Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: There are six core set measures (CSMs) of disease activity in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM). However, there is limited data on their clinical association, meaningfulness (validity) and improvement thresholds (responsiveness) using quality of life measures in myositis. The 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) assesses quality of life, functional health, and well-being. This study evaluates the association and improvement thresholds of various CSMs using SF-36 in patients with IIM.
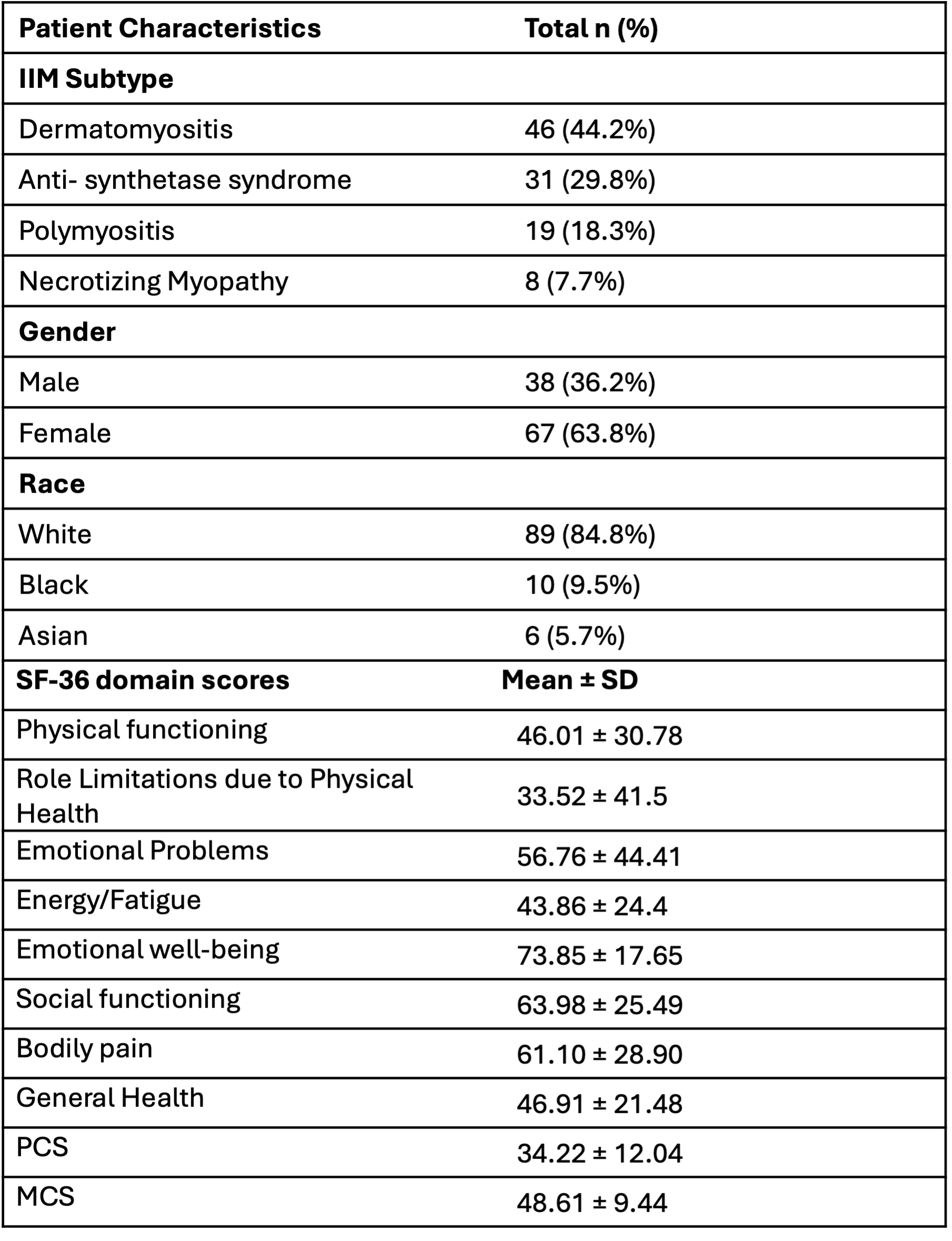
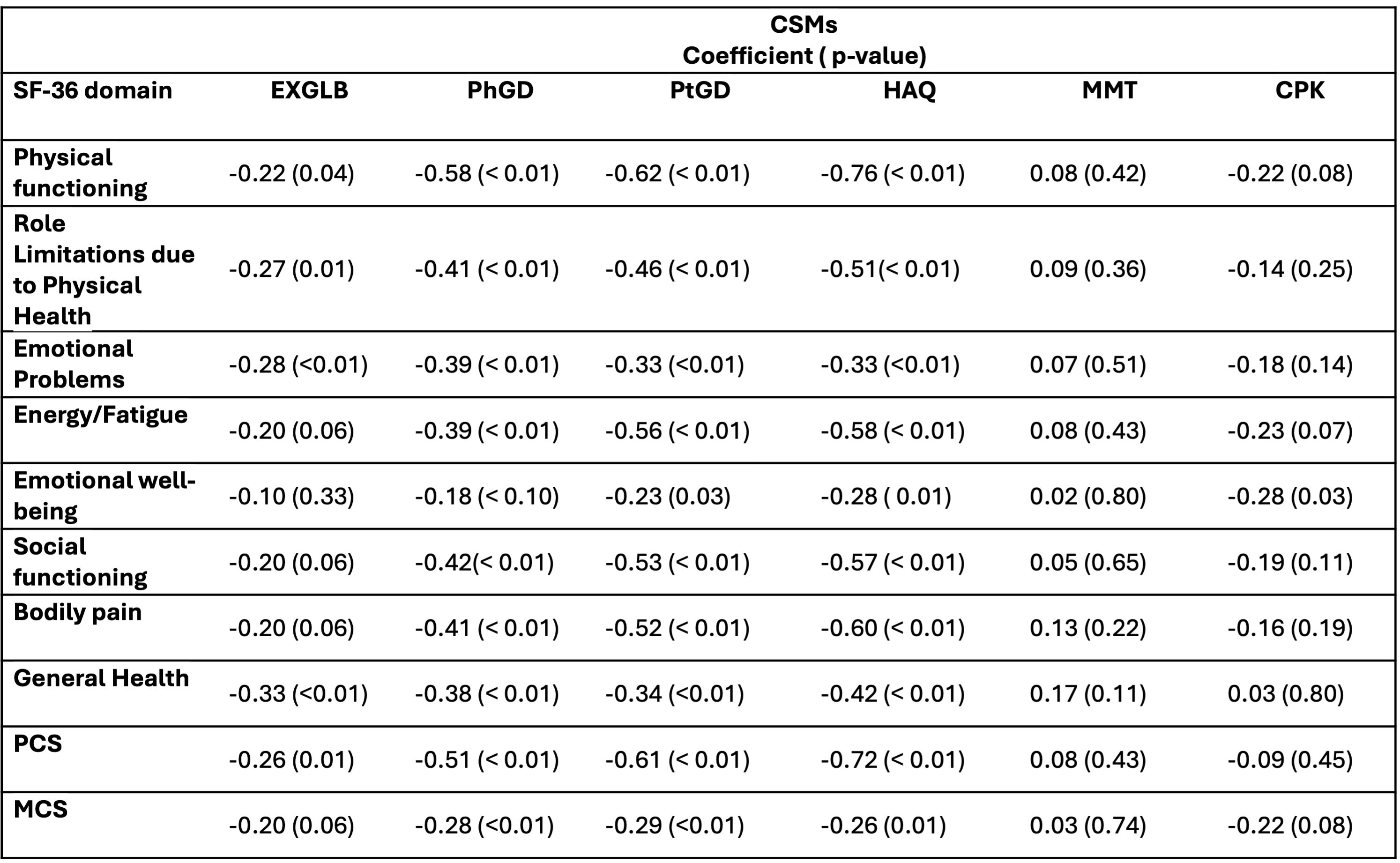
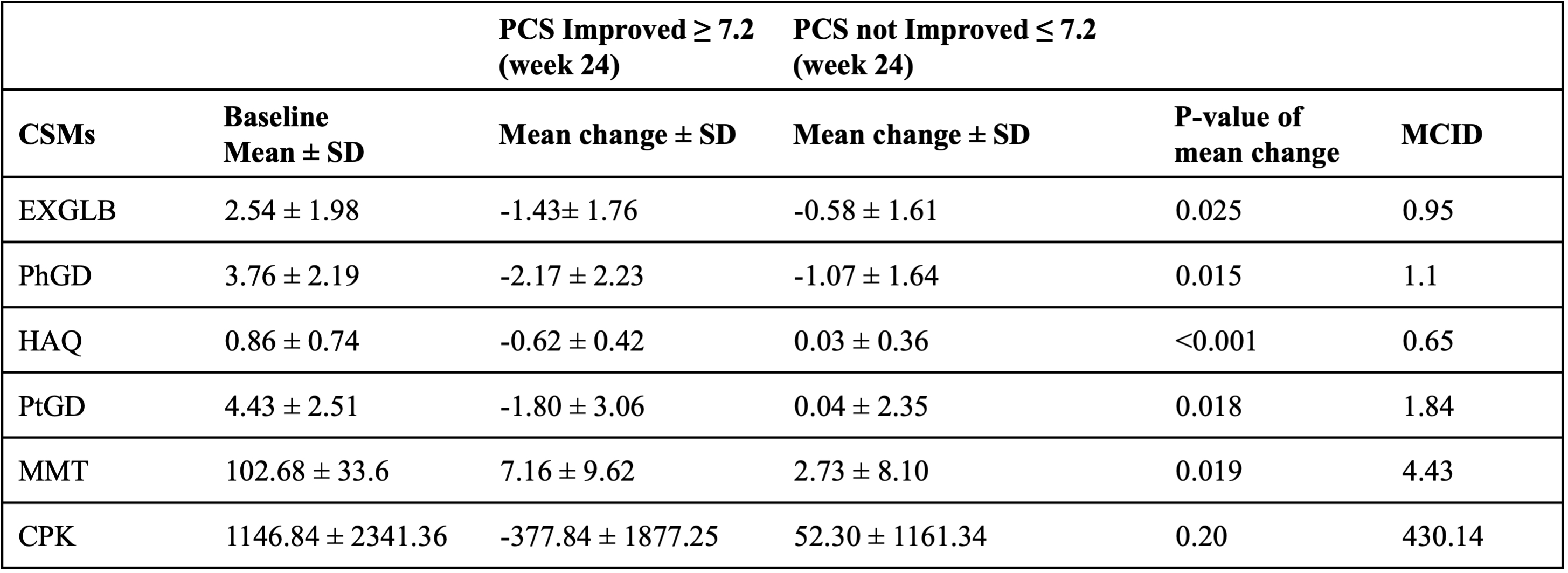
Methods: Adults with IIM enrolled in two clinical trials (AttackmyILD, Tocilizumab in Myositis) and one observational study (PAMPRO) were evaluated for the study. Data on demographics (Table 1) and CSMs including patient-global assessment (PtGD), physician-global assessment (PhGD), extra global disease activity score (EXGLB), manual muscle testing (MMT), HAQ, creatine kinase (CPK), and SF-36 were collected at baseline, 12 weeks, and 24 weeks in all three studies. Spearman’s correlation assessed associations between