Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1913–1944) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD) is an immune-mediated disease characterized by dense lymphoid-lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates with high IgG4-positive plasma cells with heterogeneous clinical manifestations. The data on IgG4-RD phenotypes variation is mounting but limited to Caucasian and Asian population. In our study we describe a IgG4-RD clinical and immunosuppressive (IS) treatment in four major ethnic groups.
Methods: This is a retrospective analysis of IgG4-RD records from Northwell Health Rheumatology seen between 2011 and December 2023. Diagnosis of IgG4RD was confirmed by manual medical records review. Demographics data, disease characteristics, IgG4 serum level and pathology descriptors were recorded. Descriptive statistics were used for statistical analysis. We calculated the chi-square test statistic using the observed frequencies among the four ethnicities.
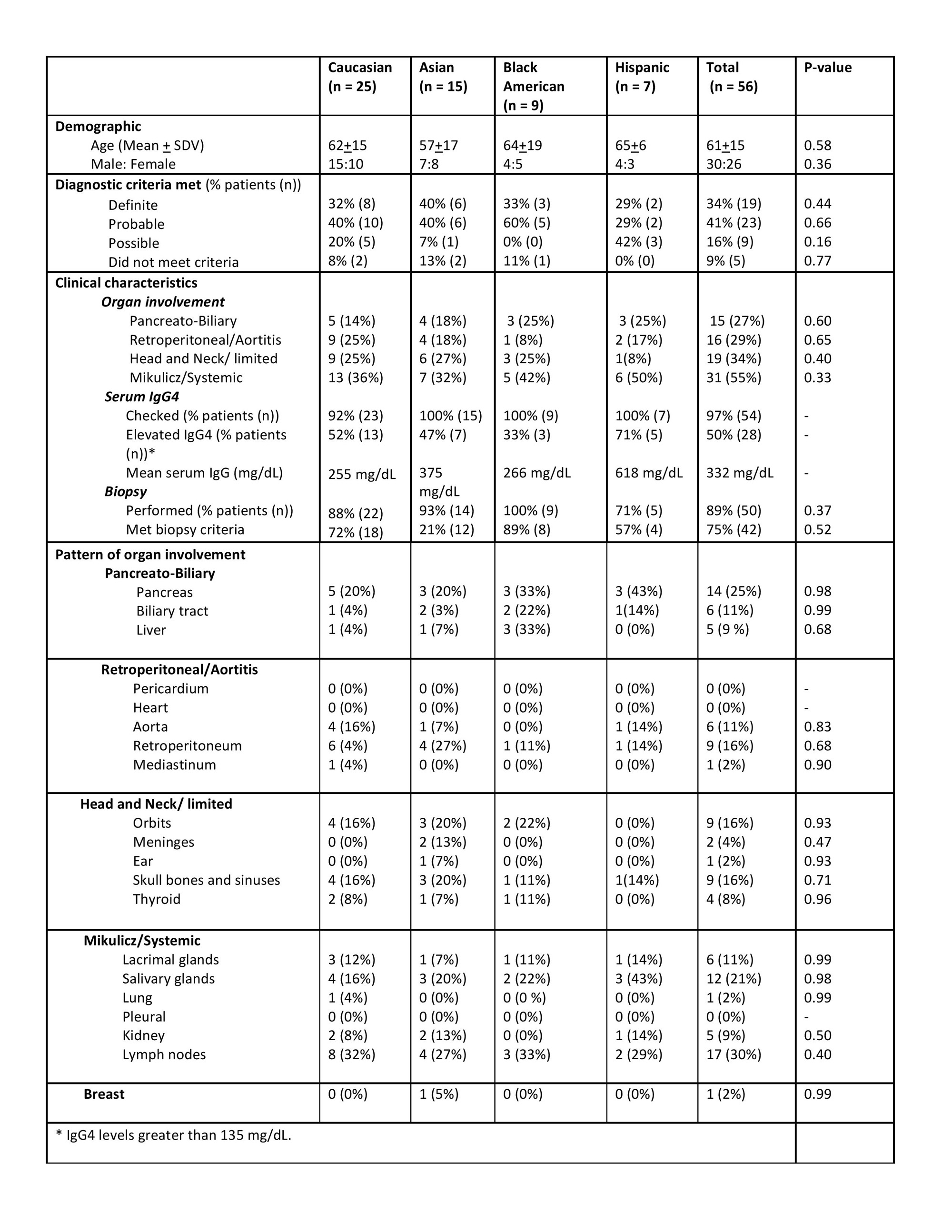
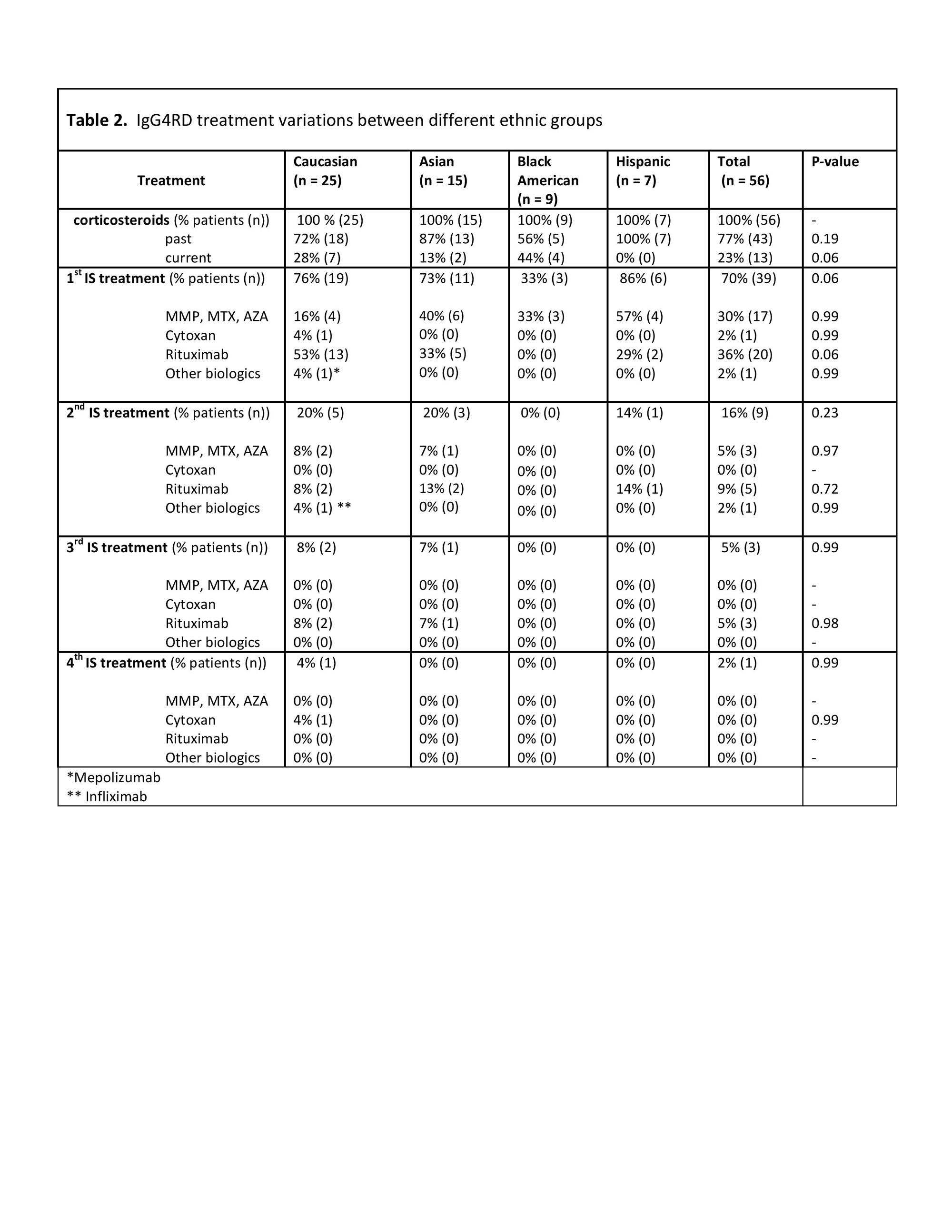
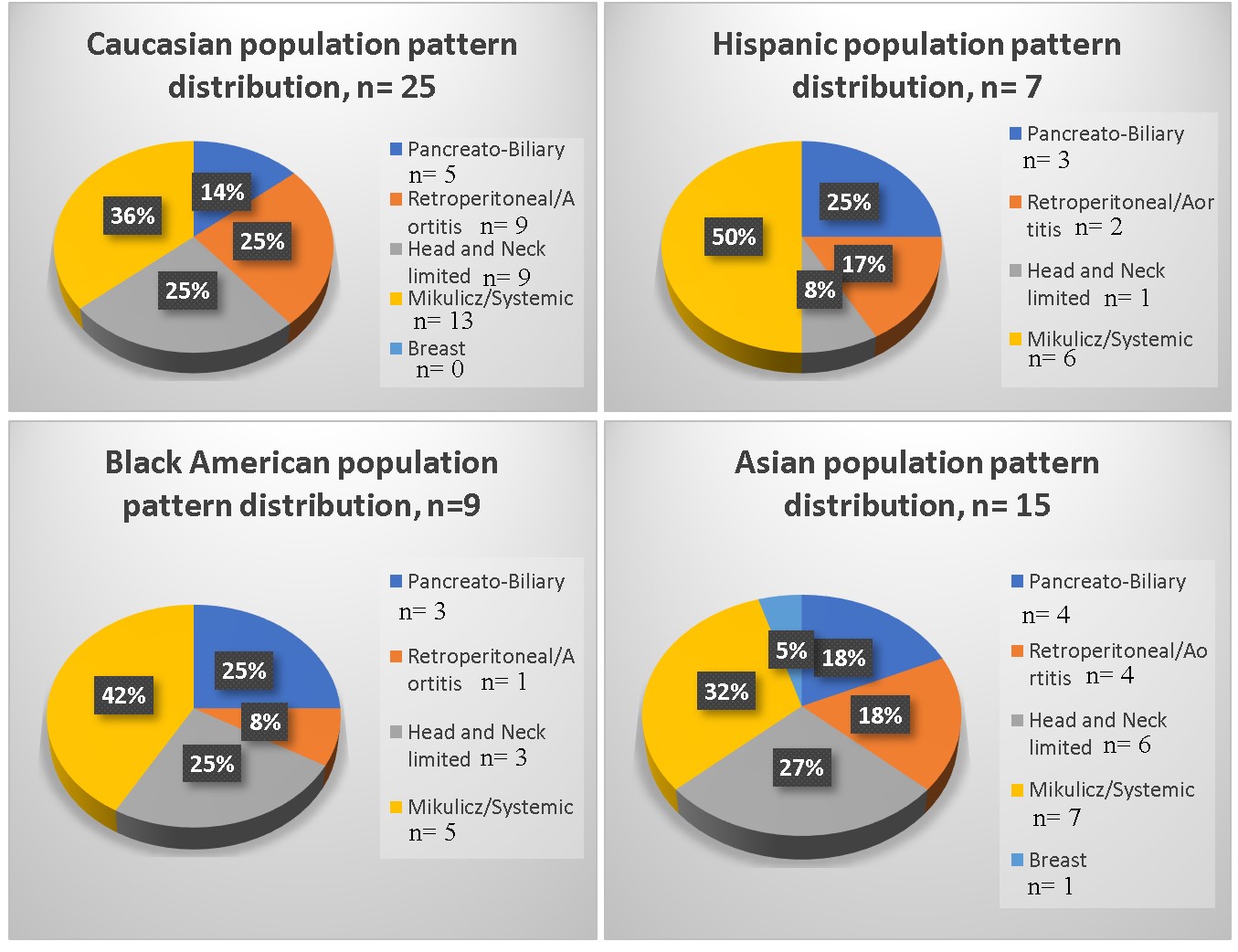
