to produce consistent yield, functionality, and molecular signatures from both healthy donors and RA participants. For dosed participants, the yield and molecular signatures of manufactured products have remained consistent with the preclinical manufacturing results.As of April 2025, four participants have received infusions of SBT777101, and no dose-limiting toxicities have been observed. Four additional participants are enrolled but are not yet dosed. Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1.All four dosed participants tolerated the infusion, with no cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxicity, or other immune-mediated toxicities detected. Clinical assessments and biomarker analyses are ongoing to assess changes in disease activity, systemic inflammation and Treg activity.
Conclusion: To date, CAR-Treg therapy targeting Cit-P demonstrates a favorable safety profile in this early phase study. Ongoing enrollment and follow-up will provide additional insights into characterization, pharmacodynamics and efficacy outcomes.
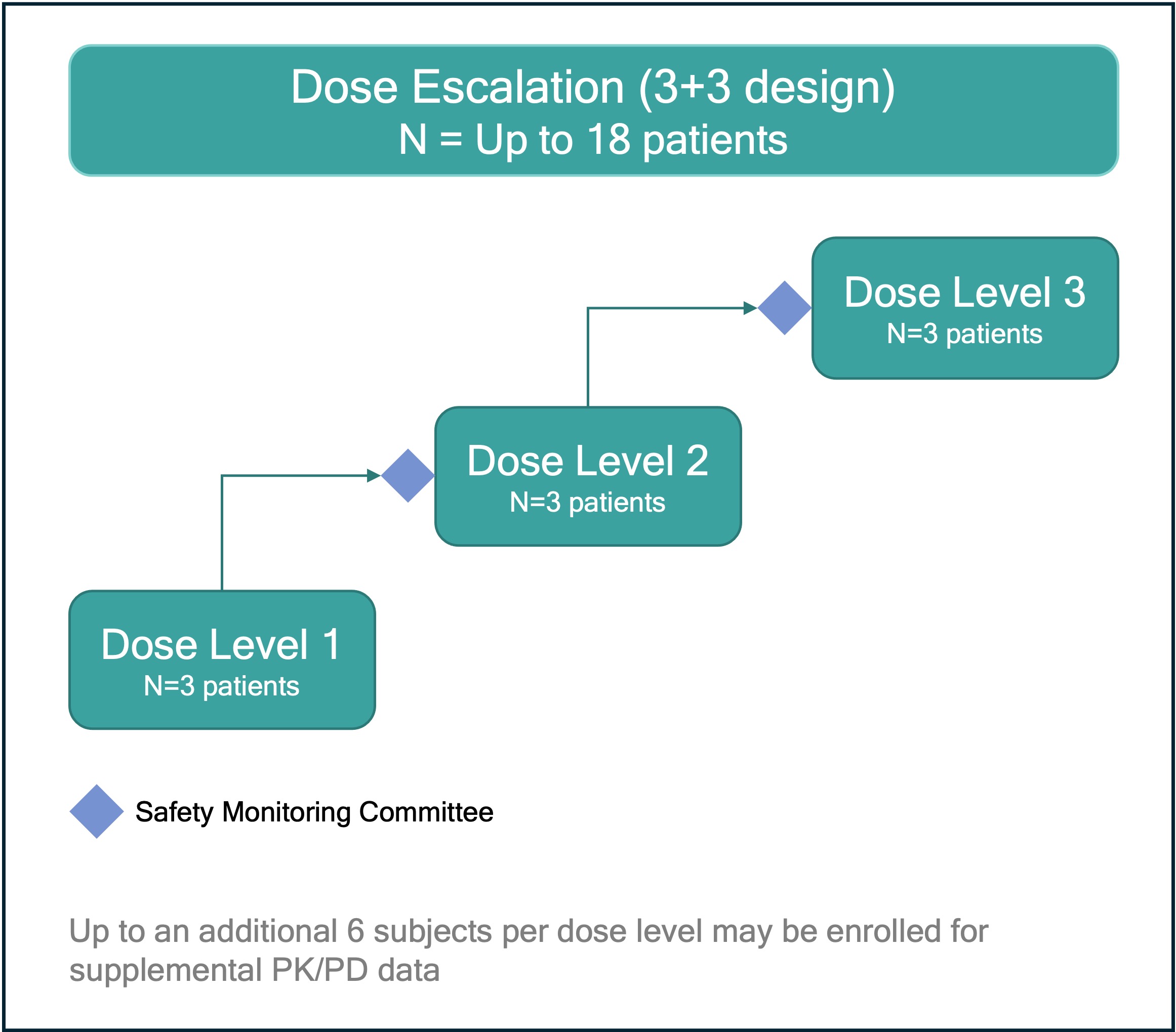 Figure 1: SBT777101 CAR-T regulatory cells target citrullinated intracellular proteins (Cit-P). Cit-P are released by activated neutrophils undergoing NETosis. Cit-P can serve as autoantigens leading to the formation of anti-CitP antibodies (ACPA), citrullinated peptides presented on HLA-DRB*01 “shared epitope” alleles activate T cells, and Cit-P-ACPA immune complexes activate macrophages. These innate and adaptive immune processes amplify inflammation leading to tissue damage. Engineered Tregs expressing a CAR reactive to Cit-P are hypothesized to down-modulate multiple inflammatory processes and promote tissue repair.
