Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) a systemic autoimmune prothrombotic disorder with long-term consequences. While secondary APS is well studied, large real-world cohorts of primary APS remain scarce. We characterised the clinical, serological, and damage profiles of patients with primary APS and identified predictors of irreversible damage using the Damage Index for APS (DIAPS).
Methods: This retrospective study included 233 primary APS patients meeting the 2006 Sydney criteria for primary APS. Clinical features, antibody profiles, obstetric outcomes, and DIAPS were analyzed. High damage was defined as DIAPS ≥3. Subgroup analyses were performed in thrombotic APS (n=185) and obstetric-only APS (n=48). Multivariable logistic regression was used to identify predictors of high damage.
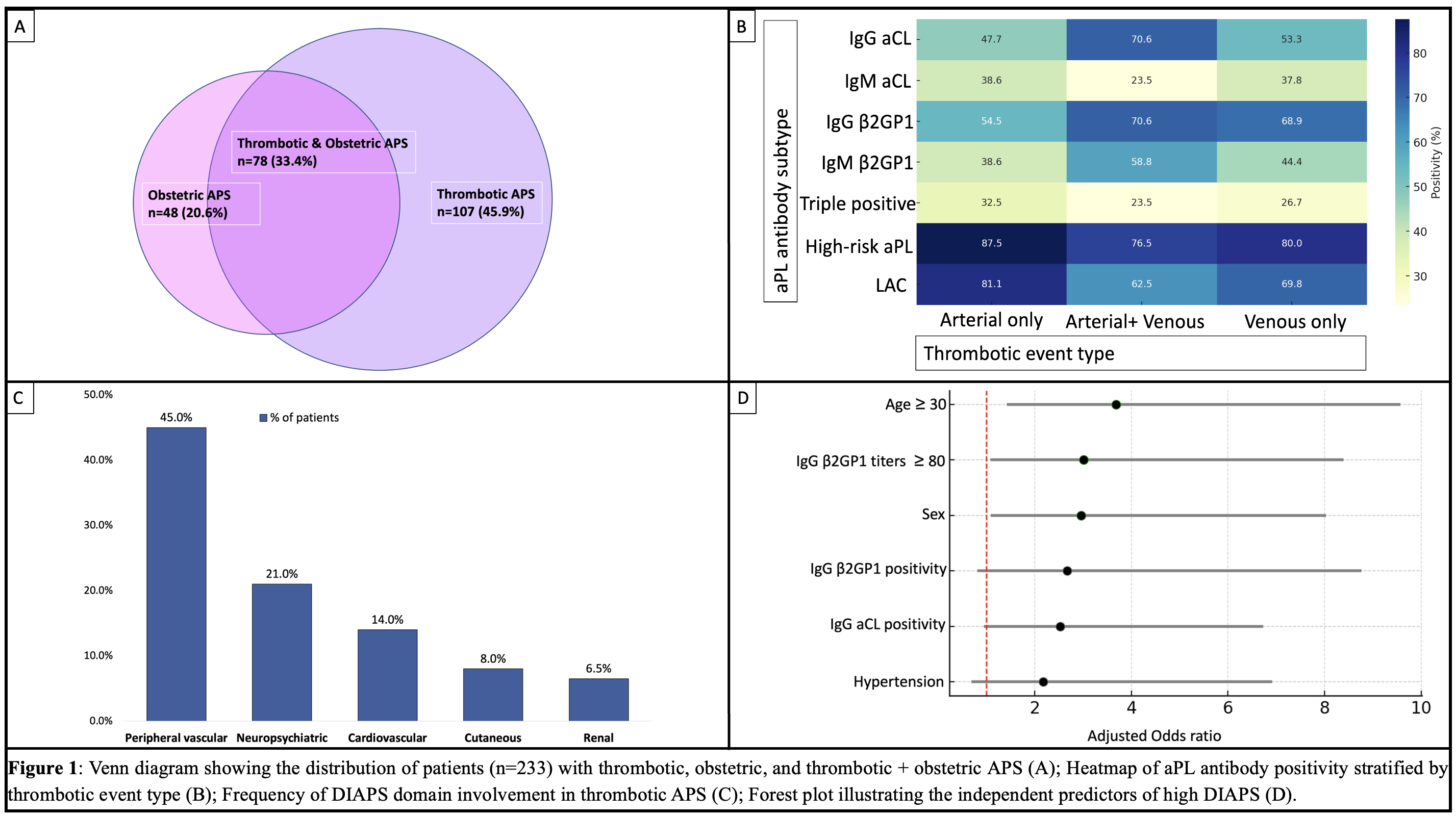
Results: Clinical spectrum: Over a median follow-up of 5.1 years (range 0.5–12.7), 107 (45.9%) had thrombotic-only APS, 78 (33.4%) had both thrombotic and obstetric APS, and 48 (20.6%) had obstetric-only APS (Fig. 1A). In the thrombotic subgroup (n=185), median age was 29 years (range 14–63), and 82.2% were female. Venous thrombosis occurred in 106 (57.8%), arterial events in 63 (34%), microvascular involvement in 27 (14.5%), and CAPS in 4 (1.7%) patients. Neurological manifestations seen were stroke/TIA: n=39 (21.1%); CVT: n=27 (14.6%); Chorea in n=3 (1.2%). Cardiac involvement included valvular lesions in 19 (8.1%), MI in 8 (4.3%). Hematological features included thrombocytopenia in 65 (27.8%) and AIHA in 16 (6.8%) (Table 1). Renal involvement (n=19, 8.2%) included aPL nephropathy (n=10) and immune-mediated glomerular injury (n=9). MI, cutaneous ulcers, and arterial thrombosis were more frequent in males (p< 0.05). Arterial events were numerically more common in patients with triple positivity, LAC, or high-risk aPL profiles (Fig.1B).In obstetric-only APS (n=48), the median number of pregnancies was 3 (IQR 2–3.25), with