Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Melanocortin receptor agonists, such as adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), are anti-inflammatory with pleotropic functions. We aimed to evaluate the effects of a repository corticotropin injection (RCI; ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.), a complex mixture of ACTH, ACTH related peptides and other porcine pituitary derived peptides, on the inflammatory response and bone damage in the mouse CIA model.
Methods: CIA was induced in six-week-old male DBA/1J mice by subcutaneous injection with CFA emulsified with chicken type II collagen, and IFA and collagen on day 21. Mice (n = 15-16 per group) received subcutaneous RCI (ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 40, or 400 U/kg twice daily), or vehicle days 21-35 (Figure 1A). Changes in hind paw thickness was measured with a caliper, and joints scored (28-point scale). Hind limbs (day 35) were imaged with a micro-computed tomography (CT) scanner, at 9 μm voxel size by standardized methods. Cortical bone analyses were performed on the femoral and tibial diaphysis. Each femur was analyzed at a region of interest 4500 μm proximal to the distal femur growth plate and extended 900 μm proximally. Each tibia was analyzed at a region of interest 4500 μm distal to the proximal tibial growth plate and extended 900 μm distally. CXCL-1 (KC), IL-6, P1NP, CTX-1, and anti-mouse CII antibody levels in sera were determined by ELISA. Statistical analyses were performed by ANOVA followed by post hoc tests.
Results: RCI administration resulted in dose-dependent decreases in ankle swelling in the 40 and 400 U/kg treatment groups compared to vehicle treated [AUC 2.90±39, 1.00±0.19, and 50±0.7, respectively; F(13, 616)=24, P< 0.001; Figure 1B] and similarly for clinical scores [AUC 47±5.3, 9.4±3.2 and 75±5.9; F(13,616)=48.59; P< 0.0001; Figure 1C]. There were no differences in the levels of anti-mouse type II collagen antibody generation between the vehicle, 40, or 400 U/kg treatment groups (67680±6637, 68670±8862, 59360±6768 arbitrary units, respectively; P=0.61; Figure 1D). There were lower levels of serum CXCL-1 in the 400 U/kg treatment compared to the vehicle treated group (P=0.016; Figure 1E) and lower levels of IL-6 (P=0.03; Figure 1F). Both serum levels of CTX-1 and PINP were significantly lower in the 400 U/kg treatment compared to the vehicle treated group (P=0.04; Figure 1G and P=0.02; Figure 1H, respectively). MicroCT measures of BV/TV, Tb.Th., and Tb.Sp. were similar between the groups; however, TMD was higher in both the tibia and femurs in the 40 U/kg and 400 U/kg treatment groups compared to the vehicle treated group (P< 0.05; Figure 1I and J).
