Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0233–0279) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a rare immune-mediated condition characterized by fibro-sclerosing inflammation, elevated serum and tissue IgG4 levels, and heterogeneous clinical manifestations. Several classification criteria have been proposed, including ACR/EULAR (2019) (1), Umehara (2011) (2), and Okazaki (2012) (3). The objective of this study is to analyze the concordance and differences among the main IgG4-RD classification criteria.
Methods: Observational multicenter study of patients diagnosed with IgG4-RD by expert rheumatologists across 25 Spanish hospitals. The ACR/EULAR, Umehara, and Okazaki classification criteria were applied to determine which patients fulfilled each set. Concordance between the criteria was assessed using PABAK index (prevalence- and bias-adjusted kappa). A Venn diagram was used to represent the overlap among the different criteria, illustrating how many patients fulfilled only one, shared more than one, or met none. Notably, patients who did not fulfill any of the established classification criteria but were diagnosed with IgG4-RD based on expert clinical judgment were categorized as having an exclusive clinical diagnosis. In addition, clinical, demographic, and laboratory data were analyzed for each subgroup.
Results: We include 68 patients (43 men/25 women) diagnosed as IgG4-RD by expert rheumatologists; mean age was 54.4 years. Of them 37 (54.4%) met Okazaki and ACR/EULAR criteria; 16 (23.5) were classified based exclusively on clinical criteria and 13 (19.1%) met Umehara. Concordance between criteria was variable. PABAK showed low-moderate agreement between ACR/EULAR and Umehara (PABAK 0.264), and between Umehara and Okazaki (PABAK 0.441), while the exclusive clinical criterion showed significant discordance, with negative PABAK values (Table 1). Patients classified according to Umehara showed a higher prevalence of pancreatic involvement (47.1%), whereas those classified by ACR/EULAR had more glandular involvement (32.4%). In contrast, the exclusive clinical group exhibited a less typical profile, with lower prevalence of pancreatic involvement (6.2%). Serum IgG4 levels were highest in the Umehara group (303.4 mg/dL). Additional clinical, laboratory, and complementary characteristics are shown in Table 2. When comparing the two most recent criteria, ACR/EULAR and Okazaki, no statistically significant differences were observed. According to the Venn diagram (Figure), only 8 patients met the three criteria simultaneously, 14 met only the Okazaki criteria, 9 met only ACR/EULAR, and none met exclusively Umehara criteria. The greatest overlap was between ACR/EULAR and Okazaki, with 15 patients meeting both sets of criteria.
Conclusion: Concordance among classification criteria was low. These results highlight the inherent challenges in diagnosing IgG4-related disease. Currently available criteria appear to prioritize different aspects of the disease, which may limit their ability to capture the complexity of the clinical picture and hinder their consistent application in clinical practice. A new universally accepted classification criteria for IgG4-related disease are still an unmet need.
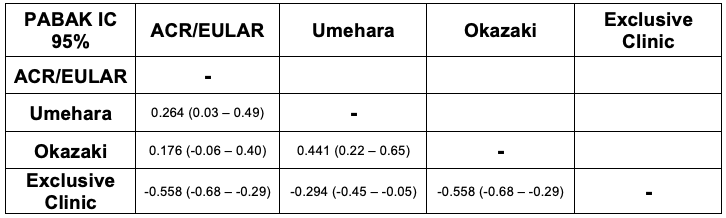 Table 1. Concordance of Classification Criteria: PABAK (95% CI) Between ACR/EULAR, Umehara, Okazaki, and Exclusive Clinic
Table 1. Concordance of Classification Criteria: PABAK (95% CI) Between ACR/EULAR, Umehara, Okazaki, and Exclusive Clinic
.jpg) Table 2: Comparison of the Different Classification Criteria for IgG4-Related Disease (Umehara, Exclusive Clinical, Okazaki, and ACR/EULAR), Including Demographic Data, Clinical Manifestations, and Complementary Tests
Table 2: Comparison of the Different Classification Criteria for IgG4-Related Disease (Umehara, Exclusive Clinical, Okazaki, and ACR/EULAR), Including Demographic Data, Clinical Manifestations, and Complementary Tests
.jpg) Figure: Venn diagram showing the overlap of patients classified as IgG4-RD according to each of the ACR/EULAR, Umehara, and Okazaki criteria.
Figure: Venn diagram showing the overlap of patients classified as IgG4-RD according to each of the ACR/EULAR, Umehara, and Okazaki criteria.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gálvez Sánchez R, Ferraz Amaro I, Lopez Gutierrez F, Loricera J, Martínez Calabuig P, Fragío Gil J, González Mazarí R, Hormigos Martín C, FREITES D, Rodríguez Laguna M, Moya Alvarado P, López I Gómez M, Corominas Macia H, Silva Díaz M, González Arribas G, García Aparicio A, Font-Urgelles J, Casafont Solé I, Castaneda E, Merino Argumánez C, Zas Vaamonde R, Molina Collada J, Rodríguez Montero S, Melero Gonzalez R, Galíndez Agirregoikoa E, Hernández A, Pantoja Zarza L, Braña Abascal I, Jovaní V, Valls Pascual E, Mena Vázquez N, GALLEGO FLORES A, Cabaleiro Raña N, Veroz González R, Andrés M, Castañeda Sainz S, Blanco R. Diagnostic Challenge of IgG4-related Disease: Comparison Between ACR/EULAR, Umehara, and Okazaki Criteria [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnostic-challenge-of-igg4-related-disease-comparison-between-acr-eular-umehara-and-okazaki-criteria/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnostic-challenge-of-igg4-related-disease-comparison-between-acr-eular-umehara-and-okazaki-criteria/
