Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) adherence is suboptimal and is associated with disease flare, DAS-28 response, radiographic damage and healthcare costs. Adherence can be measured using self-reported questionnaires such as the validated Medication Adherence Report Scale (MARS-5). Often the prescriber is blinded to patient non-adherence and self-reported adherence may be an underestimate. Our group has previously developed a sensitive biochemical assay for the detection of MTX adherence, The Methotrexate use Improvement in Rheumatoid Arthritis using Biomarker Feedback (MIRA) is a feasibility trial designed to assess the feasibility of a randomised controlled trial of MTX biochemical adherence biofeedback. Here we investigate the agreement between self-reported and biochemical adherence.
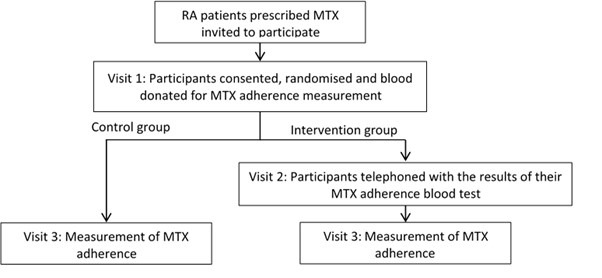
Methods: MIRA is a prospective multi-centre randomised controlled trial investigating the feasibility of a fully powered randomised controlled trial to examine if a biochemical adherence guided intervention is superior to standard clinical care in RA patients. All analyses are exploratory in nature. RA patients prescribed oral MTX for ≥ two years were randomised 1:1 to receive biochemical adherence biofeedback or control (figure 1). Clinico-demographics, biochemical MTX adherence, MARS-5 and DAS-28 were measured at baseline and three months. Self-reported MARS-5 adherence was dichotomised and agreement with biochemical adherence analysed using Cohen’s Kappa.
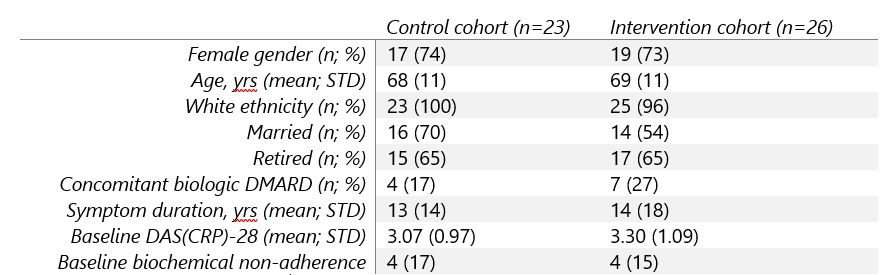
Results: 57 participants were recruited, withdrawal rate was 14% and reasons given were intercurrent illness, lost contact, withdrawn consent and one patient died during follow-up leaving full outcome data available for 49 participants. Baseline clinico-demographics were similar in control and intervention cohorts (Table 1).
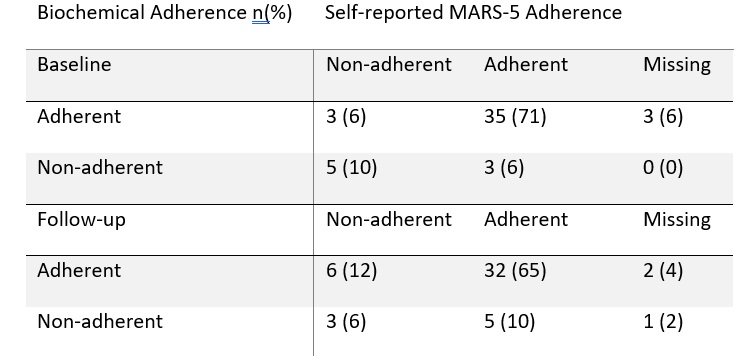
Biochemical adherence worsened in the control cohort and improved in the intervention cohort (83 to 70%, 85 to 92% respectively) whilst change in DAS(CRP)-28 worsened in the control cohort and improved in the intervention cohort (-0.04 STD 1.26 and 0.38 STD 0.78 respectively). Self-reported and biochemical adherence demonstrated fair agreement (κ=0.24) at baseline but poor (κ=0.09) at follow-up (Table 2).
Conclusion: The MIRA trial has shown early evidence of biofeedback improving MTX biochemical adherence and DAS-28 compared to control. Poor agreement between self-reported and biochemical adherence suggests biochemical adherence may be a more clinically useful measure of adherence.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bluett J, Hyrich K, Keevil B, Doran P, Barton A. Self-reported Methotrexate Adherence Underestimates Biochemical Adherence: Results from the Methotrexate Use Improvement in Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Biomarker Feedback Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-reported-methotrexate-adherence-underestimates-biochemical-adherence-results-from-the-methotrexate-use-improvement-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-biomarker-feedback-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-reported-methotrexate-adherence-underestimates-biochemical-adherence-results-from-the-methotrexate-use-improvement-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-biomarker-feedback-trial/