Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic, fibroinflammatory condition affecting almost all organs. It is a rare entity that is continuously being studied worldwide. It is considered an autoimmune disease that, in addition to the predominance of IgG4 serum elevation in most patients, has some unique immune cell abnormalities, such as the elevation of plasmablast and signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family member 7-positive (SLAMF7+) cytotoxic effector memory T cells (CD4+ cytotoxic T cells – CTL). In this study, we aimed to delve deeper into the demographic/clinical characteristics and cell profiles of patients with definite or probable diagnoses of IgG4-RD.
Methods: The patients were recruited between 2012 and 2023 at a tertiary single center in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Patients were classified using the 2019 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria of IgG4-RD as definite or probable. The immunological cell profile in the peripheral blood of patients was compared with that of healthy individuals using flow cytometry.
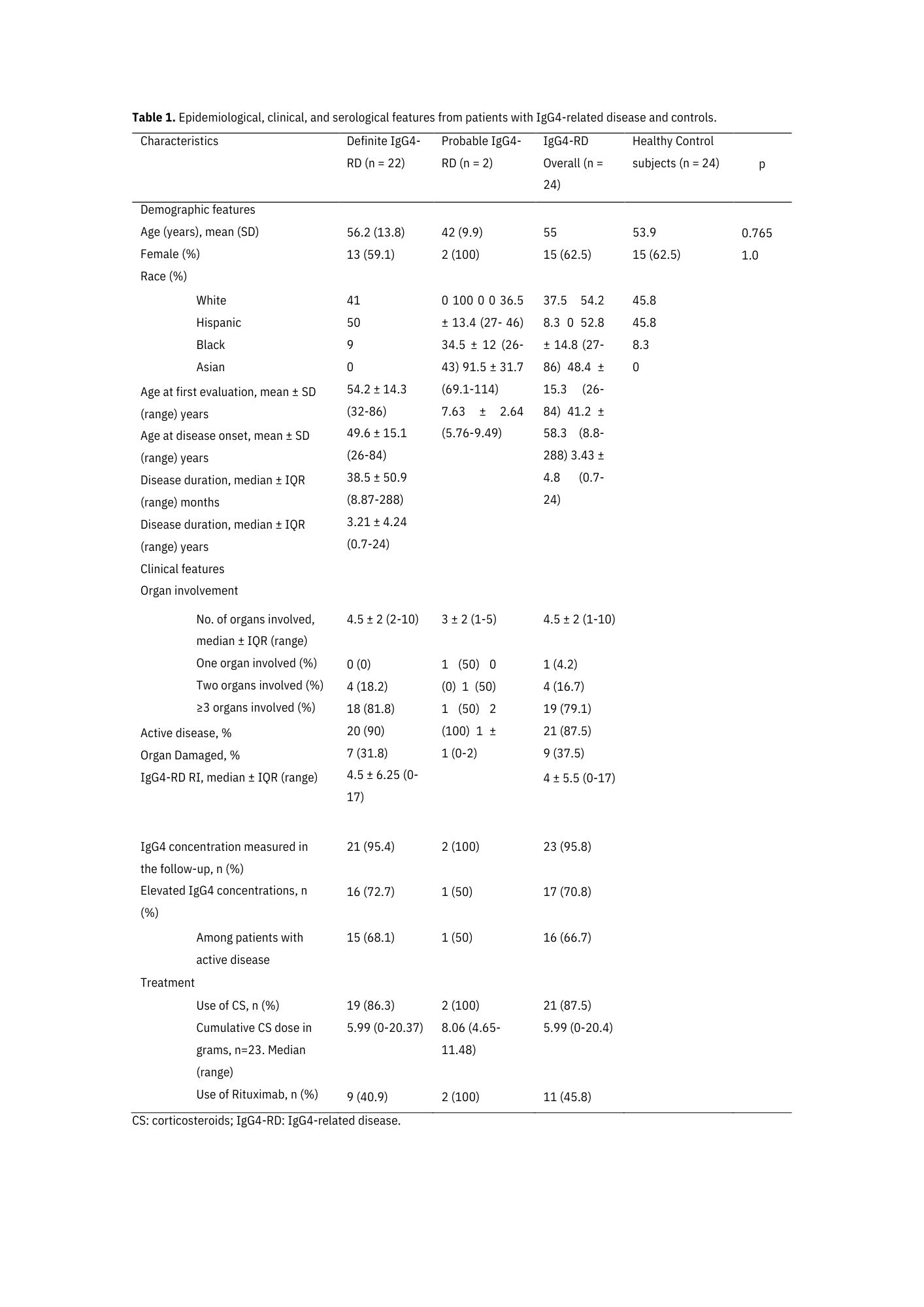
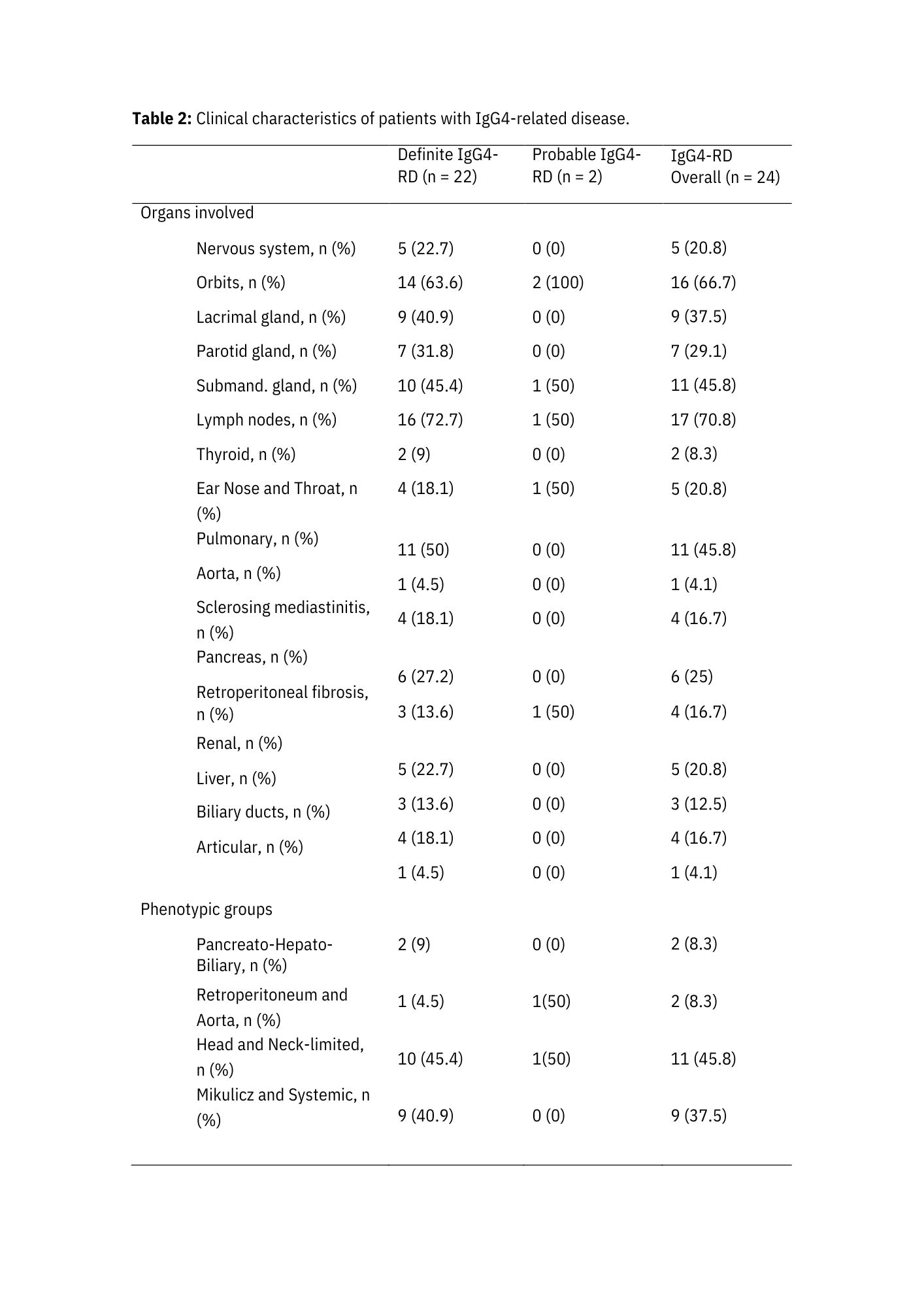
Results: Among 24 patients with IgG4-RD, 22 had definite and two probable diagnoses and were compared with 24 healthy control subjects, paired by sex and age. Demographic features are shown in Table 1. Notably, a clear predominance of females was related to a more significant proportion of patients with head and neck-limited disease (i.e., 11 patients – nine female and two male patients). Around 80% of patients had multi-organ disease and had a higher IgG4-RD responder index. Almost half of the patients were treated with glucocorticoids