Conclusion: As monotherapy, RCI significantly reduced CIA-induced joint swelling in male mice. In addition, RCI treatment resulted in a reduction in inflammatory cytokine responses, but no disruption of IgG formation and less bone loss. These findings demonstrate significant reductions in systemic inflammation in the CIA arthritis model with RCI treatment.
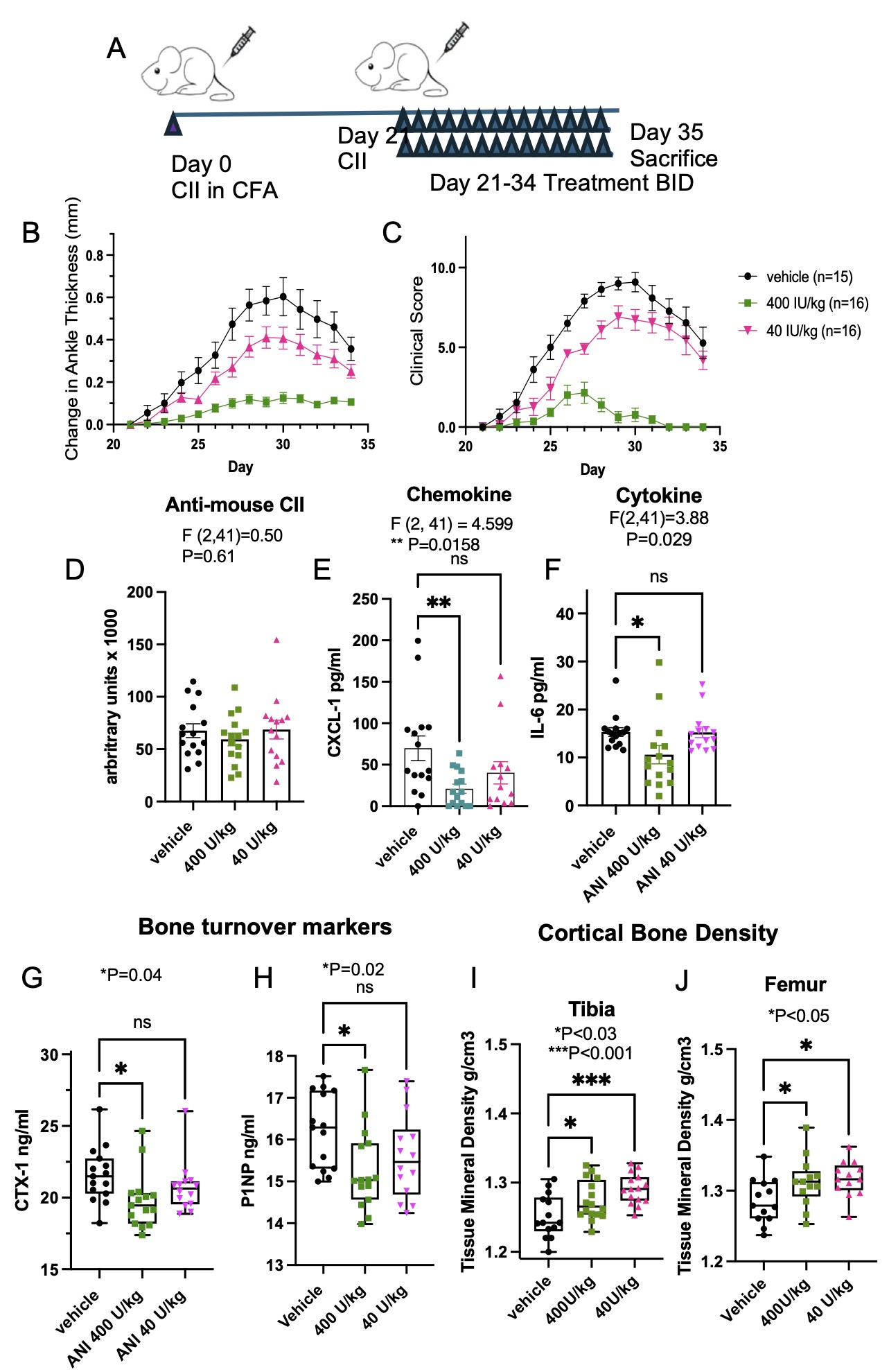 Figure 1. Effects of RCI on CIA. Schematic of experimental protocol (A). DBA/J mice were injected with type II chicken collagen in CFA on day 0 and in IFA on day 21. Starting day 21 mice received RCI or vehicle s.c. injections BID. The ankle widths of the mice were serially measured (B) and the joint inflammation scored (C) demonstrating a reduction in the RCI treated mice compared to vehicle treated. After 14 days of treatment the mice were sacrificed and serum obtained. There were no differences in anti-type II collagen antibody levels (D), but there were reduced serum levels of CXCL-1 (E), IL-6 (F), CTX-1 (G) and P1NP (H) in the 400 U/kg treatment group compared to the vehicle treated mice. Cortical bone density in the tibia (I) and femur (J) of RCI treated mice were greater than the vehicle treated mice.
Figure 1. Effects of RCI on CIA. Schematic of experimental protocol (A). DBA/J mice were injected with type II chicken collagen in CFA on day 0 and in IFA on day 21. Starting day 21 mice received RCI or vehicle s.c. injections BID. The ankle widths of the mice were serially measured (B) and the joint inflammation scored (C) demonstrating a reduction in the RCI treated mice compared to vehicle treated. After 14 days of treatment the mice were sacrificed and serum obtained. There were no differences in anti-type II collagen antibody levels (D), but there were reduced serum levels of CXCL-1 (E), IL-6 (F), CTX-1 (G) and P1NP (H) in the 400 U/kg treatment group compared to the vehicle treated mice. Cortical bone density in the tibia (I) and femur (J) of RCI treated mice were greater than the vehicle treated mice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Corr M, Hsueh G, place A, Lucas D, LANE N. Repository Corticotropin Injection Reduces Inflammation and Bone Turnover Markers in the Murine CIA Model [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/repository-corticotropin-injection-reduces-inflammation-and-bone-turnover-markers-in-the-murine-cia-model/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/repository-corticotropin-injection-reduces-inflammation-and-bone-turnover-markers-in-the-murine-cia-model/
