Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with RA are at a heightened risk of developing significant adverse events (AEs) such as MACE, VTE, and serious infectious events (SIE). Limited data are available evaluating whether effective disease control reduces the risk of AE development. This post hoc analysis assesses the relationship between disease activity and development of significant AEs in RA patients treated with the JAK inhibitor upadacitinib (UPA) 15 mg in the SELECT phase 3 program.
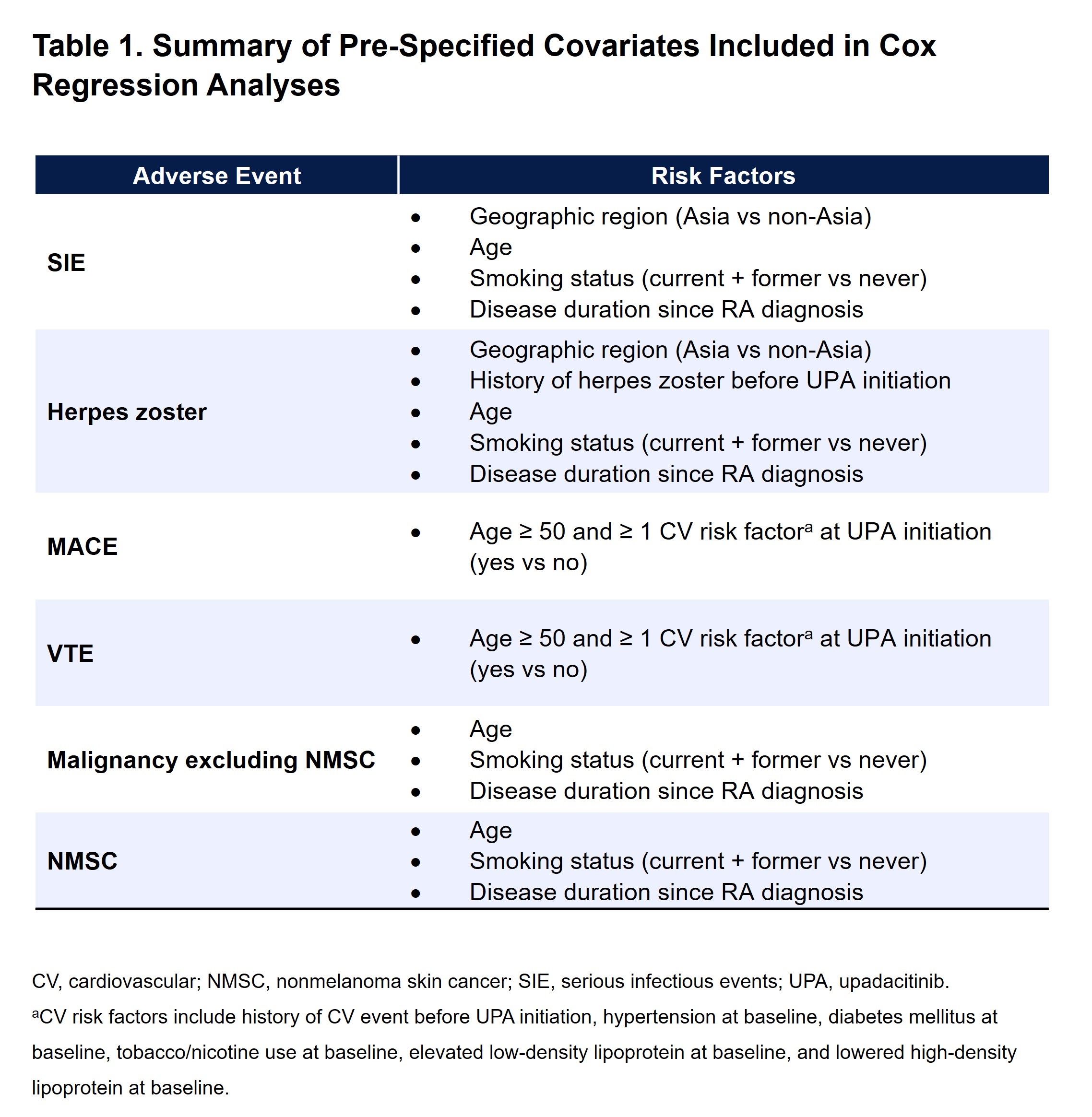
Methods: This post hoc analysis of data from six UPA phase 3 trials included patients randomized to UPA 15 mg once daily and those who switched from placebo, MTX, or adalimumab to UPA 15 mg. Data were analyzed up to ~5 years (week 260; except for data from SELECT-CHOICE, which was analyzed to the final patient visit at 4.2 years [week 216]). All patients who received at least one dose of UPA 15 mg and had a CDAI score >10 at the time of UPA initiation were included. Cox regression analysis was performed for each AE of interest using time-dependent variables (CDAI categories or hsCRP per 5 mg/L increment) along with pre-specified covariates based on the literature (Table 1). CDAI categories were remission (CDAI ≤2.8), low ( >2.8–≤10), moderate ( >10–≤22), or high ( >22) disease activity (LDA, MDA, and HDA, respectively). Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to compare the cumulative time-weighted average CDAI between patients with or without AE occurrence. All P values are nominal.
