Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The web-based ChRonic nonbacterial Osteomyelitis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring (CROMRIS) portal was developed to assess specific features of bone and soft tissue inflammation in MRI of patients with CNO in a user-friendly interface1. Primary objective of this study is to evaluate the absolute agreement of components of and summary CROMRIS scores at each body site, and the inter-rater reliability across raters.
Methods: A reliability module including 29 de-identified whole body (WB) MRI scans (coronal images of the entire body and sagittal images of entire spine, acquired with short tau inversion recovery [STIR] sequences without contrast) from children with CNO and normal controls was created. Three pediatric radiologists (TSS, RSI, JS), all with >10 years of expertise in pediatric musculoskeletal imaging independently scored these cases directly on the web platform. Prior to scoring, all the readers reviewed a training atlas and video. Readers scored individual bone units to indicate presence of: bone marrow hyperintensity (HI) on STIR images (score 0-1); soft tissue/periosteal HI of surrounding tissue (score 0-1); bony expansion (score 0-1), and quantify the signal size of CNO lesion (score 1-3 defined as < 25%, 25-50% or >50% of estimated volume, respectively). The sum of these parameters for lesions detected on fluid-sensitive sequences was the CROMIS Activity Index (maximum score 722). Pairwise comparisons of the specific parameters and CROMRIS Activity Index were made. Absolute agreement was defined when the summary score difference between any 2 raters was ≤ 2. For specific variables (bone marrow HI, signal size, soft tissue/periosteal HI, bony expansion), the absolute agreement was defined as all the raters assigning the exact same score. Inter-rater reliability for abnormal signal and severity were assessed using free-marginal kappa (k) statistics.
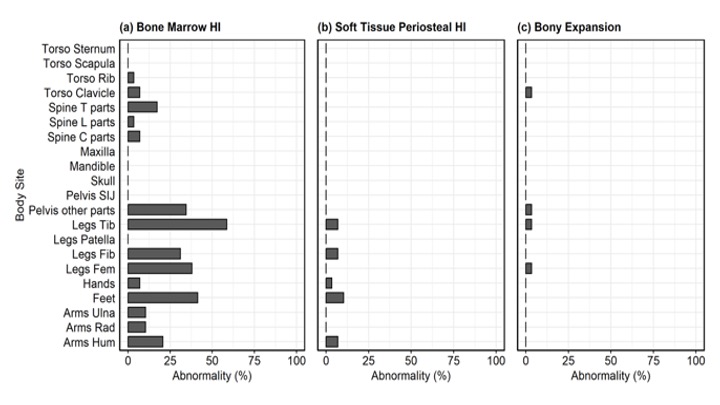
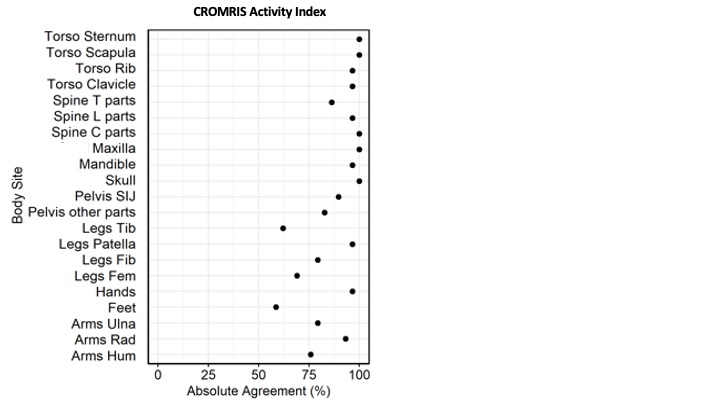
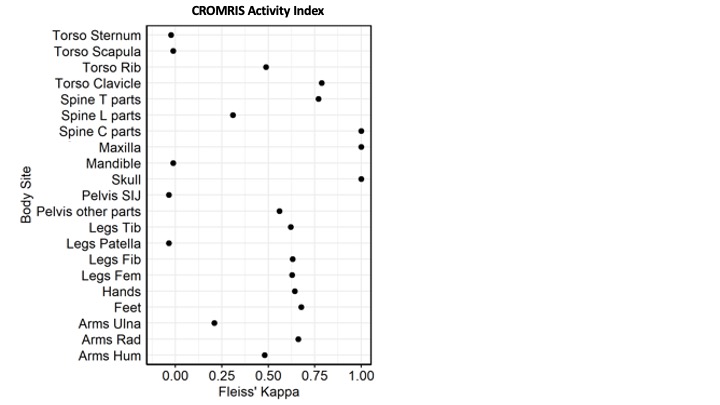
Results: Among all bone sites, the prevalence of abnormalities were the highest at the tibia (59%), feet (41%), femur (38%), and pelvis (34%) (Figure 1). The proportion of absolute agreement of CROMRIS Activity Index scores across 3 raters was greater than 70% in most bone sites (Figure 2). Mean kappa of each category of bones was near or >0.5 demonstrating moderate inter-rater reliability amongst radiologists for most bone sites (Figure 3), except in lumbar spine, ulna, patella, mandible, sternum, scapula, and sacroiliac joints, which had mean k scores ranging from -0.04 to 0.21, correlating with sites of lowest prevalence of abnormalities in this module.
Conclusion: The web-based CROMRIS portal shows moderate agreement of CROMRIS Activity Index total scores amongst experienced radiologists after self-guided learning of atlas and video. A consensus-based set of scans for reader calibration will be developed to enhance inter-rater reliability for clinical trials.
The authors wish to acknowledge CARRA, CARE Arthritis and the ongoing Arthritis Foundation financial support of CARRA
- Nuruzzaman F, et al. Development and Usability Testing of Web-based Standardized Scoring Tool for Magnetic Resonance Images from Children with Chronic Nonbacterial Osteomyelitis (CNO) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 4).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nuruzzaman F, Sato T, Stimec J, Iyer R, Carbert A, Paschke J, Potts L, Zhang X, Maksymowych W, Ferguson P, Zhao Y. Absolute Agreement and Inter-rater Reliability of a Web-based Standardized Scoring Tool for Magnetic Resonance Images from Children with Chronic Nonbacterial Osteomyelitis (CNO) Amongst Radiologists [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/absolute-agreement-and-inter-rater-reliability-of-a-web-based-standardized-scoring-tool-for-magnetic-resonance-images-from-children-with-chronic-nonbacterial-osteomyelitis-cno-amongst-radiologists/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/absolute-agreement-and-inter-rater-reliability-of-a-web-based-standardized-scoring-tool-for-magnetic-resonance-images-from-children-with-chronic-nonbacterial-osteomyelitis-cno-amongst-radiologists/