Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0430–0469) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Optimization of biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) may be feasible in those who have maintained remission for at least six months. However, this approach carries the risk of disease flare, underscoring the need for reliable predictors to guide clinical decisions. Identifying robust clinical and molecular markers can help design personalized strategies that enhance safety and therapeutic success.The aim of this study was to identify clinical and molecular predictive variables and develop two models (one for sustained remission and another for joint flare) in RA patients undergoing bDMARD optimization. Both models integrated clinical and molecular data.
Methods: Data were obtained from the OPTIBIO clinical trial (Eudra-CT 2012-004482-40) and the REMRABIT Project (PMP15/00032), a multicenter, open-label, randomized, phase IV trial. Adults with RA (1987 ACR criteria), in remission for ≥6 months on TNFi or tocilizumab, were randomized (1:1) to continue or taper bDMARD. The optimization group (n=96) was analyzed. Logistic and Cox regression models were developed for sustained remission and flare, respectively. Model performance was assessed using AUC-ROC and concordance index (C-index) over a 12-month follow-up. Analyses were performed using SPSS v28 and R v4.3.1.
Results: Of 195 randomized patients, 74/96 in the optimization group achieved successful tapering after 12 month follow up. In the remission model, older age (8% lower odds per year) and higher 3v-DAS28-CRP (90% lower odds per unit) were significant predictors. The C allele of rs5746065 (TNFRSF1B) and the G allele of rs1560011 (CLEC2D) were associated with sustained remission, with a potential role for rs6555900 (KCNIP1). This model yielded an AUC of 0.88, sensitivity 84%, specificity 83%, and NPV/PPV of 60% and 95%. In the flare model, significant predictors included higher 3v-DAS28-CRP, joint erosions, pain VAS, low hemoglobin, systolic blood pressure, anti-IFN-γ antibodies, and two SNPs. The C allele of rs5746065 (TNFRSF1B) reduced flare risk by 69%, and the C allele of rs9594987 in gene ENOX1 (T/C) by 85%. The model showed a C-index of 0.884, AUC of 0.911 (95% CI: 0.82–0.99), sensitivity 75%, specificity 93%, and NPV/PPV of 93% and 76%.
Conclusion: Combination of predictive clinical, proteomic and genomic biomarkers are crucial for guiding treatment optimization in RA. These models provide promising tools to support personalized bDMARD dose reduction. Further external validation is needed to confirm their generalizability across diverse populations and clinical settings.
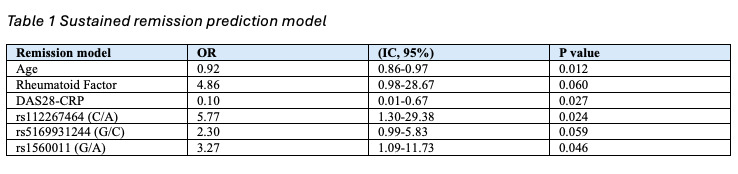 Sustained remission prediction model
Sustained remission prediction model
.jpg) Image 1 AUC of prediction models
Image 1 AUC of prediction models
a. Joint flare prediction model b. Sustained remission model
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Galindo Domínguez L, Acasuso B, Balboa V, Cañete J, Fernández-Gutiérrez B, Gonzalez-Alvaro I, Pablos j, Bejerano-Herreria C, silva M, rego Pérez I, Ruiz-Romero C, De-Toro-Santos F, Oreiro N, Blanco f. Models to predict flare and sustained remission in Rheumatoid Arthritis patients on optimization treatment with bDMARDs: clinical and molecular insights [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/models-to-predict-flare-and-sustained-remission-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-on-optimization-treatment-with-bdmards-clinical-and-molecular-insights/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/models-to-predict-flare-and-sustained-remission-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-on-optimization-treatment-with-bdmards-clinical-and-molecular-insights/

.jpg)