Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In this open-label Phase 1 study, 22 participants were enrolled in 3 cohorts, 10 participants with normal kidney function (eGFR ≥90 ml/min/1.73m2 and no proteinuria), 6 participants mild CKD (eGFR 60-89 ml/min/1.73m2), and 6 participants with moderate CKD (eGFR 30-59 ml/min/1.73m2). Each subject was dosed with a single oral dose of 2.0 mg of ABP-671. PK, PD, and safety were assessed in serial samples of blood and fractionated urine samples over 24 h post-dose. PD was assessed as serial blood and urine uric acid levels. ABP-671 is a novel, selective and potent URAT1 inhibitor in Phase 2b/3 development for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. ABP-671 reduces reabsorption of uric acid (UA) from renal proximal tubules, and significantly decreases serum uric acid (sUA) levels in gout or hyperuricemia patients. ABP-671 exhibited dose-dependent sUA lowering effect and was well tolerated in hyperuricemia and gout patients in a phase 2a study. ABP-671 is renally cleared primarily as unchanged drug and approximately 30% metabolites. It was hypothesized that PK and PD of ABP-671 are impacted by renal impairment.
Methods: In this open-label Phase 1 study, 22 participants were enrolled in 3 cohorts, 10 participants with normal kidney function (eGFR ≥90 ml/min/1.73m2 and no proteinuria), 6 participants mild CKD (eGFR 60-89 ml/min/1.73m2), and 6 participants with moderate CKD (eGFR 30-59 ml/min/1.73m2). Each subject was dosed with a single oral dose of 2.0 mg of ABP-671. PK, PD, and safety were assessed in serial samples of blood and fractionated urine samples over 24 h post-dose. PD was assessed as serial blood and urine uric acid levels.
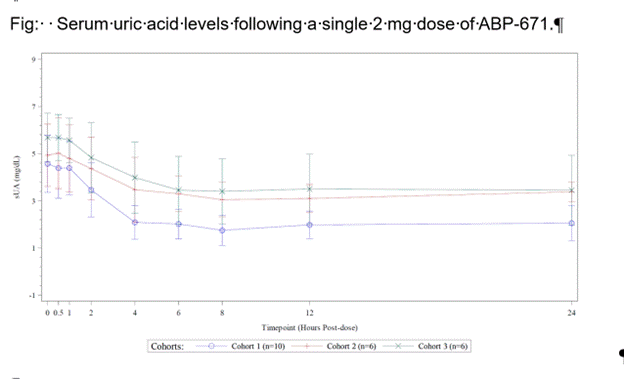
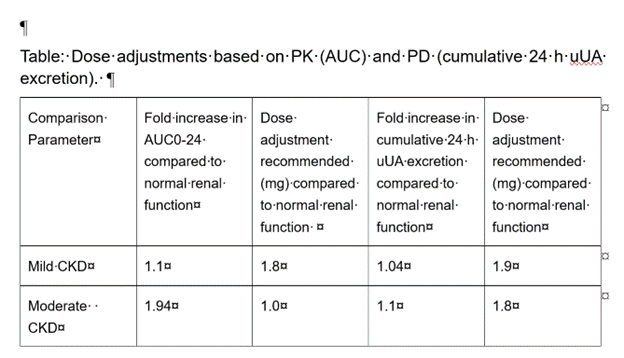
Results: Following a single oral dose of ABP-671 of 2.0 mg, ABP-671 plasma exposures (AUC) and Cmax were increased (167% for AUC and 119% for Cmax) in participants with moderate CKD compared to normal kidney function participants and marginally (119% for AUC, and similar Cmax) in participants with mild CKD. The baseline sUA and serum creatinine (sCr) levels were elevated in subjects with decreased eGFR. sUA in renal impairment decreased in parallel to sUA in normal renal function after ABP-671 dosing. Mean change (SD) in sUA (mg/dL) from baseline at 24h post dose in normal KF, mild, and moderate CKD were: -2.375 (1.185); -1.550 (1.091); -2.233 (0.819) respectively (Fig). Modeling of PK and PD parameters in these 3 cohorts suggested a dose adjustment to attain a similar AUC of ABP-671 as compared to normal renal function for moderate renal impairment to 1.0 mg ABP-671 (Table). However, when 24h urine UA excretion across cohorts was compared between the groups, a dose adjustment to achieve comparable total 24 h urine UA excretion in moderate renal impairment was 1.8 mg and 1.9 mg for mild renal impairment (Table).
Conclusion:
It is concluded that no dose adjustment is required to achieve comparable UA clearances in all cohorts studied, when treated with 2 mg QD. ABP-671 appeared generally safe and well tolerated in participants with normal kidney function and CKD. There were no deaths, serious, or severe TEAEs reported, and no participants were discontinued from the study due to TEAEs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
schwertschlag u, Shi w, PERRY r, Ayesu K, WU r, liu j, Lin J, Jin A. A Phase 1 Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics (PK) and Pharmacodynamics (PD) of a Single Dose of ABP-671 in Participants with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-1-study-to-evaluate-the-safety-tolerability-pharmacokinetics-pk-and-pharmacodynamics-pd-of-a-single-dose-of-abp-671-in-participants-with-chronic-kidney-disease-ckd/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-1-study-to-evaluate-the-safety-tolerability-pharmacokinetics-pk-and-pharmacodynamics-pd-of-a-single-dose-of-abp-671-in-participants-with-chronic-kidney-disease-ckd/