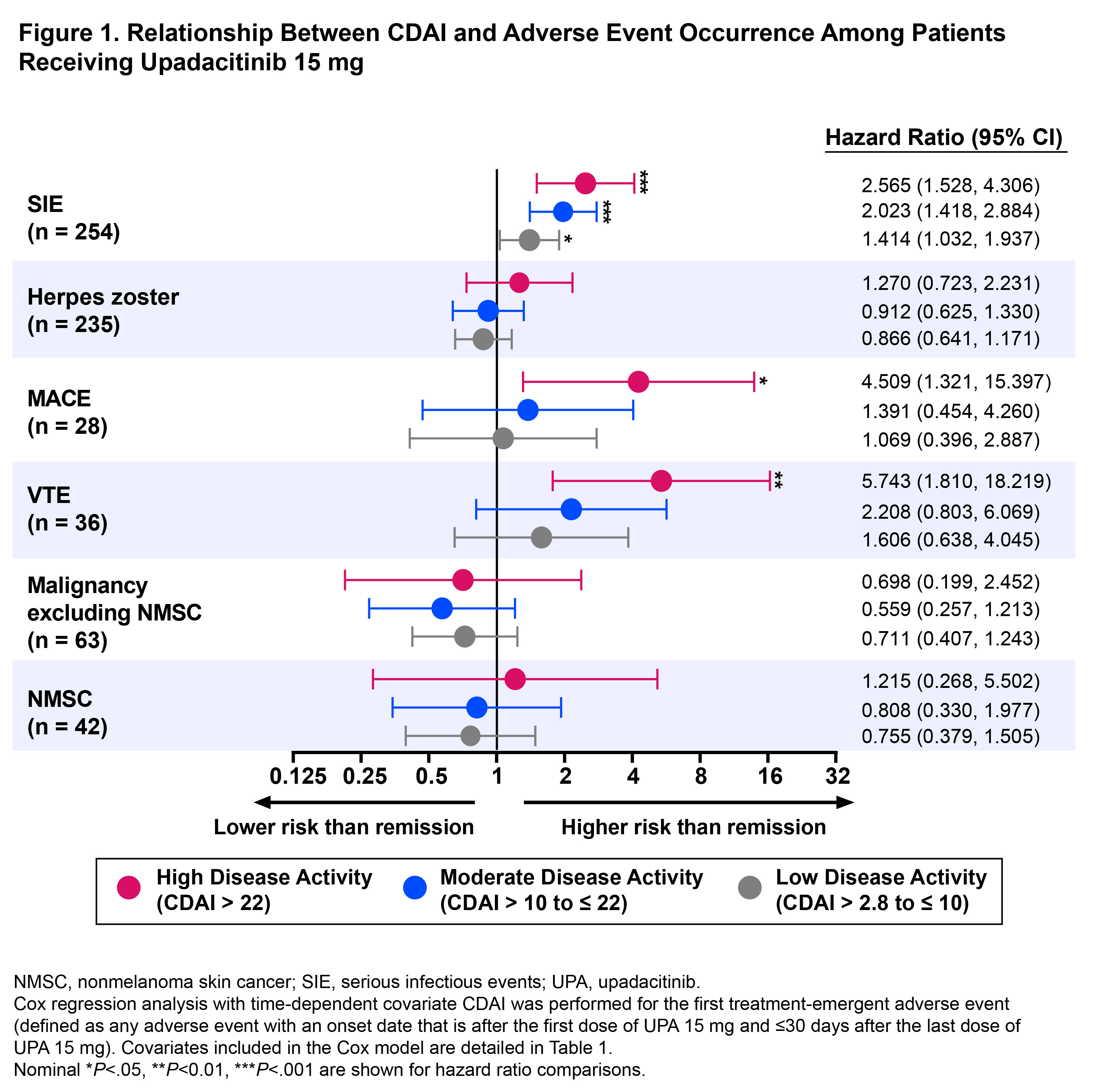
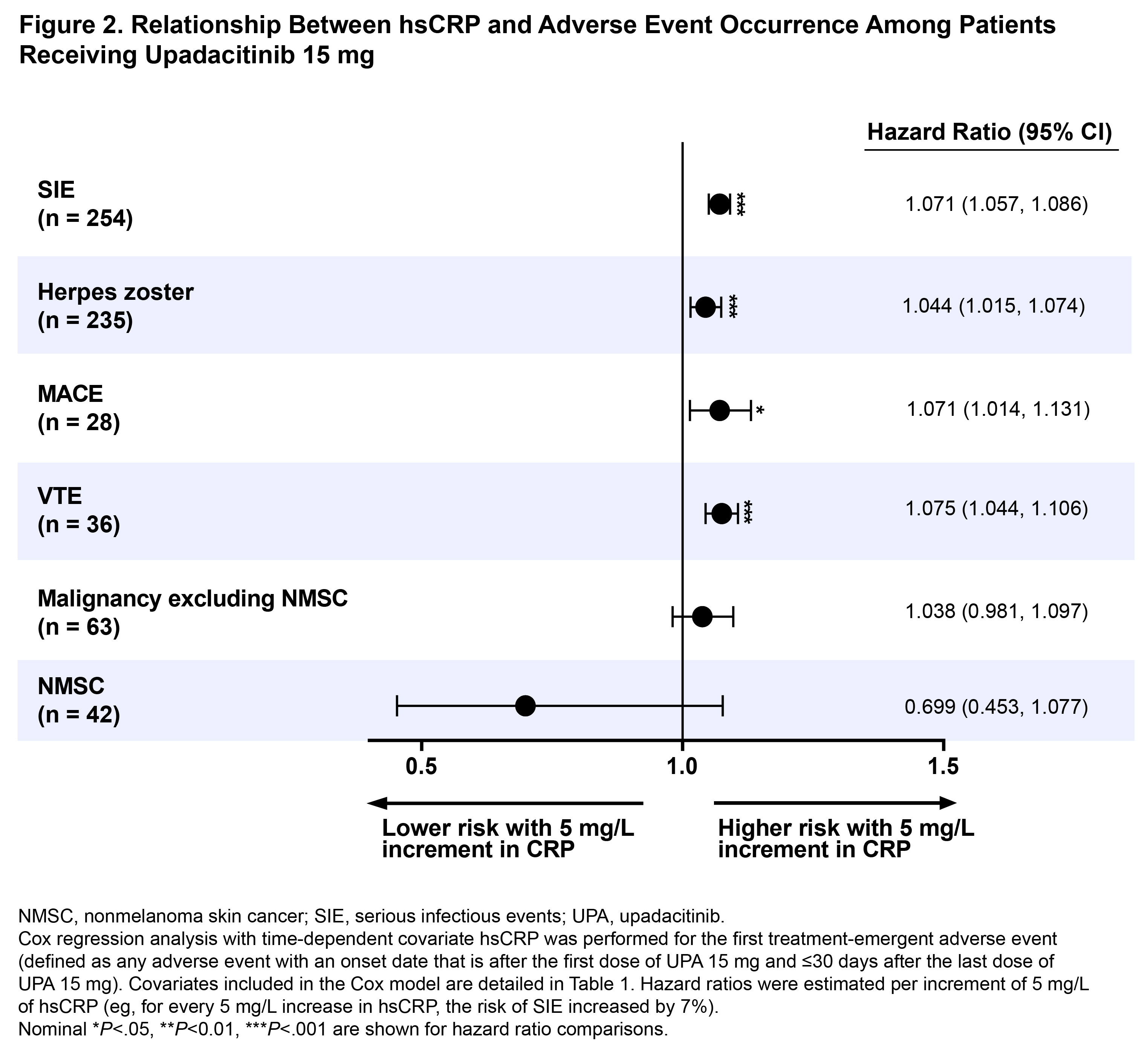
Results: A total of 2623 UPA 15 mg-treated patients were included in this analysis. At 4.2 years, which is the latest date at which data was available from all 6 trials, 43% (n=723), 40% (n=660), 14% (n=240), and 3% (n=43) were in CDAI remission, LDA, MDA, and HDA, respectively. Cox regression analysis showed that patients in CDAI HDA had a ~5-fold greater likelihood of MACE or VTE than those in remission over a 5-year period (hazard ratios [95% CI]: MACE, 4.5 [1.3, 15.4], P< .05; VTE, 5.7 [1.8, 18.2], P<.01) (Figure 1). In addition, patients with active disease trended toward a higher risk of developing MACE and VTE versus patients in remission. Residual disease activity also significantly increased the probability of developing SIE, but no relationship was observed for herpes zoster or malignancy. Additionally, 5 mg/L elevation in hsCRP increased the risk of MACE, VTE, and SIE by 7.1%–7.5% and increased the risk of herpes zoster by 4.4% (Figure 2). In analyses based on the time-weighted average disease activity, mean CDAI scores were 4.2 units higher in patients who experienced VTE than those who did not (P< .05). Comparisons of average CDAI between patients with/without other examined AEs were not statistically different, although patients with MACE had numerically higher average disease activity than those who did not (mean CDAI difference: 3.1 units).
Conclusion: In patients receiving UPA 15 mg in the SELECT RA program, decreased risk of MACE, VTE, and SIE were observed in patients in remission versus those with high disease activity levels. Overall, our findings support the importance of remission and inflammation reduction in mitigating the risk of some AEs, although results should be interpreted with caution due to the limited number of events.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleischmann R, Szekanecz Z, Mysler E, Winthrop K, Yamaoka K, Famulla K, Song Y, Kovacs B, Strengholt S, Burmester G. Relationship Between Disease Activity and Adverse Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Integrated Post Hoc Analysis of Upadacitinib Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-disease-activity-and-adverse-events-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-integrated-post-hoc-analysis-of-upadacitinib-phase-3-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-disease-activity-and-adverse-events-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-integrated-post-hoc-analysis-of-upadacitinib-phase-3-trials/