Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0357–0386) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: As part of a five-year cooperative agreement with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Lupus Foundation of America (LFA) has implemented the digital lupus self-management (SM) education program, “Strategies to Embrace Living with Lupus Fearlessly (SELF).” Launched online in January 2022, and as a mobile app in September 2023, SELF offers user-tailored SM education, tracking tools, and support. As engagement is a primary challenge for mobile health (mHealth) apps generally1, this effort used social media promotion as a way to explore incentives to improve app engagement.
Methods: In January 2025, we launched a social media promotion to incentivize engagement by offering a gift box of lupus self-care items to new and existing SELF users who used the app at least four times during the month. Users were asked to complete any of the following actions on any four days: an SM skill-building activity, an entry in the symptom tracker, or an entry in the medication tracker. We compared this to a previous social media promotion period in September 2024 when new users were incentivized to sign-up for SELF with a similar gift. Across the two promotion periods, September 2024 (P1) and January 2025 (P2) we examined new user sign-ups, retention beyond the initial day in new users, and engagement for four or more days in new and existing users. Categorical comparisons of new user sign-ups, retention beyond the initial day, and engagement for four plus days were assessed using Chi Square test. User feedback was evaluated qualitatively.
Results: Likely due to wider promotional efforts, total SELF users was higher in P1 (n = 1946) than P2 (n = 455). The proportion of new user sign-ups decreased from P1 (91%; n = 1777) to P2 (61%; n = 301), while the proportion of existing users increased over the same period (p = 0.00) (Fig 1.). In new users, retention beyond the initial day increased from 47% in P1 to 55% in P2 (p = 0.00) (Fig. 2.). In all users, engagement for four or more days increased from P1 (4%) to P2 (16%) (p = 0.00) (Fig. 3). During both promotion periods, the most popular areas of focus for SM skill-building activities were managing symptoms and managing stress. Satisfaction with the app was high.
Conclusion: New users in P1 were higher because of the focus on sign-ups, but the P2 effort was more effective at increasing retention and engagement. Including all users the promotion and focusing on the behavior we aimed to improve, brought more existing users back to SELF in P2. By linking the incentive to retention and engagement rather than sign-ups, we prompted users to do more in the app, use the program as intended, and depart satisfied. 1Amagai, S. et al. (2022). Challenges in Participant Engagement and Retention Using Mobile Health Apps: Literature Review. Journal of medical Internet research, 24(4), e35120. https://doi.org/10.2196/35120
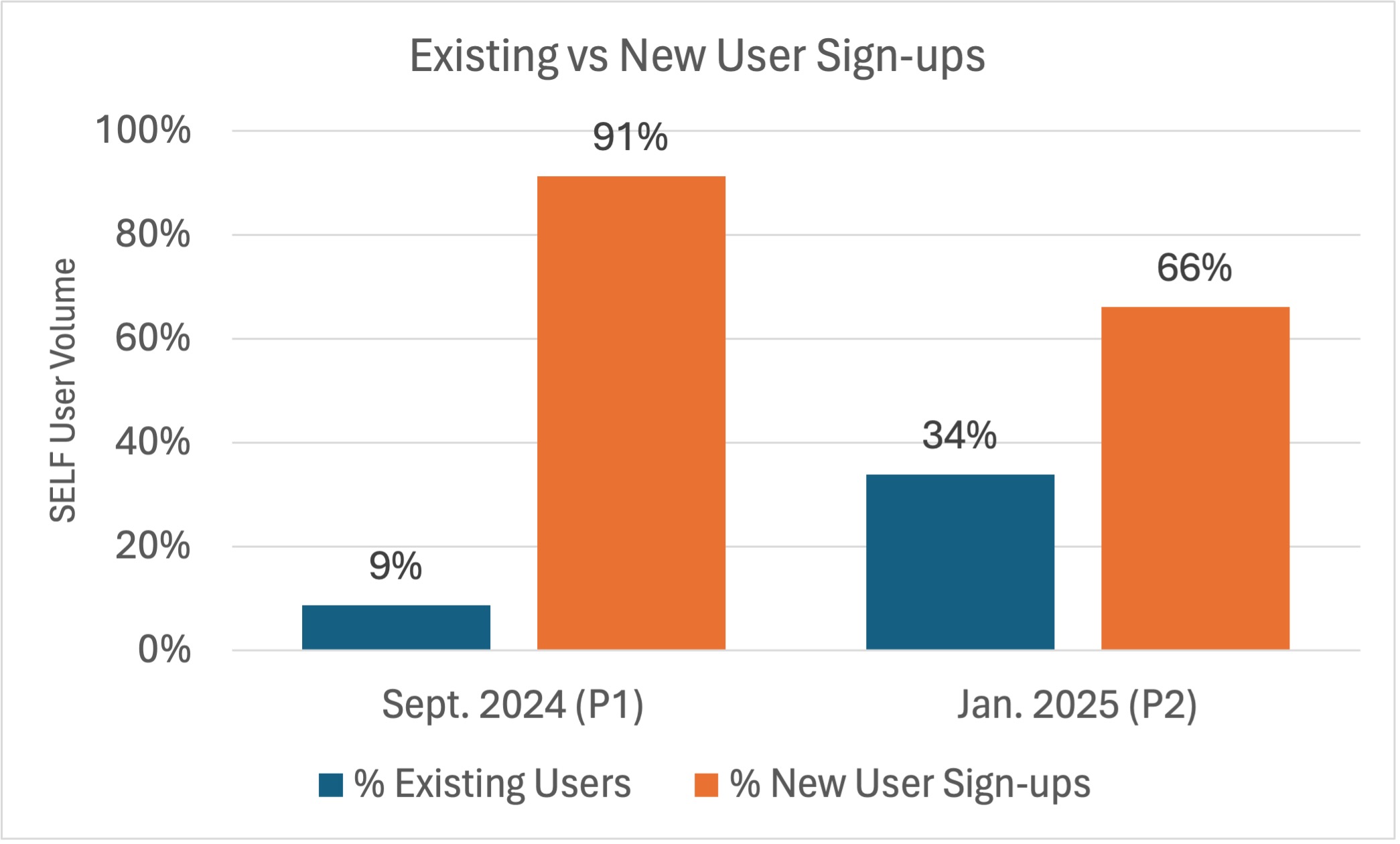 The proportion of new user sign-ups decreased from P1 (91%; n = 1777) to P2 (66%; n = 301), while the proportion of existing users increased from P1 (9%; n = 169) to P2 (34%; n = 154) (p = 0.00).
The proportion of new user sign-ups decreased from P1 (91%; n = 1777) to P2 (66%; n = 301), while the proportion of existing users increased from P1 (9%; n = 169) to P2 (34%; n = 154) (p = 0.00).
.jpg) In new users, retention beyond the initial day increased from 47% in P1 (n = 834) to 55% in P2 (n = 165) (p = 0.00).
In new users, retention beyond the initial day increased from 47% in P1 (n = 834) to 55% in P2 (n = 165) (p = 0.00).
.jpg) In all users, engagement for four or more days increased from 4% in P1 (n = 83) to16% in P2 (n = 72) (p = 0.00).
In all users, engagement for four or more days increased from 4% in P1 (n = 83) to16% in P2 (n = 72) (p = 0.00).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
French M, Carpenter K, Johnson E, Miller M, Crimmings M. Implementation of a Lupus Self-Management mHealth App: Using Incentives to Drive Engagement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/implementation-of-a-lupus-self-management-mhealth-app-using-incentives-to-drive-engagement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/implementation-of-a-lupus-self-management-mhealth-app-using-incentives-to-drive-engagement/
