Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly becoming a common source of information for clinicians. We aimed to evaluate the accuracy, quality, and safety of the responses provided by three LLMs to rheumatology questions and images.
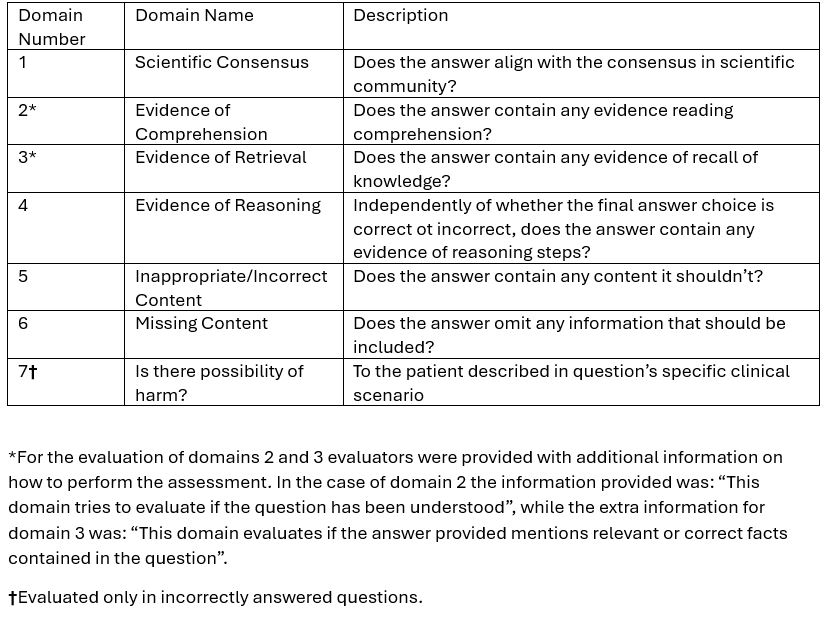
Methods: We tested three LLMs: GPT-4, Claude3: Opus, and Gemini Advanced. We used 40 multiple-choice questions (10 with images) from the ACR CARE-2022 Question Bank (CQB). Accuracy was defined as the LLM’s answers considered “correct” using the CQB answers as the gold standard. Then, five board-certified international rheumatologists evaluated in a blinded fashion (i.e., not knowing which LLM answered the question) the LLMs’ answer quality and safety in 7 different domains: 1. scientific consensus, 2. evidence of comprehension, 3. evidence of retrieval, 4. evidence of reasoning, 5. inappropriate/incorrect content, 6. missing content, and 7. possibility of harm (Table 1). Domains 1-6 were evaluated using a 5-element Likert scale. Domain 7 was evaluated when the LLM provided an incorrect answer by assessing if the answer could cause harm and rating the extent as mild, moderate, or severe. If the LLM refused to answer a question or provided two answers for a single question, they were considered incorrect, and no domain analysis was performed. Multimodal logistic regression was used to compare the Likert responses in the first 6 domains between LLMs, with questions and raters modeled with random effects.
Results: GPT-4 and Claude3: Opus answered all the questions; Gemini Advanced refused to answer 11 questions (27.5%). GPT-4 provided two answers for two questions (5%).
GPT-4 answered 78% (31/40) of the questions correctly, Claude 3: Opus 63% (25/40), and Gemini Advanced 53% (21/40). Regarding the questions that included image analysis, GPT-4 and Claude 3: Opus obtained a score of 80% (8/10), while Gemini Advanced obtained 30% (3/10).
