Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2177–2194) Sjögren’s Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sjögren’s disease (SjD) is a debilitating disease that has been shown to impact patients’ quality of life (QoL). Though oral and ocular dryness are well-recognized causes of reduced QoL, there is limited evidence on impact of dental decay and vaginal dryness on QoL. Our study aims to describe the disease burden of patients with SjD, as measured by clinical testing and patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures in real-world clinical settings.
Methods: Data were drawn from the 2018 Adelphi Primary Sjögren’s Disease Specific Programme™, a cross-sectional survey with retrospective data collection of rheumatologists and their consulting patients with SjD in France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the United States. Rheumatologists completed patient record forms for their next 6 primary SjD patients with systemic disease activity and reported on patient demographics, clinical characteristics, and patient assessments. Patients were invited to complete a form capturing PROs, including EQ-5D-3L, the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire (WPAI), and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue Scale (FACIT-F). QoL, work productivity, and fatigue were evaluated and all data were analyzed descriptively.
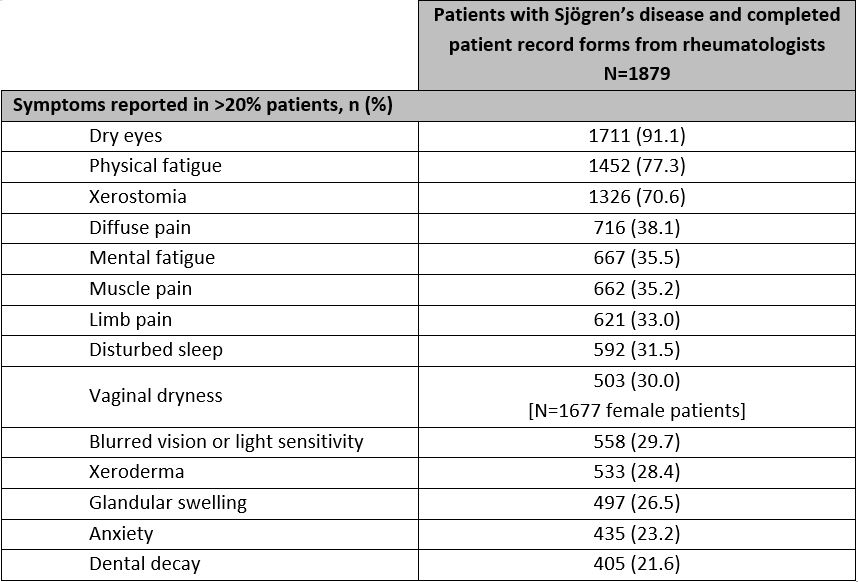
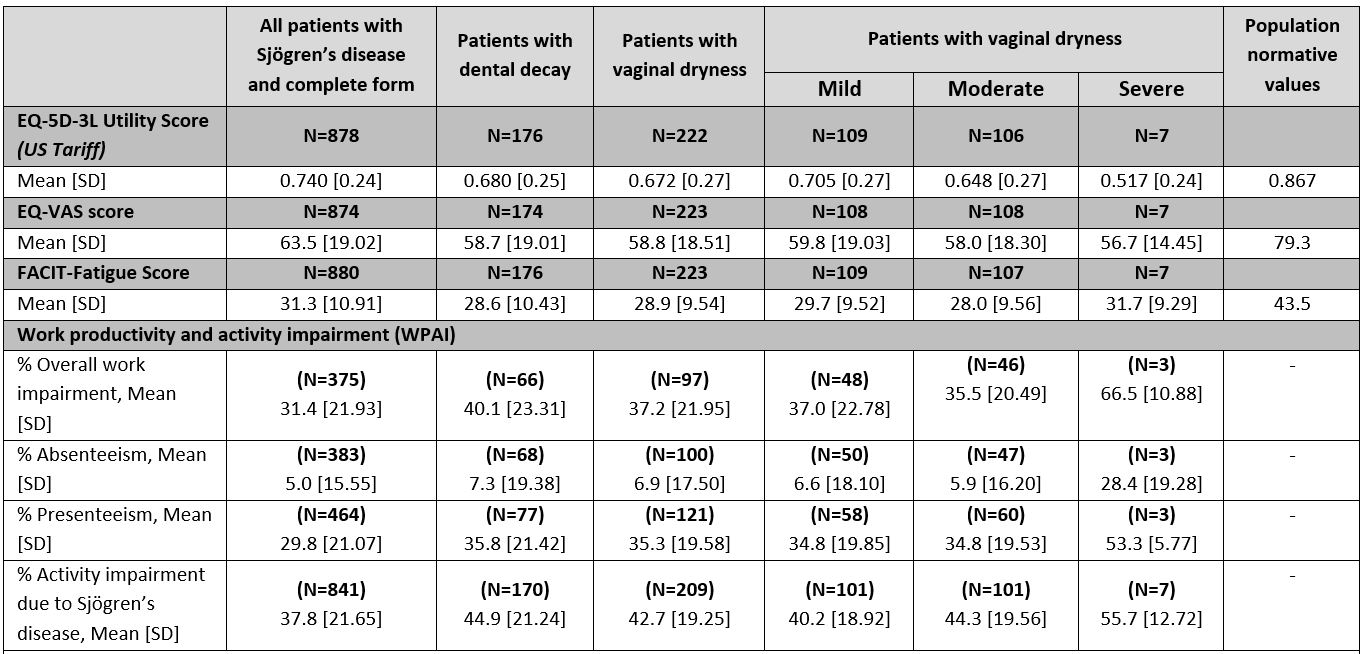
Results: 316 rheumatologists provided data for 1,879 patients: mean [SD] age 53 [12] years, 89% female, 89% White. Patients had a mean [SD] of 13 [7] tests leading up to diagnosis and 7 [12] consultations in the past 12 months. Patients are most commonly co-managed by PCP/GPs (48%) and ophthalmologists (47%), with other health care professional types co-managing < 20% of patients. Rheumatologists recorded dry eyes, physical fatigue, and dry mouth as the most common symptoms in 91%, 77%, and 71% of patients respectively. Of note, 22% of patients reported dental decay and nearly 1 in 3 female patients experienced vaginal dryness (Table 1). EQ-5D-3L utility, EQ-5D-3L VAS, and FACIT-F scores were 0.741, 63.5 and 31.3 across all SjD patients respectively, compared to the population norms of 0.867, 79.3 and 43.5. Patients with SjD experiencing dental decay or vaginal dryness reported lower PRO scores than the overall SjD population (Table 2).
