Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0430–0469) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at increased risk of developing cardiovascular (CV) events compared to the general population. However, this risk is often underestimated by current CV event risk prediction algorithms that do not take the characteristics of RA into account. The expanded cardiovascular risk prediction score for rheumatoid arthritis (the ERS-RA) has been shown to be superior to models that only incorporate traditional risk factors in predicting the risk of CV in patients with RA. This study aims to externally validate the ERS-RA for predicting 10-year CV event risk in Chinese patients with RA.
Methods: Patients with RA from a Chinese nationwide, multicenter, prospective cohort, enrolled between October 2008 and May 2024 were included as the external validation cohort. Discrimination was evaluated using C-index, and calibration was examined using comparisons of observed versus predicted risks.
Results: A total of 10,721 patients with RA were included. The incidence rate of CV events was 5.65 per 1,000 person-years. The C-index of the ERS-RA in this Chinese cohort was 0.831 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.801 – 0.861). The overall calibration slope was 1.012 (95% CI 0.873 – 1.152), and the observed-to-expected ratio was 0.796 (95% CI 0.676 – 0.937). Across clinically relevant risk intervals, the ERS-RA slightly overestimated CV event risk by 1.41%–2.18% for patients with the predicted risks of < 5%, 5–7.5%, and 7.5–10%, but underestimated CV risk by 10.46% for patients with the predicted risk ≥10%.
Conclusion: The ERS-RA model demonstrated excellent discrimination and calibration for 10-year CV risk prediction in Chinese patients with RA. These results add to growing evidence for the clinical utility of ERS-RA in US, European, and now Chinese populations.
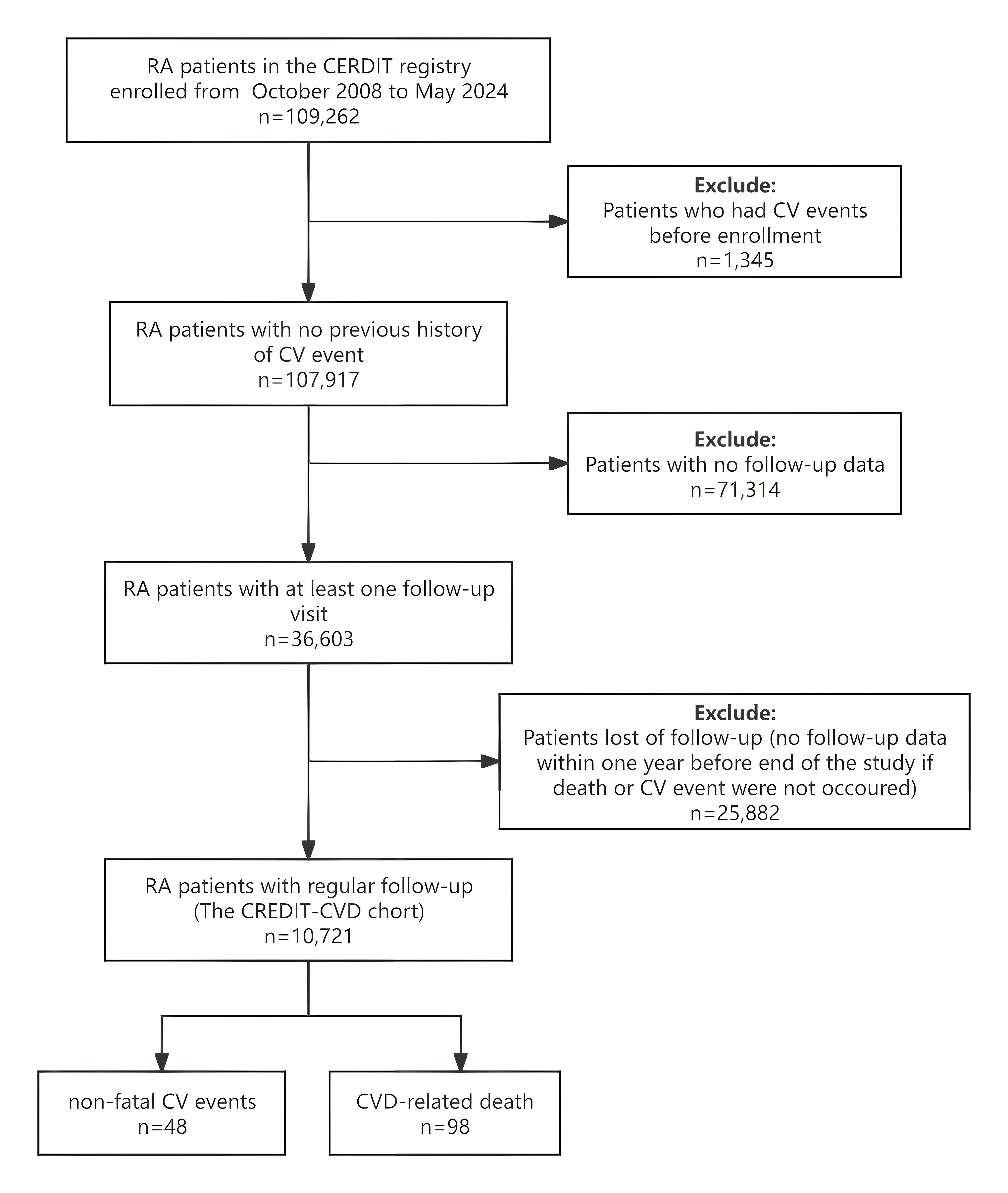 Figure 1. Study flow chart. *RA, rheumatoid arthritis; CREDIT, The Chinese Registry of Rheumatoid Arthritis; CV, cardiovascular; CVD, cardiovascular disease