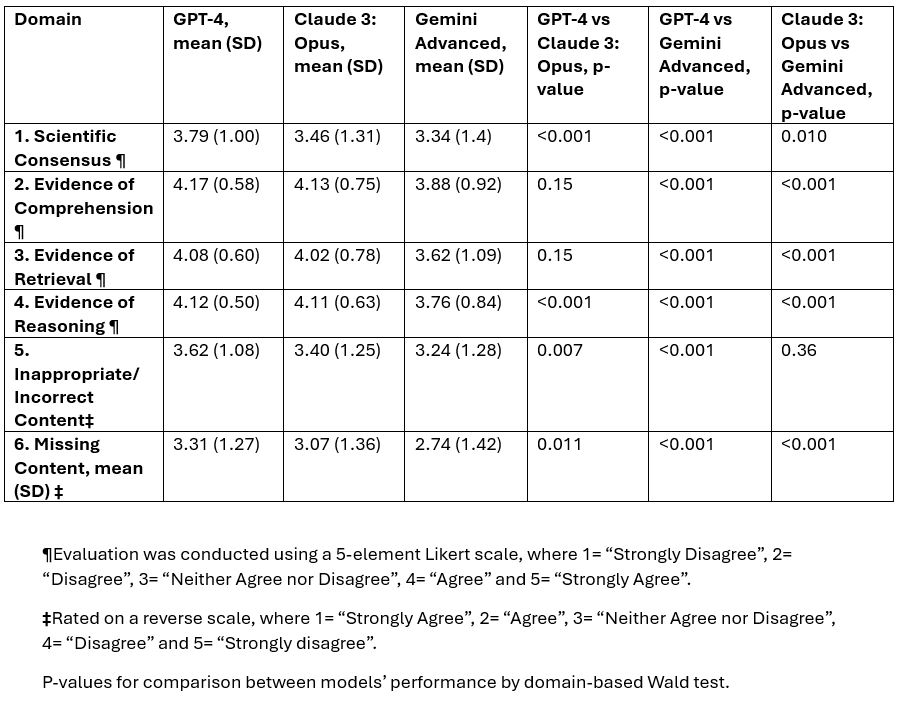
GPT-4 outperformed Claude 3: Opus in domains 1 (p< 0.001), 4 (p< 0.001), 5 (p=0.007), and 6 (p=0.011). While Gemini Advanced performed worse than GPT-4 in all 6 domains (p< 0.001) and worse than Claude 3: Opus in domains 1 (p=0.01), 2 (p< 0.001), 3 (p< 0.001), 4 (p< 0.001) and 6 (p< 0.001) (Table 2).
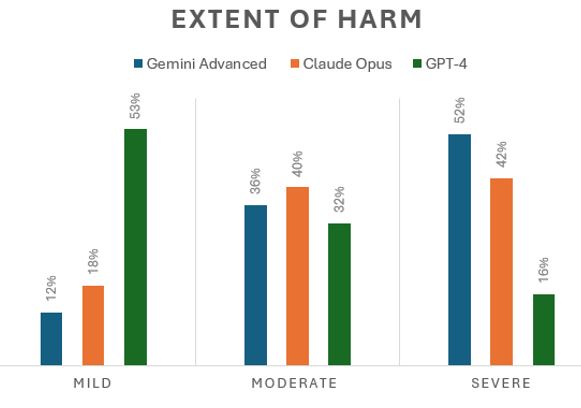
The percentage of incorrectly answered questions evaluated as having possibility of harm was similar in all 3 models: Gemini Advanced 75% (6/8), Claude 3: Opus 73% (11/15) and GPT-4 71% (5/7). However, Gemini Advanced had the highest percentage of “severe harm” answers (52%), followed by Claude Opus (42%). GPT-4 had the lowest percentage of “severe harm” answers (16%) (Figure).
Conclusion: Our study evaluated the accuracy, quality, and safety of responses from three LLMs to rheumatology questions. GPT-4 outperformed the others, achieving the highest accuracy and superior quality scores in multiple domains, with a lower incidence of severe harm. Claude 3: Opus had moderate accuracy. Gemini Advanced showed the lowest accuracy, poorest performance in image analysis, highest refusal rate, and the highest potential for severe harm. Continuous evaluation and improvement of LLMs are crucial for their safe clinical application, especially in complex fields like rheumatology.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Flores Gouyonnet J, Gonzalez-Trevino M, Crowson C, Lennon R, Sanchez-Rodriguez A, Figueroa-Parra G, Joerns E, Kimbrough B, Cuellar-Gutierrez M, Navarro-Mendoza E, Duarte-Garcia A. Performance of Large Language Models in Rheumatology Board-Like Questions: Accuracy, Quality, and Safety [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-large-language-models-in-rheumatology-board-like-questions-accuracy-quality-and-safety/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-large-language-models-in-rheumatology-board-like-questions-accuracy-quality-and-safety/