Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Janus kinase inhibitors have been shown to ameliorate pain as well as inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Pain response trajectories were modeled in patients treated with filgotinib in the FINCH 1 trial.
Methods: FINCH 1 (NCT02889796) was a 52-week trial in which patients with RA and an inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX) received filgotinib 200 mg or 100 mg, adalimumab or placebo, each with MTX. Patients reported pain on a visual analog scale (VAS) ranging from 0 mm (no pain) to 100 mm (worst possible). Moderate pain was defined as a score of 40–60 mm, with scores >60 mm indicating severe pain. Group-based trajectory modeling1 was used to identify patient groups with similar pain responses over a 12-month period.
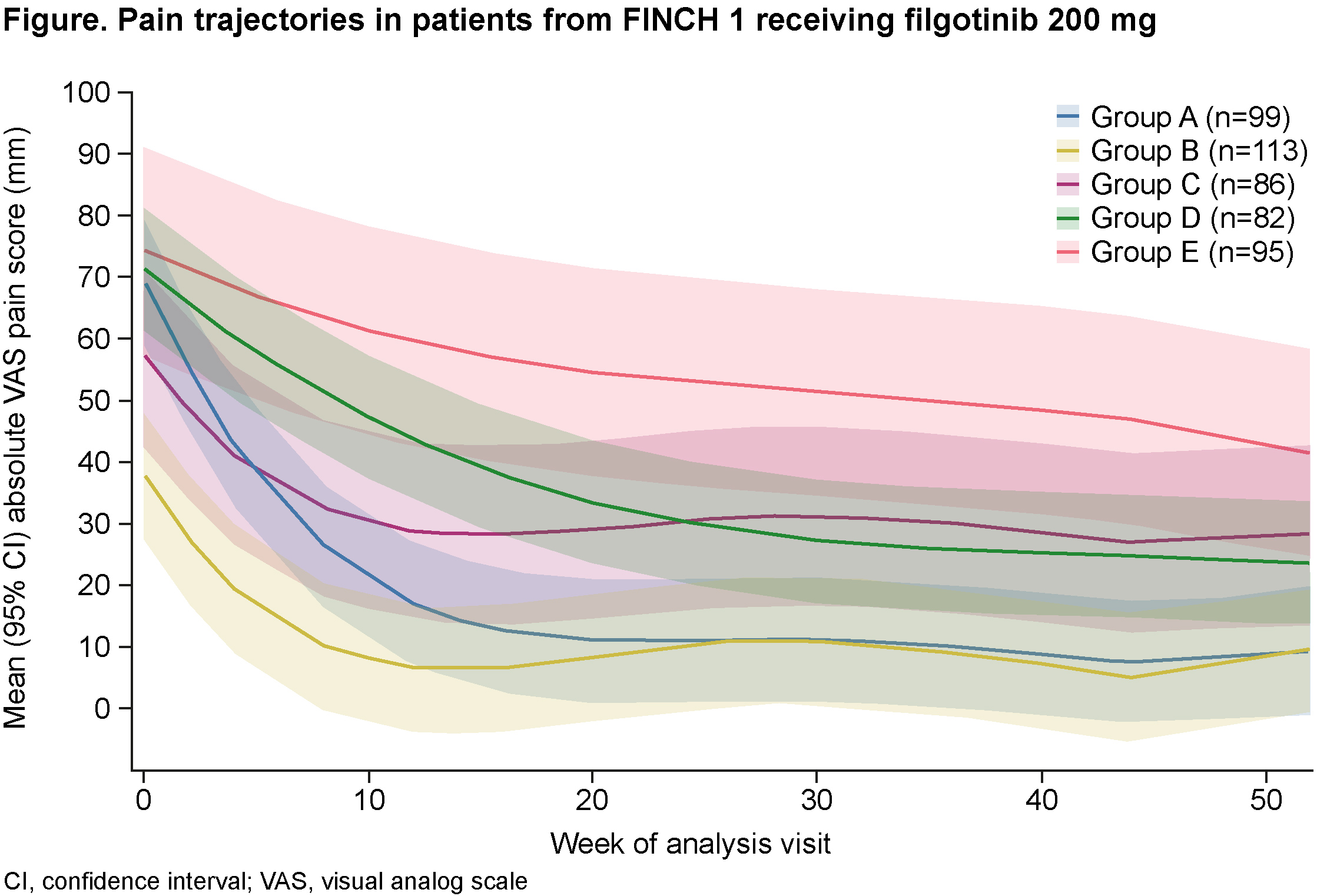
Results: Among patients receiving filgotinib 200 mg (n=475), modeling produced five distinct groups of pain response trajectory (Figure). Age, disease duration and erosion score were similar across all groups at baseline. Groups A and B (45% of patients) had a rapid reduction in pain in the first 3 months, with the improvement maintained over 12 months. Group A had the greatest reduction in pain. Groups C and D (35% of patients) had a slower response but achieved a 50% pain reduction after 6 months. Group E (20% of patients) had severe pain at baseline (mean VAS pain approx. 75 mm) and persistent, moderate pain over 12 months. Mean VAS pain score was < 40 mm at Month 3 in Groups A, B and C (approx. 60% of patients) and at Month 6 in Groups A, B, C and D (80% of patients). At Months 3, 6 and 12, the greatest absolute changes in Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) and 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36) Physical Component Summary (PCS) scores were seen in patients with the most rapid pain responses (Groups A and B) (Table). At Month 6, 50% of patients in Group A and 53% in Group B were in remission (by Clinical Disease Activity Index), compared with 3% in Group E (noted for highest median DAS28-CRP and lowest [worst] median SF-36 PCS score at baseline). At Months 6 and 12, the greatest improvements in patient’s and physician’s global assessment of disease activity occurred in Group A. Lack of efficacy was the most common reason for discontinuation in Group E (10.5%); 2.1% discontinued due to adverse events. In Groups A, B, C and D, the leading reason for discontinuation was adverse events (6.1%, 4.4%, 7.0% and 8.5%, respectively), followed by lack of efficacy (5.1%, 2.7%, 5.8% and 7.3%, respectively). Similar pain trajectories were observed in patients receiving filgotinib 100 mg (n=480).
Conclusion: Of patients with prior inadequate response to MTX treated with filgotinib 200 mg, 80% achieved a substantial reduction in pain within 6 months. The most rapid pain responses with filgotinib were associated with the greatest improvements in other disease-related measures. Overall, these data illustrate the heterogeneity of treatment response in patients with RA and underscore the importance of communicating realistic expectations and timelines to patients.Reference: 1. Nagin DS, et al. Stat Methods Med Res 2018;27:2015–23.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor P, Tanaka Y, Dron L, Van Beneden K, Burmester G, Fautrel B. Characterization of Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Distinct Patterns of Pain Improvement Following Treatment With Filgotinib: A Post Hoc Analysis of FINCH 1 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-based-on-distinct-patterns-of-pain-improvement-following-treatment-with-filgotinib-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-finch-1/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-based-on-distinct-patterns-of-pain-improvement-following-treatment-with-filgotinib-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-finch-1/

.jpg)