Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
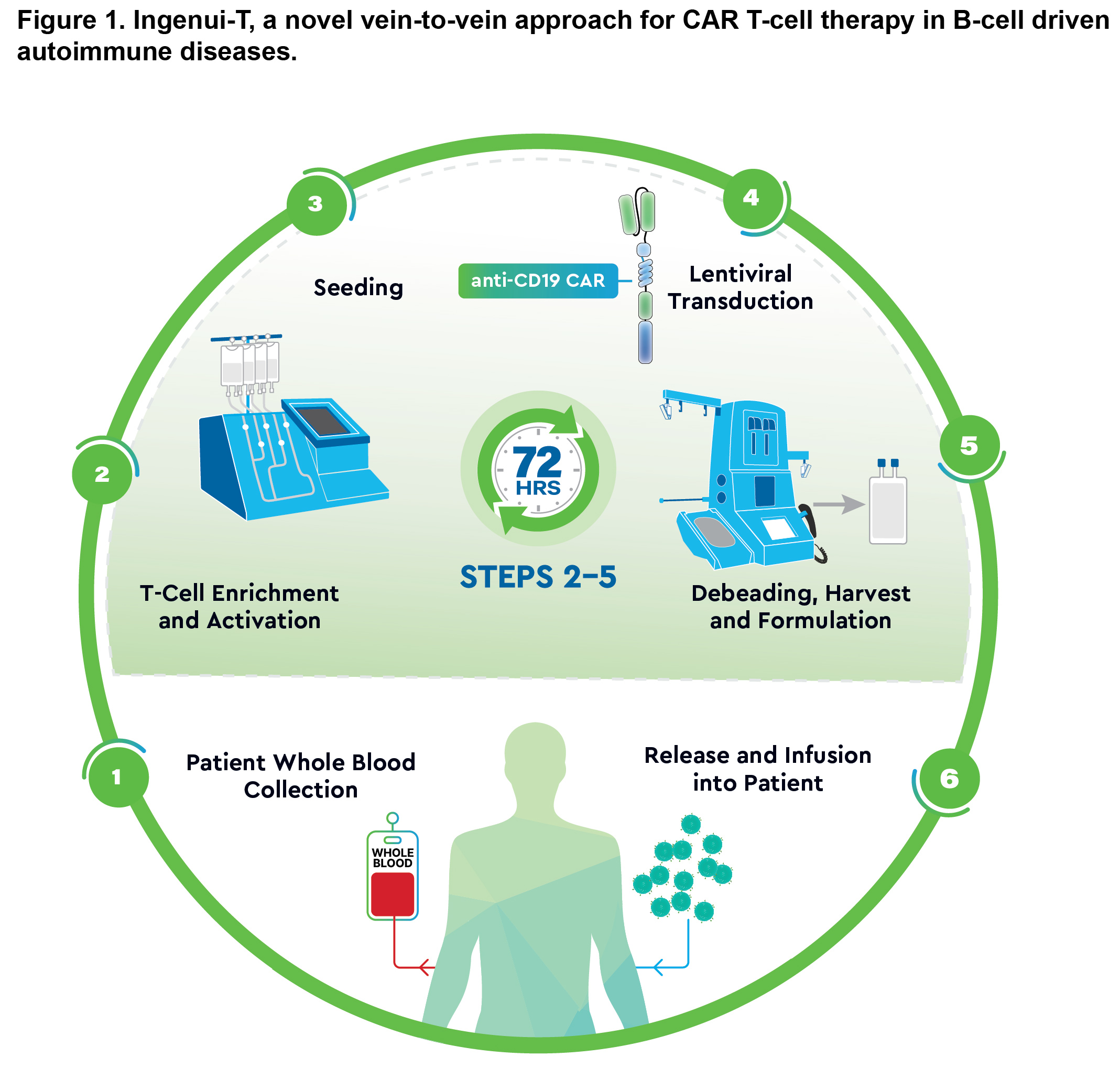
Background/Purpose: Apheresis in conventional chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy can be burdensome, and conventional manufacturing cultures apheresis-derived cells for 7-14 days, leading to a more differentiated T-cell memory phenotype and reduced functionality (Ghassemi, S. Nat Biomed Eng. 2022). The cost to manufacture and treat with CAR T-cell therapy is high and can be a potential barrier for the autoimmune patient population. Ingenui-T mitigates these challenges by utilizing whole blood (WB) and a streamlined < 3-day culture, minimizing ex vivo memory differentiation and enhancing therapeutic potential. Ingenui-T aims to improve patient experience, eliminate apheresis-related limitations, and lower the dose required for therapeutic benefit in autoimmune disease, leading to overall cost reduction. This study explored Ingenui-T manufacturing feasibility for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods: WB samples were collected from patients with SLE (n=2) and healthy donors (HDs; n=4). KYV-102 was manufactured using the Ingenui-T platform (Fig. 1). T cells were isolated from WB, activated, and < 24 hours post-seeding transduced with lentivirus encoding the same CAR construct used in KYV-101, a first-in-class, fully human autologous anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy (Brudno, J. Nat Med. 2020). CAR expression and memory T-cell phenotypes of the final drug product (DP) were assessed. In vitro co-culture assays examined CD19-dependent cytolysis and cytokine release. In vivo function was assessed with a CD19+ tumor xenograft mouse model.
