Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The triglyceride/glucose index (TGI) is a metabolic marker associated with insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk. In patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), chronic inflammation and prolonged use of glucocorticoids can contribute to metabolic disturbances, including dyslipidemia and dysglycemia. Therefore, the TGI could provide an integrated view of the metabolic status of patients with RA and potentially correlate with functional capacity. Our aim was to evaluate the association between the TGI and functional capacity, as assessed by the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), in patients with RA.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional analysis of an established RA cohort constituted by patients referred to a Peruvian tertiary care center (the Almenara RA cohort). Patients are being followed every six months with a standard protocol that includes an interview, medical records review, physical examination (including 28 joint counts), and laboratory tests that included fasting glucose and triglycerides. For the present study, we included patients who had a visit between March 2014 and December 2017
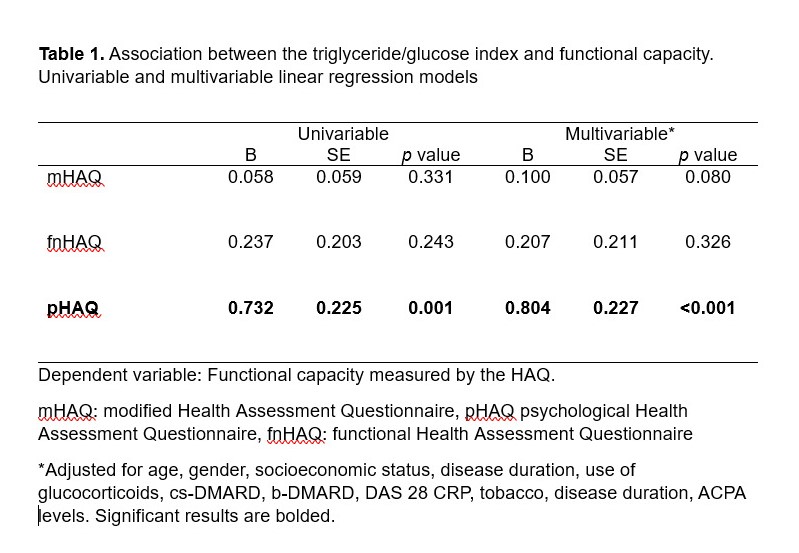
For categorical variables, frequencies and percentages were obtained whereas for continuous variables medians and interquartile ranges (IQR) were. A normality test of Kolmogorov-Smirnov was performed. To evaluate the association between TGI with the HAQ [the modified HAQ (mHAQ), the functional HAQ (fnHAQ) and the psychological HAQ (pHAQ)], univariable linear regression models were used. Subsequently, a multivariable linear regression model, adjusted for gender, age, socioeconomic status, tobacco use, disease duration, ACPA (Anti–citrullinated protein antibodies) levels, disease activity (Disease Activity Score-28 with C reactive protein [DAS-28 CRP]), treatment (average dose of glucocorticoids over the last 3 months, cs- DMARDs and b-DMARDs use) and the Charlson comorbidity index.
Results: Two hundred and forty-seven patients were included. The average (SD) age was 63.0 (12.8) years, disease duration was 8.45(1.26) years; nearly all the patients were Mestizo (99.6%) and 229 (92.7%) were women. In the univariable analysis, a higher TGI was associated with higher pHAQ with B=0.73 (p˂0.01) no significant correlation was found with either the mHAQ or the fnHAQ. In the corresponding multivariable analysis, this correlation remained significant with B=0.80 (p˂0.01). The univariable and multivariable analyses are shown in Table 1.
Conclusion: The study demonstrated a significant association between TGI and pHAQ in patients with RA. This finding highlights the potential role of metabolic dysregulation in contributing to psychological distress in RA patients. Further research is warranted to explore the mechanisms underlying the observed associations and to evaluate whether interventions targeting metabolic factors in RA patients could improve psychological outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Velarde Mejia Y, Ugarte-Gil M, Perich R, Pastor C, Alarcon G, Gamboa-Cardenas R. Correlation Between Triglyceride/Glucose Index and Functional Capacity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-between-triglyceride-glucose-index-and-functional-capacity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-between-triglyceride-glucose-index-and-functional-capacity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/