Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Both RF and anti-CCP are associated with erosive disease, increased disease activity, and adverse outcomes in RA. However, there have been limited studies investigating how RF and anti-CCP interact to influence outcomes. We aimed to compare the radiographic erosions, disease flares, and mortality in four cohorts of patients defined by the presence or absence of RF and anti-CCP.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study includes residents of a geographically defined area with incident RA between 2003 and 2019. The index date was defined as the date of fulfillment of either the 1987 ACR or 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria. Patient characteristics were abstracted from medical records. RF and anti-CCP seropositivity status were determined prior to the index date or within one year following to determine the impact of baseline seropositivity on prognosis. Comparison of baseline characteristics between cohorts was performed using chi-square and rank-sum tests. Cox models adjusted for age, sex, smoking status, comorbidities, and calendar year were used to examine the association between seropositivity status and all-cause mortality.
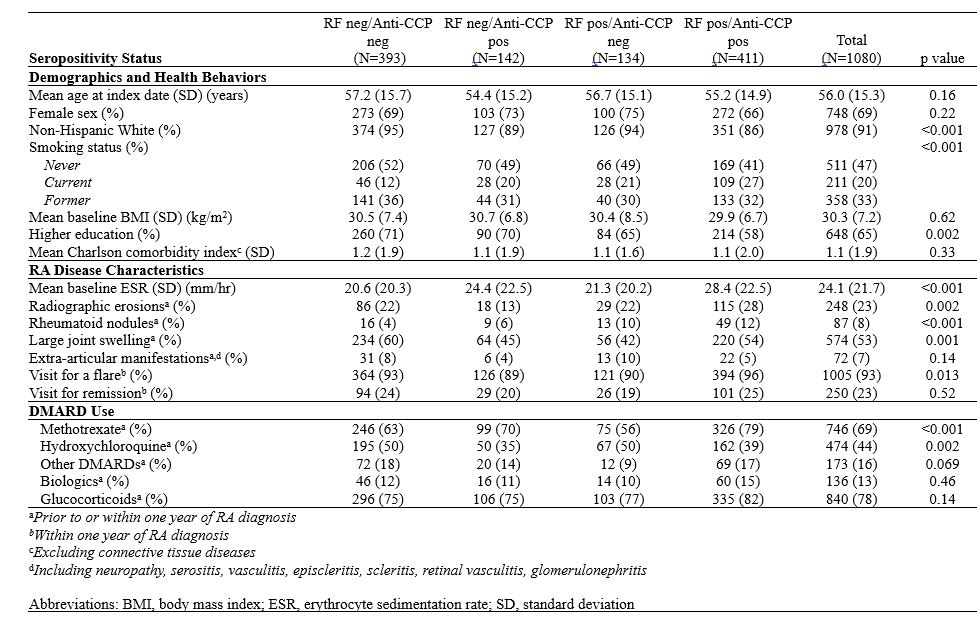
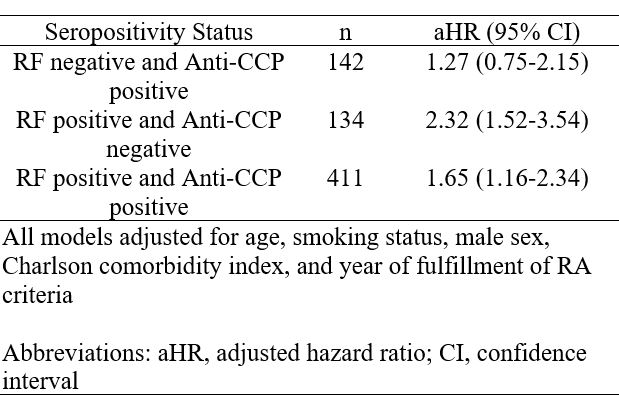
Results: The study included a total of 1,080 patients with RA, with a mean age of 56 years, 69% female and 36% being seronegative, 38% dual seropositive, 13% seropositive for only anti-CCP, and 12% seropositive for RF only. At baseline, 70% of the cohort only seropositive for anti-CCP had been prescribed methotrexate and only 56% of the cohort seropositive for RF only had a prescription for methotrexate. At baseline, 28% of the dual seropositive cohort had radiographic evidence of erosions. Surprisingly, 22% of the cohort seronegative for RA had evidence of erosions along with 22% of the cohort with only RF seropositivity. In contrast, the cohort only seropositive for anti-CCP had 13% of patients with erosions. 96% of the patients in the dual seropositive cohort had at least one visit within the first year of diagnosis for an RA flare. The cohort with the highest percentage of severe extra-articular manifestations was seropositive for RF only (Table 1). Patients with only RF seropositivity had over two times higher mortality compared to patients with seronegative RA (aHR 2.32 [95% CI 1.52-3.54]). Although patients with dual seropositivity had an increase in mortality, it was lower with only a 65% increase (aHR 1.65 [95% CI 1.16-2.34]) and patients with only anti-CCP seropositivity had only a 27% increase in mortality (aHR 1.27 [95% CI 0.75-2.15]) (Table 2).
Conclusion: Among patients with RA, almost a quarter of the seronegative, only RF seropositive, and dual seropositive cohorts had radiographic evidence of erosions at baseline, and the majority of all cohorts had at least one visit for a RA flare within the first year. Interestingly, the cohort that was seropositive for RF only had the highest mortality. This could partially be explained due to the delay in treatment with DMARDs such as methotrexate. Our study suggests that seropositivity for RF is a driver of increased mortality and that it does not interact with anti-CCP to further increase mortality. To optimize the long-term outcomes in RA, increased attention to RF seropositivity at baseline may be warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brooks R, Achenbach S, Kronzer V, Myasoedova E, Crowson C, Davis J. Comparison of Dual RF and Anti-CCP Seropositive, Single Seropositive, and Seronegative RA on Radiographic Changes, Flares, and Mortality [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-dual-rf-and-anti-ccp-seropositive-single-seropositive-and-seronegative-ra-on-radiographic-changes-flares-and-mortality/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-dual-rf-and-anti-ccp-seropositive-single-seropositive-and-seronegative-ra-on-radiographic-changes-flares-and-mortality/