Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: There are several tools for assessing disease activity in spondyloarthritis (SpA). The literature reveals gender differences, with unfavorable Patient Reported Outcomes in women compared with men. The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of gender on the tools used to assess disease activity in axial SpA, and their ability to discriminate Patient Acceptable Symptom State (PASS), depending on gender.
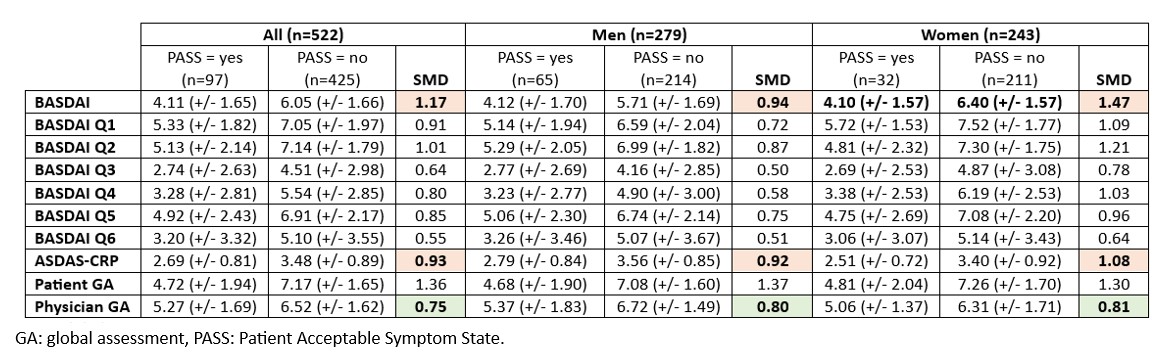
Methods: This is an ancillary analysis of the Predict-SpA cross-sectional study (NCT03039088). Patients had a diagnosis of axial SpA according to their rheumatologist and an indication to start a TNF inhibitor. Disease activity was assessed prior to initiation of treatment using BASDAI, ASDAS-CRP scores, patient and physician global assessment of disease activity. Patients were also asked to rate whether their health status in relation to axial SpA was considered acceptable or unacceptable (PASS, yes/no). To analyse the ability of disease activity assessment tools to discriminate PASS, we calculated a standardized mean difference (SMD) for each tool in the total population, in men and in women.
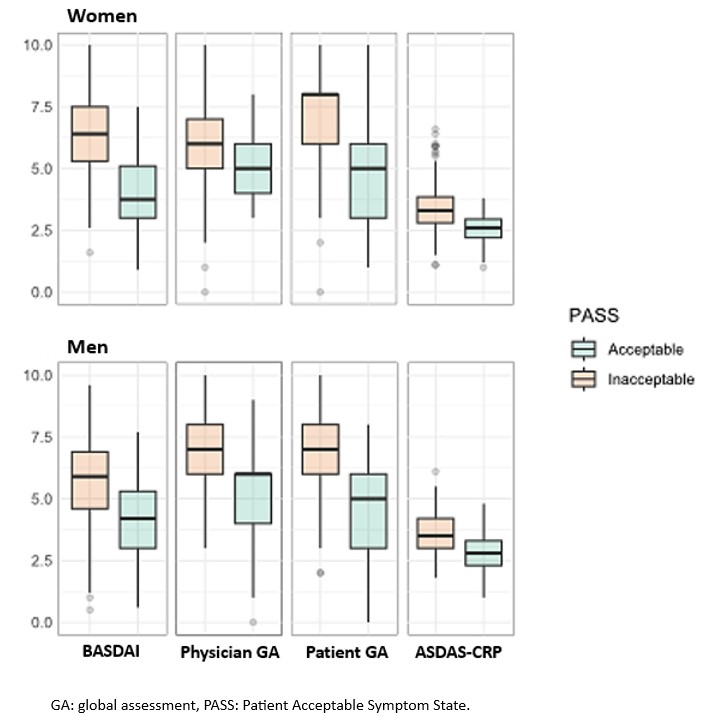
Results: Of the 526 patients included in Predict-SpA, 522 had an available PASS and were analysed, including 279 (53.4%) men and 243 (46.6%) women. Overall, women with a PASS had comparatively lower activity scores than men with a PASS. In the overall population, the BASDAI, ASDAS-CRP and patient global assessment of disease activity performed well in discriminating PASS (SMD 1.17, 0.93 and 1.36, respectively). However, there were gender differences, with BASDAI score performing better in women than in men (SMD 1.47 and 0.94, respectively). The physician global assessment was the least discriminating tool, with no gender differences (SMD 0.75, 0.80 and 0.81 in the overall population, in men and in women, respectively).
Conclusion: The disease activity assessment tools appear to be able to discriminate PASS, apart from the physician global assessment of disease activity, in the whole population. The ASDAS-CRP performs homogeneously according to gender, which argues in its favour at the population level. As the BASDAI has a better discriminating performance in women, it could be used in studies including only women.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hamroun S, Gossec L, Perrot S, Dougados M, Molto A. Gender-specific Performance of Disease Activity Assessment Tools in Axial Spondyloarthritis: Ancillary Analysis of the PREDICT-SpA Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gender-specific-performance-of-disease-activity-assessment-tools-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-ancillary-analysis-of-the-predict-spa-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gender-specific-performance-of-disease-activity-assessment-tools-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-ancillary-analysis-of-the-predict-spa-study/