and rituximab. The most frequent organ involvement were lymph nodes (70%) and orbits (66%) (Table 2). In the immunological evaluation (Table 3), there were a higher number of B cells in healthy control subjects versus patients (225.3 vs. 127.2, p=0.024), transitional B cells (53.3 vs. 32.2, p=0.017), memory B cells (51.4 vs. 22.1, p=0.004), naïve CD4+ T cells (145.7 vs. 69.7, p=0.019), and percentage of naïve CD8+ T cells (43.4 vs. 33.8, p=0.044). In contrast, IgG4-RD patients had a higher percentage of effector memory CD4+ T cells (23.1 vs. 18.2, p=0.002), a percentage of plasmablasts (8.74 vs. 3.1, p=0.048), and a percentage of T CD4+ SLAMF7+ (18.4 vs. 8.6, p=0.001).
Conclusion: We found a clear female predominance in patients with the head and neck-limited phenotype. Although a significant portion of the IgG4-RD patients received rituximab treatment, there was a higher percentage of plasmablasts and T CD4+ SLAMF7+ cells. These findings suggest the potential value of including these immunological evaluations in patient follow-up. However, it is crucial to underscore the need for additional studies to fully understand the worldwide prevalence of IgG4-RD, emphasizing the importance of the immunological patient’s profile.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pinheiro F, Orikaza C, Keppeke G, Sato E, de Souza A. IgG4-related Disease Features and Immunological Profile in a Tertiary Center in Sao Paulo-Brazil [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg4-related-disease-features-and-immunological-profile-in-a-tertiary-center-in-sao-paulo-brazil/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg4-related-disease-features-and-immunological-profile-in-a-tertiary-center-in-sao-paulo-brazil/