Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2177–2194) Sjögren’s Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Salivary gland hypofunction, manifested as xerostomia in Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), causes dental, language, and nutritional problems, leading to a detriment in oral health. The Geriatric/General Oral Health Assessment Index Spanish Version (GOHAI-SP) is a useful tool that has been used to assess the self-perception of oral status in SS patients (1). This study aims to associate and correlate the subjective EULAR SS Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI) and GOHAI-SP results with objective data from unstimulated salivary flow in 15 minutes (USF/15min).
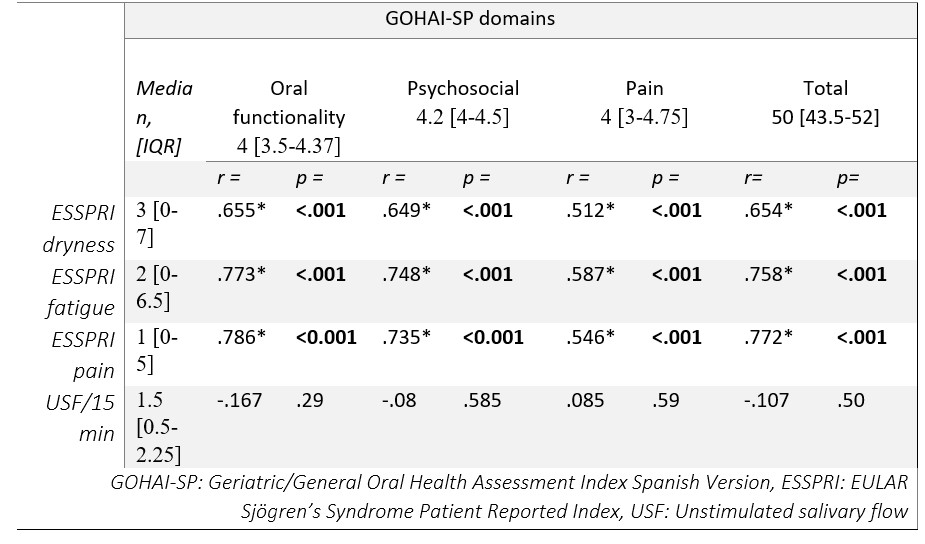
Methods: A cross-sectional and observational study was conducted from October to December 2022 in the rheumatology service at Hospital Universitario “Dr. José Eleuterio González”, Mexico. Patients meeting ACR/EULAR criteria for pSS and sSS were included and assessed with ESSPRI and GOHAI-SP during their follow-up appointment or reached by telephone. The latter index consists of 12 questions on a 1 to 5 Likert-type scale. The lowest obtainable score is 12 and the maximum is 60. Scores ≤ 44 were classified as poor oral health, moderate from 45 to 50, and good ≥ 51. Questions 1-4 assess oral functionality, 6, 7, 9-11 psychosocial status; 8 and 12 for pain. Data of USF/15min was obtained from patients’ charts.
Results: A total of 41 patients were included: 31 (75.6%) with pSS and 10 (24.4%) with sSS most of whom were women (n=40, 97.6%) with a mean age of 53.41 (SD: 12.58). The median score of GOHAI-SP was 50 [IQR 43.5-52], medians for dryness, fatigue, and pain reported in ESSPRI domains were: 3 [0-7], 2 [0- 6.5] and 1 [0-5]; for USF/15min 1.5 [0.5-2.25]. The self-perceived health status was classified as good in 19 (46.3%), moderate and poor both in 11 (26.8%). We found that the worse the self-perceived oral condition, the higher ESSPRI medians for dryness (p < 0.001), fatigue (p 0.003), and pain (p 0.002) were reported. No significant differences were found when compared to USF/15min. Results of Spearman’s correlation model are shown in Table 1. No significant differences were found between pSS and sSS groups.
Conclusion: The greater the severity of dryness, fatigue, and muscular or joint pain, the greater the functional impairment of mouth and oral pain; as well as the worse the psychosocial aspect manifested as concern, nervousness, discomfort, and limitation of interaction with people due to the dental appearance.
1. Leung KC, McMillan AS, Wong MC, Leung WK, Mok MY, Lau CS. The efficacy of cevimeline hydrochloride in the treatment of xerostomia in Sjögren’s syndrome in southern Chinese patients: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. Clin Rheumatol. 2008;27(4):429-436. doi:10.1007/s10067-007-0723-x
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alvarez-González O, Guerra H, Quintana-Aguilar E, Arroyo-Sánchez S, Cortez-Gutierrez J, Cardenas-De la Garza J, Torres-Quintanilla F, Riega-Torres J, Skinner-Taylor C, Galarza-Delgado D. Association of Self-perceived Oral Health Status with ESSPRI Reported by Sjögren’s Syndrome Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-self-perceived-oral-health-status-with-esspri-reported-by-sjogrens-syndrome-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-self-perceived-oral-health-status-with-esspri-reported-by-sjogrens-syndrome-patients/