Figure 1: SBT777101 CAR-T regulatory cells target citrullinated intracellular proteins (Cit-P). Cit-P are released by activated neutrophils undergoing NETosis. Cit-P can serve as autoantigens leading to the formation of anti-CitP antibodies (ACPA), citrullinated peptides presented on HLA-DRB*01 “shared epitope” alleles activate T cells, and Cit-P-ACPA immune complexes activate macrophages. These innate and adaptive immune processes amplify inflammation leading to tissue damage. Engineered Tregs expressing a CAR reactive to Cit-P are hypothesized to down-modulate multiple inflammatory processes and promote tissue repair.
.jpg) Figure 2: REGULATE-RA is a first-in-human phase 1 dose-escalation study. Each dose level cohort comprises three participants, with a safety monitoring committee evaluation prior to escalation to the next dose cohort.
Figure 2: REGULATE-RA is a first-in-human phase 1 dose-escalation study. Each dose level cohort comprises three participants, with a safety monitoring committee evaluation prior to escalation to the next dose cohort.
.jpg) Table 1: Participant Characteristics. Eight participants have been enrolled in the study as of April 2025; four participants have received drug product. Abbreviations: Pt – Participant; AI- American Indian; AN- Alaska Native; RF- Rheumatoid Factor; ACPA- Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies; CRP- C-reactive Protein; ESR- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; DAS28- Disease Activity Score; DMARDs- disease modifying antirheumatic drugs; b/ts- Biologic/targeted-synthetic; MOA- Mechanism of Action
Table 1: Participant Characteristics. Eight participants have been enrolled in the study as of April 2025; four participants have received drug product. Abbreviations: Pt – Participant; AI- American Indian; AN- Alaska Native; RF- Rheumatoid Factor; ACPA- Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies; CRP- C-reactive Protein; ESR- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; DAS28- Disease Activity Score; DMARDs- disease modifying antirheumatic drugs; b/ts- Biologic/targeted-synthetic; MOA- Mechanism of Action
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baxter S, Bitton A, Yuan V, Aslam F, Challener G, Graf J, Griffith M, Katsumoto T, Kohler M, Massarotti E, Moreland L, Rosenthal A, Sparks J, Vlad S, Yinh J, Clauw A, Arai S, Carvidi A, Chavez A, Gabriel O, Gyurko R, Hall M, Seifert J, Stainton E, Blake M, Fox-Bosetti S, Fromhold M, Jensen M, Lebrec H, O'Bryan S, Pace A, Wang M, Xiao Y, Arron J, Bluestone J. Phase 1b Study of SBT777101, an Engineered CAR-T-Regulatory Cell Product, in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Interim Demographics and Safety [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/phase-1b-study-of-sbt777101-an-engineered-car-t-regulatory-cell-product-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-interim-demographics-and-safety/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/phase-1b-study-of-sbt777101-an-engineered-car-t-regulatory-cell-product-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-interim-demographics-and-safety/
