Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the joints and other parts of the musculoskeletal system. Early diagnosis and initiation of treatment are essential for patients with RA given the potentially irreversible damage to the joints and the considerable impact on quality of life.
Upadacitinib is an oral reversible JAK inhibitor with greater selectivity for JAK1 over JAK2, JAK3 and TYK2, which has been approved for the treatment of moderately to severely active RA in adult patients with inadequate response or intolerance to one or more disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Despite its extensive clinical development in RA, few studies with a significant number of patients reflect efficacy and safety data of the drug in real clinical practice.
We aim to evaluate the efficacy (DAS28-CRP) and safety of upadacitinib in treating RA in routine clinical practice.
Methods: This is a multicenter, observational and retrospective study that includes the use of Upadacitinib in real clinical practice. To this end, 202 patients diagnosed with RA according to the EULAR/ACR 2010 criteria are included and followed up for up to 52 weeks. Five visits were carried out (baseline, 3 months, 6 months, 9 months and 12 months) although when collecting data according to clinical practice, the data analysis was registered as observed. In addition to disease activity data, comorbidity, previous treatments, use of Upadacitinib in monotherapy, use of corticosteroids and previous or incident HZV infection are collected. Association and correlation studies were performed using SPSS v.25.
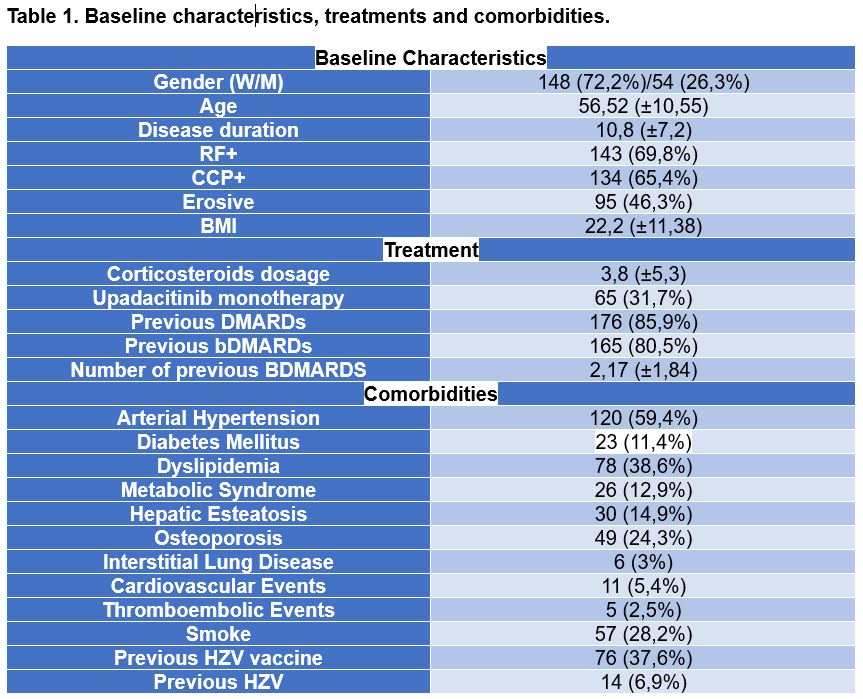
Results: 202 patients were included, of whom 148 were women, with a mean age of 56.52 years. The rest of baseline characteristics are reflected in Table 1. In 32.18% of patients, upadacitinib was used in monotherapy, while in the rest of the patients, its use was combined with csDMARDs, mostly with methotrexate (87.63%). We found not statistical differences between patients who started with monotherapy or had previous bDMARDs regarding drug interrumption (p >0,05).
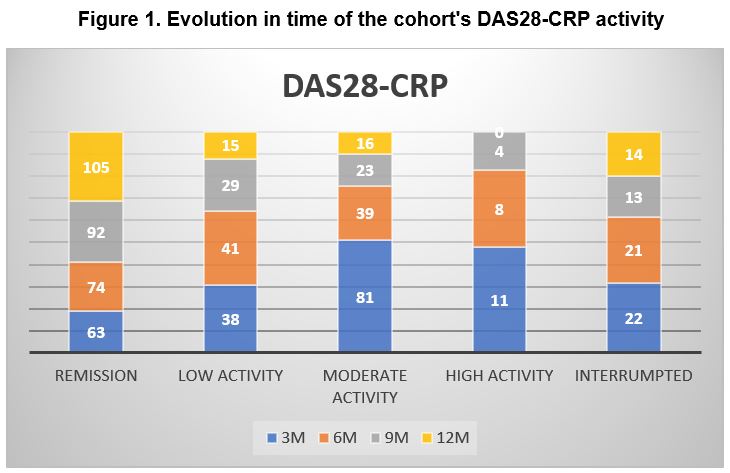
Three months after starting treatment, 32.64% (63) of the patients were in remission while 19.69% (38) were in low, 41.97% (81) moderate and 5.7% (11) in high activity. At 6 months after starting treatment, 45.68% (74) of the patients were in remission while 25.3% (41) were in low, 24.07% (39) in moderate and 4.94% (8) in high activity. At 12 months after starting treatment, of the patients who continued with treatment or for whom a recorded visit was available, 77.2% (105) of patients were in remission while 11.02% (15) were in low, 11.76% (16) in moderate and none in high activity.
Treatment was suspended in 32.67% (66) of the patients, of which 33.3% (22) were due to primary failure, 34.85% due to secondary failure, 15.15% (10) due to adverse effect, 13.63% (9) due to the patient’s request and 3.03% (2) for other reason.
Conclusion: Concording with literature this study demonstrates the drug’s effectiveness, reaching more than half of the sample at the end of the year with low activity or complete remission, and presenting expected side effects. There are no differences in starting with monotherapy or combined bDMARDs regarding drug interrumption.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gomez-Lechon Quiros L, Sequí-Sabater J, Rueda A, Nerea C, Valera-Ribera C, López-Gómez J, Alvarez-Cienfuegos A. One-year Real World Evidence Outcomes from the Cohort RADIUS (Real-world Analysis of Upadacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients for Improved Understanding and Safety) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/one-year-real-world-evidence-outcomes-from-the-cohort-radius-real-world-analysis-of-upadacitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-for-improved-understanding-and-safety/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/one-year-real-world-evidence-outcomes-from-the-cohort-radius-real-world-analysis-of-upadacitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-for-improved-understanding-and-safety/