Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: PsA disease activity (DA) and impact on patients (pts) are measured with clinical and pt-reported outcomes1. Minimal clinically important improvement (MCII), the smallest improvement perceived by pts as clinically meaningful2, has been defined for multiple PsA outcome measures, mainly using observational data3,4. We determined MCII thresholds for PsA outcomes in subsets of PsA pts from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) stratified by treatment history and baseline (BL) DA.
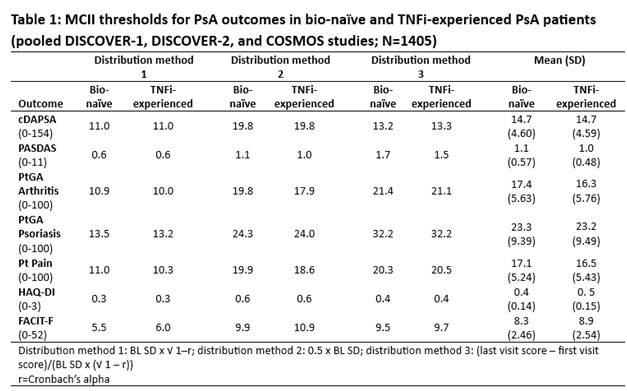
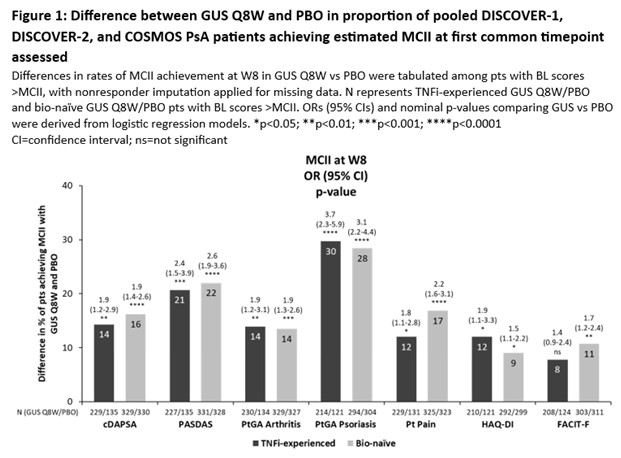
Methods: Data from 3 Phase 3 RCTs of 1405 PsA pts receiving guselkumab (GUS) every 4 weeks (Q4W) or at W0, W4 and Q8W, or placebo (PBO) were pooled: DISCOVER-1 (NCT03162796); DISCOVER-2 (NCT03158285); COSMOS (NCT03796858). MCII thresholds were assessed in bio-naïve and TNF inhibitor (i)‑experienced cohorts for clinical DA Index for PsA (cDAPSA), PsA DA Score (PASDAS), pt global assessment (PtGA) Arthritis, PtGA Psoriasis, Pt Pain, HAQ-Disability Index (DI), and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT‑F) using 3 BL distribution-based methods (Table 1). MCII achievement at W8 (1st timepoint common to all outcomes) was compared in GUS Q8W (regimen common to all studies) vs PBO via logistic regression (Fig 1). To assess impact of BL PsA DA on measures of joint and overall DA, MCII thresholds were estimated in the pooled population stratified by PsA DA (15/16% and 84/84% of pts had moderate and high DA by cDAPSA/PASDAS, respectively) using a method based on standard deviation (SD) of change from BL to W24.
Results: Mean BL scores in TNFi-experienced (N=403) vs bio-naïve (N=1002) cohorts for cDAPSA, PASDAS, PtGA Arthritis, PtGA Psoriasis, Pt Pain, HAQ-DI, and FACIT‑F of 43.7/44.4, 6.4/6.5, 65.0/63.6, 61.4/60.5, 63.7/60.8, 1.3/1.2, and 29.0/30.1, respectively, indicated high overall BL PsA DA. Although some variation was observed between methods, mean MCII thresholds for outcomes were generally consistent across cohorts, representing 16-39% mean improvement from BL (Table 1). At W8, GUS Q8W pts were significantly more likely to achieve estimated MCII cutoffs vs PBO for all outcomes (except FACIT‑F in TNFi‑experienced pts), with odds ratios (ORs) ranging from 1.5 to 3.7 (Fig 1). Relative to previous reports3,4, mean cDAPSA MCII thresholds were higher in these RCT cohorts (both 14.7) and mean HAQ-DI MCII cutoffs were somewhat higher than reported5 (0.4/0.5 in bio-naïve/TNFi‑experienced pts; Table 1). When stratifying by BL joint and PsA DA in the pooled RCT population, estimated MCII thresholds were higher in pts with high (MCII cDAPSA: 9.1; PASDAS: 0.8) than moderate (cDAPSA: 4.1; PASDAS: 0.7) DA (Table 2).
Conclusion: In a pooled RCT population of pts with active PsA, estimated MCII thresholds were consistent across bio-naïve and TNFi-experienced pts. Pts receiving GUS Q8W were significantly more likely to achieve early (W8) MCII vs PBO. MCII cutoffs were greater for pts with higher BL cDAPSA and PASDAS, indicating BL DA impacts MCII and assessment of response achievement.
References:
- Ogdie. Arthritis Care Res 2020;72:82
- Kvien. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66:iii40
- Ogdie. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:1173
- Karmacharya. Arthritis Care Res 2022;75:2182
- Mease. J Rheumatol 2011;38:2461
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogdie A, Mease P, Nantel F, Lavie F, Sharaf M, Rampakakis E, Marzo-Ortega H, Gossec L. Impact of Prior Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Treatment and Baseline Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity on Minimal Clinically Important Improvement Thresholds for Efficacy Outcomes: Post Hoc Analysis of Three Phase 3 Studies of Guselkumab in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-prior-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-treatment-and-baseline-psoriatic-arthritis-disease-activity-on-minimal-clinically-important-improvement-thresholds-for-efficacy-outcomes-post-hoc-analy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-prior-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-treatment-and-baseline-psoriatic-arthritis-disease-activity-on-minimal-clinically-important-improvement-thresholds-for-efficacy-outcomes-post-hoc-analy/