Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Managing inflammatory arthritis patients on biologics with a history of cancer remains a complex task in daily rheumatology practice and requires a thoughtful, individualized approach. The objective of the study is to investigate changes in utilization patterns and timing of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) after cancer diagnosis.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective observational cohort study at Cochin Hospital in Paris, involving over 500 RA patients. Follow-up time was calculated from the index date (cancer diagnosis) to the date of the last follow-up visit (January 2024). Descriptive statistics were used to summarize patient characteristics, bDMARD utilization, and the time from cancer diagnosis to the initiation of bDMARD therapy.
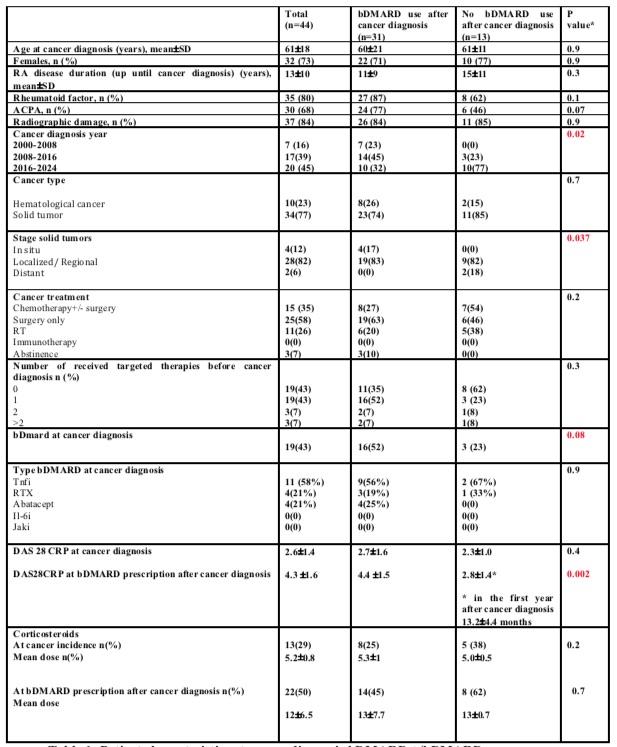
Results: Out of 44 RA patients, 32 (73%) were women, with a mean age of 61±18 years at cancer diagnosis. The mean disease duration until malignancy diagnosis was 13±10 years. The total follow-up time was 405 patient-years after the index visit. Demographic and clinical characteristics at the index visit are summarized in Table 1.
Most patients experienced a transient discontinuation of bDMARD during cancer treatment. Afterwards, 31 patients initiated bDMARDs, including 16 with bDMARDs history before cancer diagnosis and 15 without. Table 1 compares RA, cancer and treatment characteristics between these 31 patients and the 13 patients not treated with bDMARDs post-cancer diagnosis. 42% patients resumed bDMARDs during the first year after cancer diagnosis. Factors associated with bDMARD prescription post-cancer were RA disease activity (DAS 28 4.3 ±1.6 at bDMARD post-cancer initiation vs 2.8±1.4 in patients not receiving bDMARD p=0.002), incidence of RA flares (93%, 14/15 of RA flares at initiation of new bDMARD therapy) and cancer-related characteristics such stage and year of cancer diagnosis. Corticosteroid dose did not influence bDMARD prescription post-cancer in our cohort. Rituximab was the most prescribed bDMARD post-cancer (62%), followed by TNFa inhibitors (26%), IL-6R inhibitors (6%), and Abatacept (6%). Only 2 patients experienced cancer relapse during the nine-year surveillance period: one with localized melanoma and one with metastatic prostate cancer under tocilizumab, with no interruption of bDMARD therapy thereafter.
Conclusion: Discontinuation of RA therapies following cancer diagnosis was associated with increased disease activity and flares. Disease activity was the main factor for initiating bDMARD therapy post-cancer diagnosis, predominantly within the first five years, with Rituximab being the preferred option. These findings align with expert society recommendations and highlight the need for further studies to address evidence gaps in this setting.
*p-value2 ( Welch Two Sample t-test; Fisher’s exact test; Pearson’s Chi-squared test)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ghossan R, Portier E, FOGEL O, Hecquet S, Dauchez A, AL TABAA O, THOMAS M, Herrou J, Allanore Y, Avouac J. Exploring Two Decades of Therapeutic Challenges: A Monocentric Experience in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Battling Cancer [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-two-decades-of-therapeutic-challenges-a-monocentric-experience-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-battling-cancer/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-two-decades-of-therapeutic-challenges-a-monocentric-experience-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-battling-cancer/