Figure 1. Study flow chart. *RA, rheumatoid arthritis; CREDIT, The Chinese Registry of Rheumatoid Arthritis; CV, cardiovascular; CVD, cardiovascular disease
.jpg) Figure 2. Comparison of cumulative hazard of cardiovascular events between four predicted 10-year cardiovascular event risk levels ( < 5%, 5.0-7.5%, 7.5-10%, and ≥10.0%) in the CREDIT-CVD cohort with imputed mHAQ (A) and without mHAQ (B)
Figure 2. Comparison of cumulative hazard of cardiovascular events between four predicted 10-year cardiovascular event risk levels ( < 5%, 5.0-7.5%, 7.5-10%, and ≥10.0%) in the CREDIT-CVD cohort with imputed mHAQ (A) and without mHAQ (B)
* CVD, cardiovascular disease.
.jpg) Figure 3. Calibration plots comparing the observed and predicted 10-year risk of cardiovascular event by the ERS-RA score in the CREDIT-CVD cohort with imputed mHAQ (A) and without mHAQ (B)
Figure 3. Calibration plots comparing the observed and predicted 10-year risk of cardiovascular event by the ERS-RA score in the CREDIT-CVD cohort with imputed mHAQ (A) and without mHAQ (B)
*Short black bars at the x-axis indicate distribution of predicted risks.
**ERS-RA, expanded risk score for cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dong X, Jiang N, Li H, Paudel M, Liu J, Duan X, Wu D, Li H, Li F, Wang Y, Liu J, Xu S, Luo H, dai h, Chi S, Xu J, Wu L, zheng z, Xue J, Yu X, Huang Q, Shi X, Zhang X, Huo Y, Wang Q, Zeng X, Solomon D, Li M, Tian X. Performance of the expanded cardiovascular risk prediction score for rheumatoid arthritis (ERS-RA) in a nationwide multicenter Chinese cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-the-expanded-cardiovascular-risk-prediction-score-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-ers-ra-in-a-nationwide-multicenter-chinese-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-the-expanded-cardiovascular-risk-prediction-score-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-ers-ra-in-a-nationwide-multicenter-chinese-cohort/