Results: 56 patients with diagnosis of IgG4RD were identified from the Rheumatology Northwell database. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the total cohort and ethnic subgroups in (Table 1). 45% (25/56) of patients were Caucasian, 27% (15/56) – Asian, 16% (9/56) – Black, and 13% (7/56) – Hispanic. 99% (51/56) met 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic criteria for definite, probable, possible IgG4RD. 89 % met pathologic criteria (Table 1). Clinical manifestations showed significant overlap of clinical clusters among the four ethnicities (Figure 1). The most prevalent manifestation was Mikulicz/systemic, observed in half of all patients, followed by 34 % head and neck limited and 29% retroperitoneal. Retroperitoneal domain was more commonly recorded in Caucasians (36 % (9/25)) with 16 % of aortitis while frequency in Black patients was 11 % (1/9) and no aortitis was observed. Meningeal and ENT involvement was much more common in Asian subgroup (40%) compared to only 10 % in other ethnicities. The only case of breast IgG4RD was recorded in Asian subgroup. All patients across all ethnic groups received corticosteroids as initial therapy. 1st line immunosuppressive agent was used in more than 70% of all patients. Similar distribution was recorded for Caucasians, Asians, and Hispanics. Blacks were less likely (33%) to be on IS and none was on 2nd line IS therapy. Furthermore, 8-14% of Caucasians, Hispanics and Asian patients received rituximab, it was not used for Blacks patients (Table 2). No statistically significant evidence among the four ethnicities was found.
Conclusion: Significant overlap of clinical clusters was observed among the four ethnicities. Mikulicz /systemic pattern was highly predominant among entire cohort and all 4 ethnicities. Asian patients had more common ENT and meningeal involvement. The Blacks were less likely to be on IS agents and were not on rituximab. While this discrepancy with other ethnic groups could reflect more benign disease course, other factors should be investigated further. As New York is home to a highly diverse population, this study contributes important insights that can potentially be applicable to other regions with similar demographic characteristics.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cho Y, Marder G, Sangaraju K, El Khoury L, Shargani K, Fragoso J. Analysis of IgG4-Related Disease in a Diverse Long Island Population: Insights from the Rheumatology Clinic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-igg4-related-disease-in-a-diverse-long-island-population-insights-from-the-rheumatology-clinic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-igg4-related-disease-in-a-diverse-long-island-population-insights-from-the-rheumatology-clinic/