Conclusion: Analyses from this multinational survey revealed that patients with SjD are burdened with multiple diagnostic tests and physician consultations to manage their symptoms following diagnosis. There is a substantial impact of SjD on patients’ general QoL, fatigue, and work productivity, which is worsened in patients with dental decay or vaginal dryness, which highlights the systemic nature of dryness and downstream consequences of oral dryness. These findings suggest an unmet need among patients with SjD, who may require additional management by dentists or sexual health professionals who currently have limited involvement in patient care.
Note that base size fluctuates due to data completeness for all variables.
The EQ-5D_3L Utility score is measured on a scale of 0_1 where 1 indicates full health and 0 death. The EQ-VAS is measured on a 0_100 scale with 100 indicating full health. The FACIT-Fatigue is measured on a scale of 0-52 where lower scores indicate more severe fatigue. EQ-5D_3L Utility and EQ-VAS population norms are taken from Janssen, MF et al., 2019 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-018-0955-5), and the FACIT-Fatigue population norm from Montan et al., 2018 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2018.03.013). WPAI is measured using a series of questions asked to patients about how their disease affects their work and normal activities. Absenteeism refers to work time missed due to disease. Presenteeism refers to impairment whilst working due to disease.
FACIT: Functional assessment of chronic illness therapy; SD: standard deviation; US: United States; VAS: visual analogue scale
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McCoy S, Baer A, Xi A, Moorhead C, Castellano G, Amatucci A, Alevizos I, Patel H. Disease Burden of Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Disease: Results from a Multinational Real-World Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-burden-of-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-disease-results-from-a-multinational-real-world-survey/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-burden-of-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-disease-results-from-a-multinational-real-world-survey/