Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patient’s Global Assessment of disease activity (PtGA) was found to be the most relevant limiting factor for achieving Boolean 1.0 remission in patients with RA.1 The purpose of this analysis was to investigate the predominant factors responsible for near-miss of Boolean 2.0 remission after 6 months of treatment with upadacitinib (UPA) in patients with moderate-to-severe RA from the UPwArds study.2
Methods: UPwArds (NCT04267536) was a 12-month, prospective, multicenter, non-interventional post-marketing study designed to investigate the impact of baseline CRP levels on the effectiveness of UPA in adults with moderate-to-severe RA in German clinical practice.2 This post hoc analysis was conducted in patients with available data after 6 months of UPA treatment, in order to determine the predominant factors responsible for failure to achieve remission according to the revised Boolean 2.0 criteria (swollen joint count ≤1, tender joint count ≤1, CRP ≤1 mg/dL, and PtGA ≤2 [0–10 cm]) after 6 months of follow-up. Patients achieving three out of four Boolean 2.0 remission criteria were defined as near-misses. Logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the potential association of previously chosen patient‑reported outcomes (PROs), including Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease (RAID) questionnaire components and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 score, with near-miss of Boolean 2.0 remission due to PtGA >2. Additionally, a stepwise logistic regression model was employed to determine whether any of these components could be included in a predictive model for PtGA >2.
