Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0430–0469) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease associated with systemic inflammation and increased cardiovascular risk, particularly heart failure (HF). Patients with RA and cardiopulmonary involvement face worse outcomes, including higher HF incidence, mortality, and healthcare use. While earlier studies link RA to adverse cardiac events, large-scale, recent analyses on both mortality and resource utilization are limited. This study fills that gap by analyzing nationwide data (2016–2021) to compare in-hospital mortality in HF admissions with and without RA.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (2016–2021) to identify adult hospitalizations with a primary diagnosis of heart failure. Patients were stratified by the presence of rheumatoid arthritis involving the heart or lung (RAHL), defined by ICD-10 codes. In-hospital mortality was assessed using unadjusted and multivariable logistic regression analyses comparing RAHL and non-RA groups. Subgroup analyses were performed for systolic, diastolic, and combined heart failure types.Healthcare utilization (total charges and costs) was evaluated via unadjusted and adjusted linear regression. All models adjusted for demographics, comorbidities, hospital factors, and illness severity.
Results: Logistic regression models were used to examine mortality and heart failure subtypes. In unadjusted analyses, RAHL was associated with a more than twofold increased odds of mortality (OR 2.09, 95%,p < 0.01). This association persisted after adjustment for confounders (adjusted OR 2.12, 95%, p < 0.01). For combined systolic and diastolic heart failure admissions, the unadjusted model yielded an OR of 2.38 (95%, p < 0.01), which was attenuated controlling for confounders resulting in an adjusted OR of 1.51 (95%, p < 0.01). Interestingly, while systolic heart failure admissions demonstrated a significant association in the unadjusted model (OR 1.21, 95%, p < 0.01), the adjusted odds ratio was not statistically significant (OR 0.91, 95%, p = 0.09). However, diastolic heart failure admissions remained significantly elevated in both the unadjusted (OR 3.07, 95%, p < 0.01) and adjusted (OR 1.89, 95%, p < 0.01) models. Linear regression showed that RAHL was linked to higher healthcare utilization, with significantly increased total hospital charges (adjusted coefficient: $9,472.21) and costs (adjusted coefficient: $2,232.58) in both unadjusted and adjusted models (p < 0.01) among RAHL patients. From the Forest plot, RAHL, hospital type, insurance type, and certain racial/ethnic groups were strong predictors of mortality, while female sex, higher income brackets, and Midwest location showed protective associations.
Conclusion: Our analysis indicates that heart failure patients with rheumatoid arthritis have more than double the odds of mortality and higher healthcare utilization than those without RA. Despite the retrospective design and reliance on ICD coding, these results underscore the need for enhanced clinical surveillance, tailored treatment strategies, and further studies incorporating detailed therapeutic and cardiac data to better guide management.
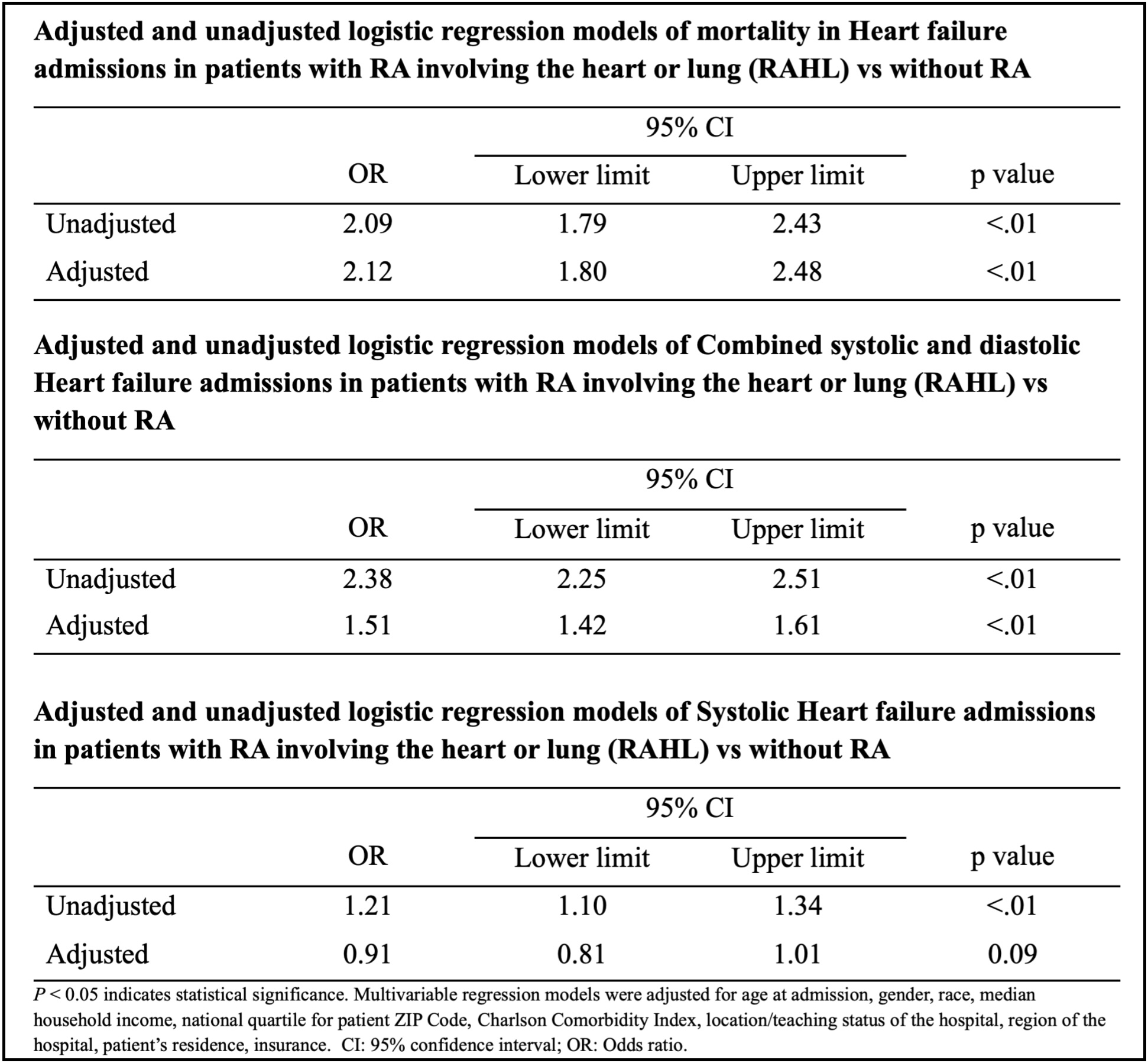 Table 1 shows Adjusted and unadjusted logistic regression models
Table 1 shows Adjusted and unadjusted logistic regression models
.jpg) Table 2 shows Adjusted and unadjusted logistic and linear regression models
Table 2 shows Adjusted and unadjusted logistic and linear regression models
.jpg) Table 3 shows Forest Plot of Odds Ratio of Predictors of Mortality in HF
Table 3 shows Forest Plot of Odds Ratio of Predictors of Mortality in HF
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sapkota N, Sule-saa S, Aryal Y, Ntow M, Bista K, Rajeev P, Alemonai j, Duodu E, Ghimire B, Hein P, Sackey J, Towfig M, Lamptey R, Gobena T, Pinkrah D, Ulysse M. Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on mortality and other outcomes in Heart failure: A nationwide analysis. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-on-mortality-and-other-outcomes-in-heart-failure-a-nationwide-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-on-mortality-and-other-outcomes-in-heart-failure-a-nationwide-analysis/