SF-36 domains (physical functioning, social functioning, emotional well-being, emotional problems, general mental health, energy/fatigue, bodily pain, general health) and summary scores for physical health (PCS) and mental health (MCS) with CSMs. A mixed-effect linear model identified CSM predictors for SF-36 domains. Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) was determined using a 7.2 score improvement in PCS as an anchor.
Results: The study included 150 IIM patients (63.8% female, 84.8% white, mean age 52 ± 13.6 years): 44.2% with dermatomyositis, 29.8% with anti-synthetase syndrome, 18.3% with polymyositis, and 7.7% with necrotizing myopathy.
Spearman correlation showed strong to moderate negative correlations of PtGD and HAQ with nearly all SF-36 domains, moderate negative correlations for PhGD, and weak negative correlations for EXGLB. MMT and CPK were not significant (Table 2). The linear-effect model identified HAQ as a strong predictor for all SF-36 domains (P < 0.05) except emotional well-being. PtGD predicted bodily pain, physical functioning, social functioning, energy/fatigue, and PCS (P < 0.001). CPK predicted bodily pain, social functioning, energy/fatigue, emotional problems, and MCS (P < 0.05). EXGLB was significant for energy/fatigue only (P = 0.01).
Using a 7.2 PCS improvement as an anchor, CSM improvements aligned with observed PCS improvements except for CPK. MCID was calculated for each of the CSMs (Table 3).
Conclusion: Most CSMs in IIM is significantly associated with multiple congruent domains and summary score of SF-36 except for the MMT and CPK. CSMs strongly predicted relevant domains and summary score of SF-36. All CSMs improved with SF-36 PCS improvement except CPK, and MCIDs were determined.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Almackenzie M, Aggarwal A, keret s, Sriram s, Chandra T, Silva R, Gkiaouraki E, Mogahadam S, Oddis C, Aggarwal R. Validity and Responsiveness of Core Set Measures in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myositis Based on 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validity-and-responsiveness-of-core-set-measures-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis-based-on-36-item-short-form-health-survey-sf-36/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validity-and-responsiveness-of-core-set-measures-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis-based-on-36-item-short-form-health-survey-sf-36/