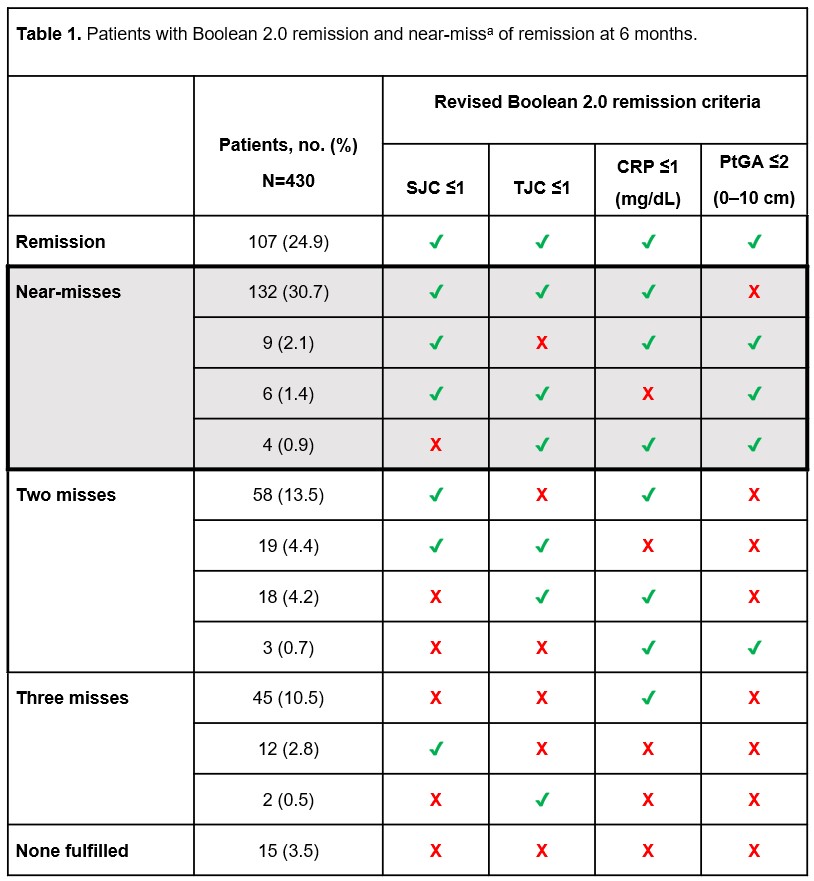
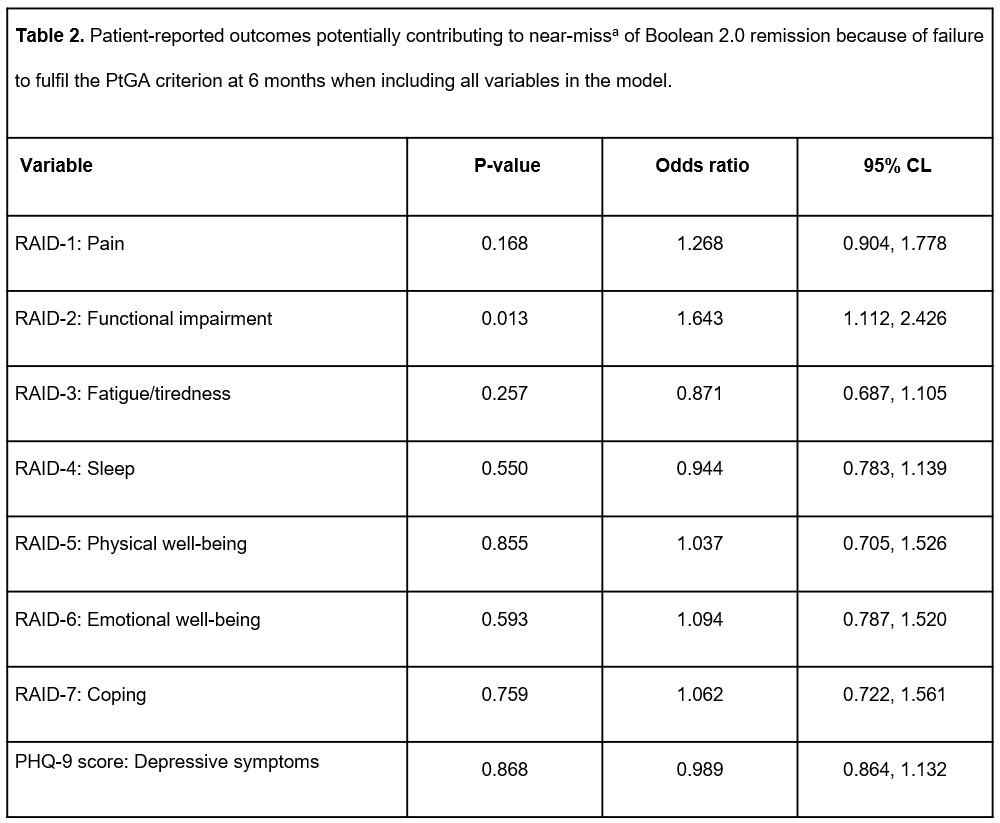
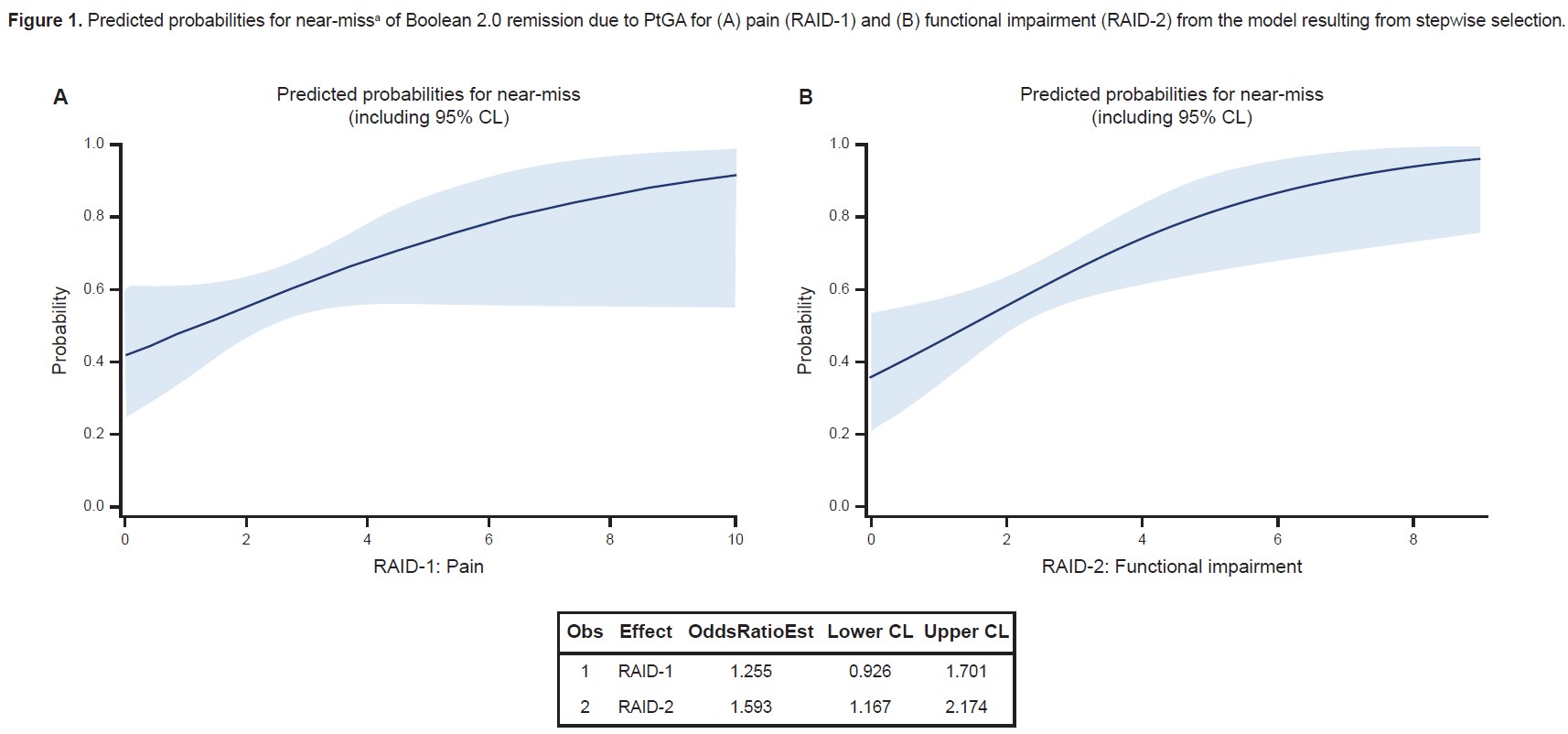
Results: Of 430 patients, 107 (24.9%) achieved Boolean 2.0 remission at 6 months. Of 323 patients who did not achieve Boolean 2.0 remission, 151 (35.1%) were characterized as near-misses, 132 of whom (87.4% of all near-misses) were due to PtGA >2 (Table 1). Functional impairment (RAID-2) was the only component found to be significantly associated with near-miss of Boolean 2.0 remission due to PtGA criterion (odds ratio [OR] =1.643 [confidence limits: 1.112, 2.426]) on logistic regression analysis of all previously chosen variables (Table 2). RAID-2 and pain (RAID-1) were the most relevant factors selected in the stepwise logistic regression model (chosen significance level for variable entry =0.15; chosen significance level for stay =0.2), while functional impairment was the only factor found to be significantly associated with near-miss of Boolean 2.0 remission because of PtGA >2 (OR =1.593 [1.167, 2.174], i.e. ~59.3% higher probability of a near-miss with each additional point in RAID-2; Figure 1). Testing HAQ-DI as the sole independent variable for predicting near-misses confirmed the significant association between functionality and near-miss of Boolean 2.0 remission due to PtGA (OR =3.160 [1.768, 5.645]).
Conclusion: In this analysis, PtGA ≤2 was found to be the main barrier for patients narrowly missing Boolean 2.0 remission, and functional impairment was the most important driver of PtGA. However, other PROs may also be of high relevance in individual patients.
PtGA, Patient’s Global Assessment of disease activity; SJC, swollen joint count; TJC, tender joint count.
The values of 232 out of 239 patients (near-misses due to PtGA >2 [n=132] and patients with Boolean 2.0 remission [n=107]) were included in the logistic regression model, which was statistically significant (P <0.001).
CL, confidence limit; PHQ, Patient Health Questionnaire; PtGA, Patient’s Global Assessment of disease activity; RAID, Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease questionnaire.
CL, confidence limit; PtGA, Patient’s Global Assessment of disease activity; RAID, Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease questionnaire.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Witte T, Kiltz U, Haas F, Riechers E, Prothmann U, Adolf D, Rössler A, Famulla K, Götz K, Krüger K. Patient’s Global Assessment of Disease Activity Is the Most Relevant Factor for Near-Miss of Boolean 2.0 Remission in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Post Hoc Analysis from the Observational UPwArds Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-global-assessment-of-disease-activity-is-the-most-relevant-factor-for-near-miss-of-boolean-2-0-remission-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-post-hoc-analysis-from-the-observation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-global-assessment-of-disease-activity-is-the-most-relevant-factor-for-near-miss-of-boolean-2-0-remission-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-post-hoc-analysis-from-the-observation/