Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: ESR and CRP are two laboratory values usedto assess inflammation. There is data to support that CRPis superior to ESR to detect/monitor inflammation or infection due to its better accuracy and reproducibility.Yet, they are often ordered on patients at the same time – essentially performing two separate tests to measure one biological process. This redundant laboratory testing is leading to higher costs to patients and the health systems, and contributes to excess phlebotomy, without any significant clinical benefits. The goal of this quality improvement project was to implement best practices to reduce ESR co-ordering with CRP within the rheumatologyclinics (one clinic in the university setting, 3 satellite clinics, and one safety net clinic)at an academic medical center.
Methods: We utilized the Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) iterative methodology for continuous improvement.We collected and analyzed baseline information on CRP and ESR ordering at all 5 rheumatology clinics. Several interventions were implementedincludinggeneral education to all rheumatology providers and clinic staff(February 2023), targeted education to a few providers with high ESR/CRP co-orders (March 2023), and removal of the ESR order from the rheumatology order set (March 2023) within the Electronic Health Record (EHR).At the safety net clinic, the ESR order had been deselected as a default order on their order set in March 2021. We monitored ESR and CRP co-ordersand total ESR orders to evaluate the impact of our interventions.
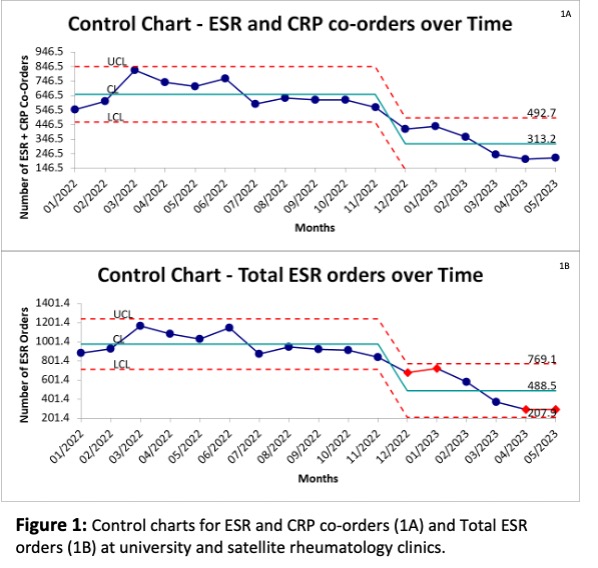
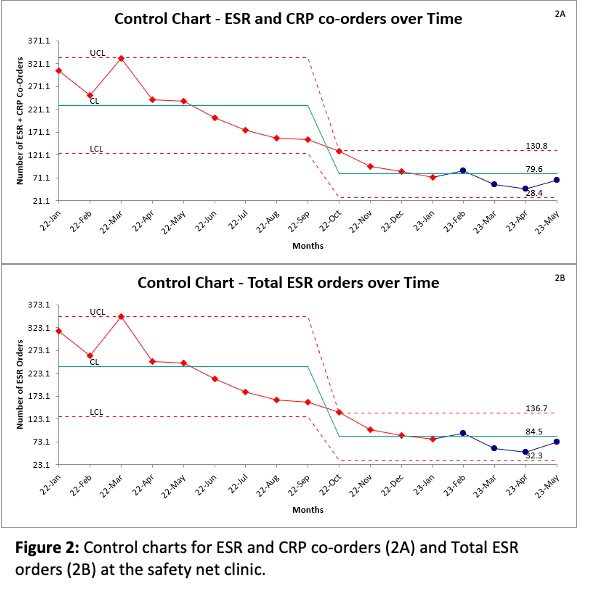
Results: Pre-intervention data analysis of CRP and ESR co-orders within the rheumatologyclinics showed that over 12 months, there were 2,392co-orders at the safety net clinic and 7,250co-orders at university clinics between 1/1/22-11/22/22.The primary reason for co-orders was high-risk medication monitoring for RA and SLE.At the university and satelliterheumatology clinics,the average number of total ESR orders decreased by 50% and the average number of ESR and CRP co-orders decreased by 52% between the time frames of 1/2022-11/2022 and 12/2022-5/2023with major changes in process seen around December 2022 and January 2023 (Figure 1).At the safety net clinic, the average number of ESR and CRP co-orders decreased by 65% and the average number of total ESR orders decreased by 64% between the time frames of 1/2022-9/2022 and 10/2022-5/2023 with major changes in process seen around October 2022 (Figure 2). Orders for CRP alone remained stable at all clinics.
Conclusion: It is feasible to reduce the unnecessary ordering of ESR tests through a systematic approach within the clinics in an academic setting.Educational and EHR interventions can be particularly effective interventions as demonstrated by the significant decrease in both ESR and CRP co-orders as well as total ESR orders.Changes seen prior to February 2023 may be due to the Hawthorne effect as rheumatology providers were aware that the department was investigating this topic. In the future, we plan to modify the ESR order with our EHR to implement changes throughout the health system covering all specialties.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Desai R, Shah N, Zhang R, Bacalao M, Galous H, Karp D, Bajaj P. Reduction in the Concomitant Ordering of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-Reactive Protein Within the Rheumatology Clinics at an Academic Medical Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduction-in-the-concomitant-ordering-of-erythrocyte-sedimentation-rate-and-c-reactive-protein-within-the-rheumatology-clinics-at-an-academic-medical-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduction-in-the-concomitant-ordering-of-erythrocyte-sedimentation-rate-and-c-reactive-protein-within-the-rheumatology-clinics-at-an-academic-medical-center/