a high burden of first-trimester loss and adverse outcomes such as preeclampsia or low birth weight in 22.2%.Serological: Of the total 233 patients, 178 (76.4%) had high-risk aPL profiles, 57 (24.5%) were triple-positive, and 83 (35.6%) had single aPL positivity.Damage Index: The median DIAPS score was 1.0 (IQR 0–2, range 0–6); 65.9% had some damage and 17.8% had high damage. The most frequently involved domains were peripheral vascular (44.9%), neuropsychiatric (21.1%), cardiovascular (14.1%), and cutaneous (8.1%) (Figure 1C).On multivariable analysis, age ≥30 (OR 3.9, 95% CI 1.5–10.1), male sex (OR 3.0, 95% CI 1.1–8.0), and IgG β2GP1 high titers (OR 3.0, 95% CI 1.1–8.4) independently predicted high DIAPS (Figure 1D). Hypertension showed a trend in the univariate analysis (table 2) but did not retain statistical significance in the multivariate model for prediction of high damage index.
Conclusion: This large single-center cohort highlights the clinical heterogeneity and damage burden in primary APS. Notably, CVT rates were higher than reported in international APS cohorts. Older age, male sex, and high IgG β2GP1 titers independently predicted irreversible damage. These findings underscore the need for early risk stratification to guide personalized monitoring and care.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
MISHRA R, PHILIP S, MENON J, NAUSHAD R, GOPAL A, MARIASELVAM C, Kavadichanda C, Thabah M, NEGI V. Landscape of Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Clinical Spectrum, Serology, and Predictors of Damage in a Single Center Cohort of 233 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/landscape-of-primary-antiphospholipid-syndrome-clinical-spectrum-serology-and-predictors-of-damage-in-a-single-center-cohort-of-233-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/landscape-of-primary-antiphospholipid-syndrome-clinical-spectrum-serology-and-predictors-of-damage-in-a-single-center-cohort-of-233-patients/

.jpg)
.jpg)