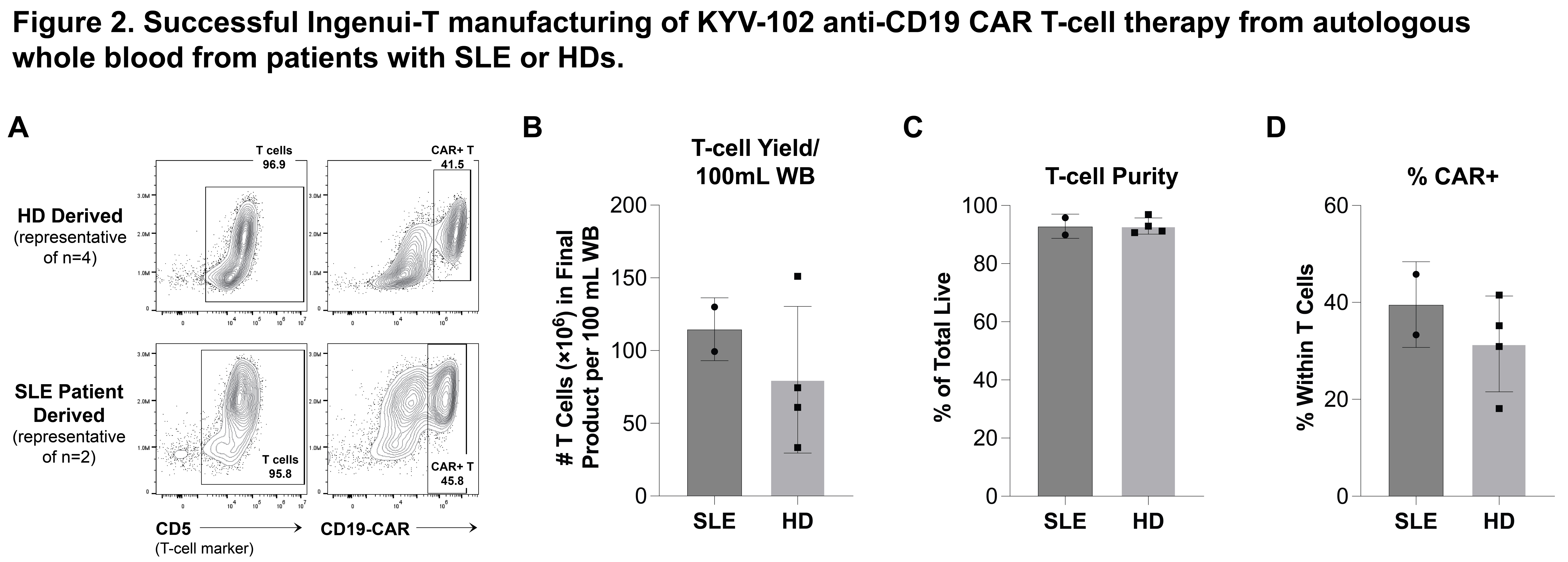
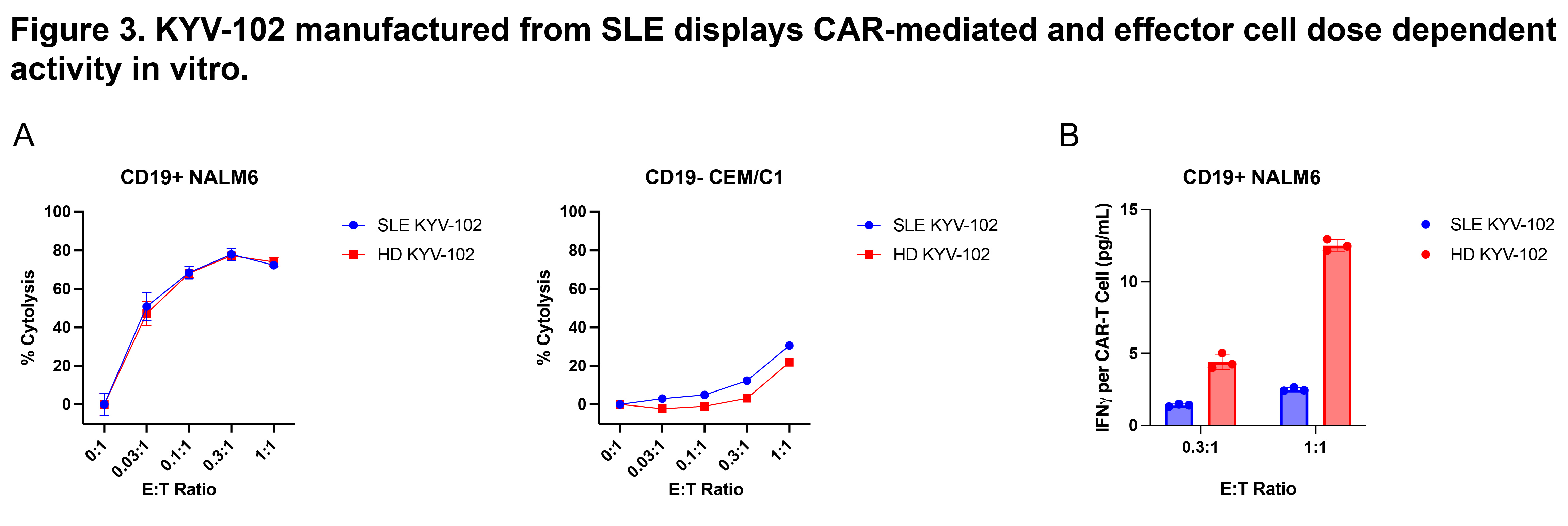
Results: KYV-102 was successfully manufactured using WB from patients with SLE and HDs. Flow cytometry of SLE- and HD-derived DPs showed high yields (mean: 114.7 and 79.9×106 cells/100 mL WB, respectively), similar T-cell purity levels (mean: 92.9% and 92.9%, respectively), and comparable percentages of CAR+ expressing T cells (mean: 40.0% and 31.4%, respectively) (Fig. 2A-2D). Naive and stem-like memory T-cell subsets were present in the final DPs, indicative of less differentiated T cells. SLE-derived KYV-102 demonstrated CD19-specific and effector cell dose-dependent cytolysis when co-cultured with CD19+ NALM6 cells, and negligible response when co-cultured with CD19– CEM/C1 cells, similar to HD-derived KYV-102 (Fig. 3A). Cytokine analysis showed target-mediated effector cell dose-dependent IFNγ secretion upon co-culture with CD19+ NALM6 cells, but SLE-derived KYV-102 secreted lower levels of IFNγ compared with HD-derived KYV-102 (Fig. 3B). Additional studies examining in vivo functionality from HD-derived KYV-102 demonstrated potent CD19+ target cell depletion at low doses.
Conclusion: With Ingenui-T, KYV-102 was successfully manufactured using WB from patients with SLE and HDs, with similar product characteristics. Undifferentiated memory T-cell subsets were maintained. SLE-derived KYV-102 showed CD19-specific cytolysis comparable to HD-derived KYV-102, with decreased IFNγ secretion, suggestive of potential added clinical benefit for patients with autoimmune disease. These preliminary findings support continued exploration of Ingenui-T as an innovative CAR T-cell therapy manufacturing approach in autoimmune diseases.
Abbreviations: CAR, chimeric antigen receptor.
Abbreviations: CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; HD, healthy donor; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; WB, whole blood.
Abbreviations: CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; E:T, effector:target; HD, healthy donor; IFNγ, interferon gamma; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kwong B, Anaya D, Park S, Biswas S, Jeevan J, Banuelos J, Strobach M, Khoshnoodi N, Klasson T, Foos-Russ S, Zeng J, Gibson C, Bravo J, Sandoval S, Sengupta S, Shah S, Van Blarcom T, Walker K. Preclinical Manufacturability and Activity of KYV-102 from Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Using Ingenui-T: A Rapid, Autologous Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Manufacturing Solution Utilizing Whole Blood [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/preclinical-manufacturability-and-activity-of-kyv-102-from-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-using-ingenui-t-a-rapid-autologous-chimeric-antigen-receptor-t-cell-manufacturing-solution-utili/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/preclinical-manufacturability-and-activity-of-kyv-102-from-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-using-ingenui-t-a-rapid-autologous-chimeric-antigen-receptor-t-cell-manufacturing-solution-utili/