Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: PsA occurs in males and females at similar rates. Females participating in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have shown lower treatment efficacy based on composite scores, especially pertaining to biologic DMARD treatments1. Important sex differences in baseline (BL) patient (pt) characteristics were identified in a large, pooled cohort of PsA pts from 3 Phase 3 RCTs of guselkumab (GUS), where females exhibited longer PsA duration; higher BMI, tender joint count (TJC) and Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI) score; and more severe PsA impact on quality of life2. Given the importance of achieving low levels of disease activity across PsA domains, we assessed sex-disaggregated GUS efficacy across multiple PsA signs and symptoms at Week (W) 24 in this same pooled cohort.
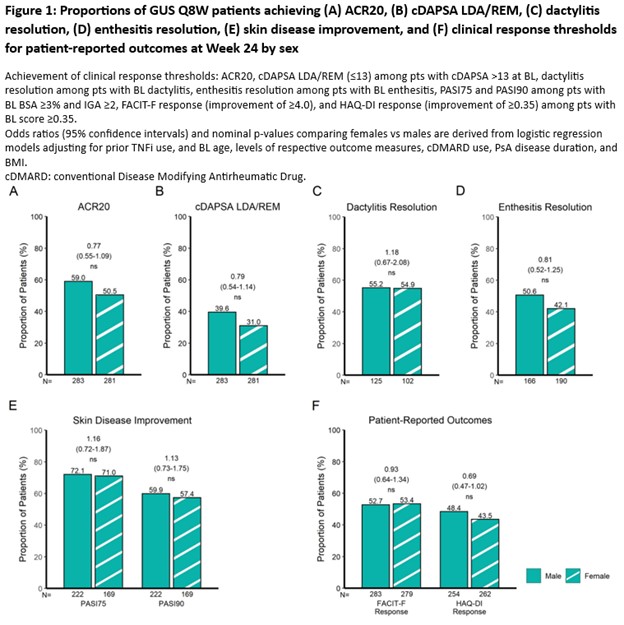
Methods: Post-hoc analyses included 381 PsA pts from DISCOVER-1 (NCT03162796), 739 from DISCOVER-2 (NCT03158285), and 285 from COSMOS (NCT03796858). Rates of achievement of ACR20, Clinical Disease Activity Index for PsA (cDAPSA) low disease activity (LDA)/remission (REM), dactylitis and enthesitis resolution, Psoriasis Area Severity Index improvement from baseline of at least 75% (PASI75), PASI90, as well as Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F) and HAQ-Disability Index (DI) response at W24 were evaluated by sex in pts receiving GUS at W0, W4 and every 8 weeks (Q8W). Non-responder imputation was applied for missing data. Achievement of clinical response at W24 was compared between GUS Q8W-treated male and female pts via adjusted logistic regression (see Fig 1).
Results: Among 564 PsA pts treated with GUS Q8W, no significant difference in GUS efficacy was observed between female and male pts as measured by the primary efficacy outcome common to the 3 RCTs (ACR20) and across PsA domains at W24 (Fig 1). After adjusting for BL characteristics with sex-specific differences in the pooled cohort, including age (female vs male; mean: 48.2 vs 46.1y; p=0.0007), PsA duration (6.9 vs 6.0y; p=0.0086), and BMI (29.9 vs 28.8 kg/m2; p=0.0007; Coates et al, ACR 2024), GUS efficacy was found to be comparable between sexes in terms of achieving ACR20 response (female vs male; 50.5 vs 59.0%; odds ratio [OR] [95% confidence interval (CI)]: 0.77 [0.55-1.09]; not significant [ns]; Fig 1A); composite measure indicating low levels of joint disease activity (cDAPSA LDA/REM: 31.0 vs 39.6%; OR [95% CI]: 0.79 [0.54-1.14]; ns; Fig 1B); dactylitis resolution (54.9 vs 55.2%; OR [95% CI]: 1.18 [0.67-2.08]; ns; Fig 1C); enthesitis resolution (42.1 vs 50.6%; OR [95% CI]: 0.81 [0.52-1.25]; ns; Fig 1D); skin disease improvement (PASI75: 71.0 vs 72.1%; OR [95% CI]: 1.16 [0.72-1.87]; ns and PASI90: 57.4 vs 59.9%; OR [95% CI]: 1.13 [0.73-1.75]; ns; Fig 1E); and clinically meaningful improvements in pt-reported outcomes (FACIT-F: 53.4 vs 52.7%; OR [95% CI]: 0.93 [0.64-1.34]; ns and HAQ-DI: 43.5 vs 48.4%; OR [95% CI]: 0.69 [0.47-1.02]; ns; Fig 1F).
Conclusion: In a large, pooled cohort of PsA pts from 3 RCTs, sex has no significant impact on GUS efficacy as measured by ACR20 and across PsA domains, after adjusting for the sex differences in BL characteristics.
References:
- Eder. Lancet Rheum 2023;5:e716-27.
- Coates et al, ACR 2024; AB1832254.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eder L, Selmi C, Mease P, Ogdie A, Nantel F, Lavie F, Sharaf M, Adelakun O, Rampakakis E, PINA VEGAS L, Coates L. Guselkumab Shows Similar Domain-Specific Efficacy in Females and Males with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Post Hoc Analyses of Three Phase 3, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-shows-similar-domain-specific-efficacy-in-females-and-males-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-post-hoc-analyses-of-three-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-shows-similar-domain-specific-efficacy-in-females-and-males-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-post-hoc-analyses-of-three-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-studies/