Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1776–1795) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Enthesitis is one of the most distinctive features and signs of ectopic bone formation in ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The Wnt/β-catenin pathway and Th17 cells are closely associated with pathological bone formation in AS, but their association has not been fully understood.
Methods: Twenty-five healthy control (HC) and seventy AS sera was subjected to ELISA for human TNF, IL-17A, and WNT5a. Ten PBMC (three HC and seven AS) and seven enthesis cells (three control- and four AS-enthesis) were conducted to RNA-sequencing. WNT5a and Receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 2 (ROR2) expression in enthesis were validated by immunohistochemistry analysis in five diseases control and seven AS patients. Next, overexpression or knockdown of ROR2 in primary enthesis was assessed bone-forming activity in the presence or absence of WNT5a treatment. Finally, enthesitis and ectopic bone formation at the ankle were evaluated in treatment with Ror2 mouse shRNA lentiviral particle in curdlan-injected SKG mice.
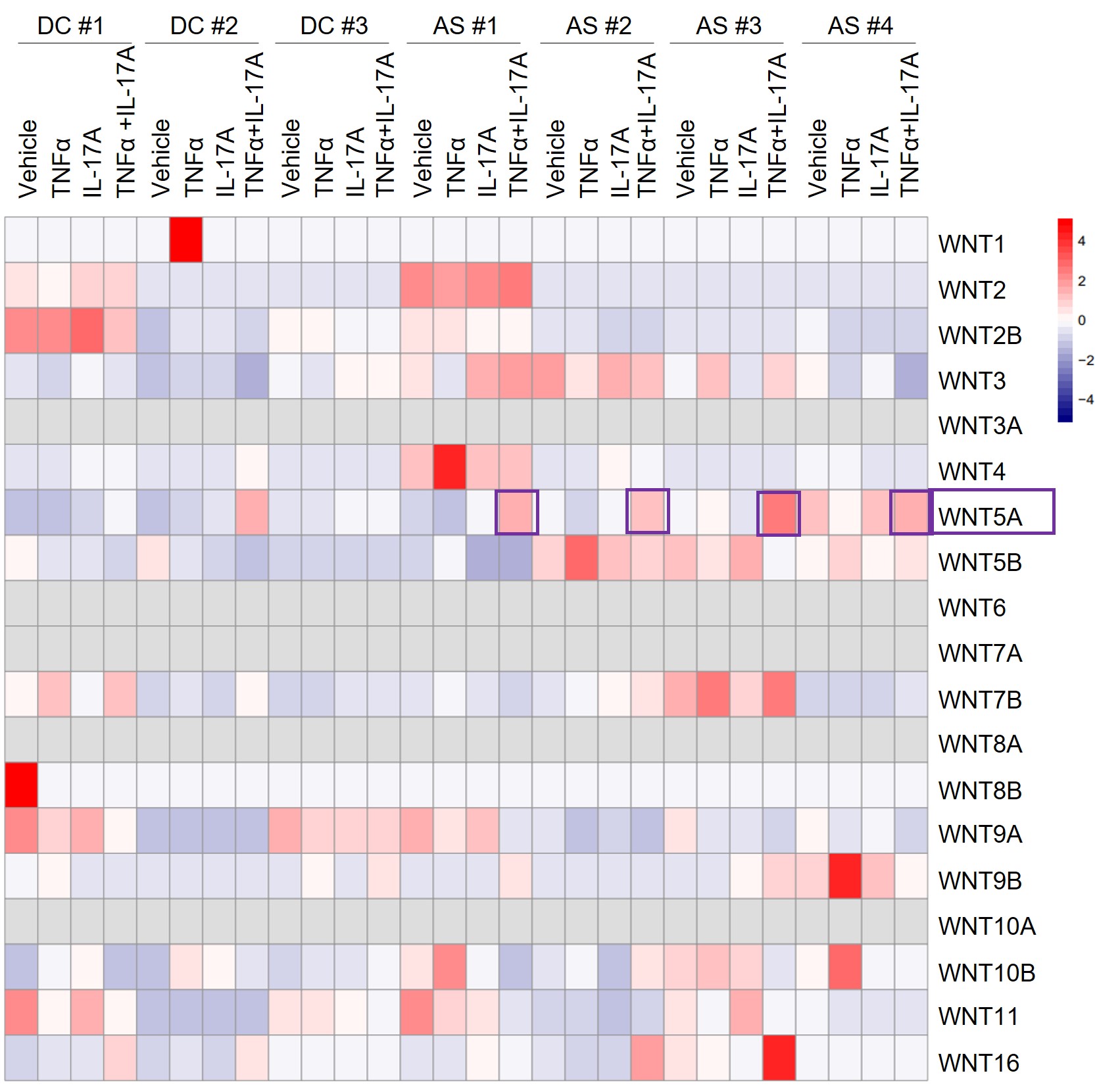
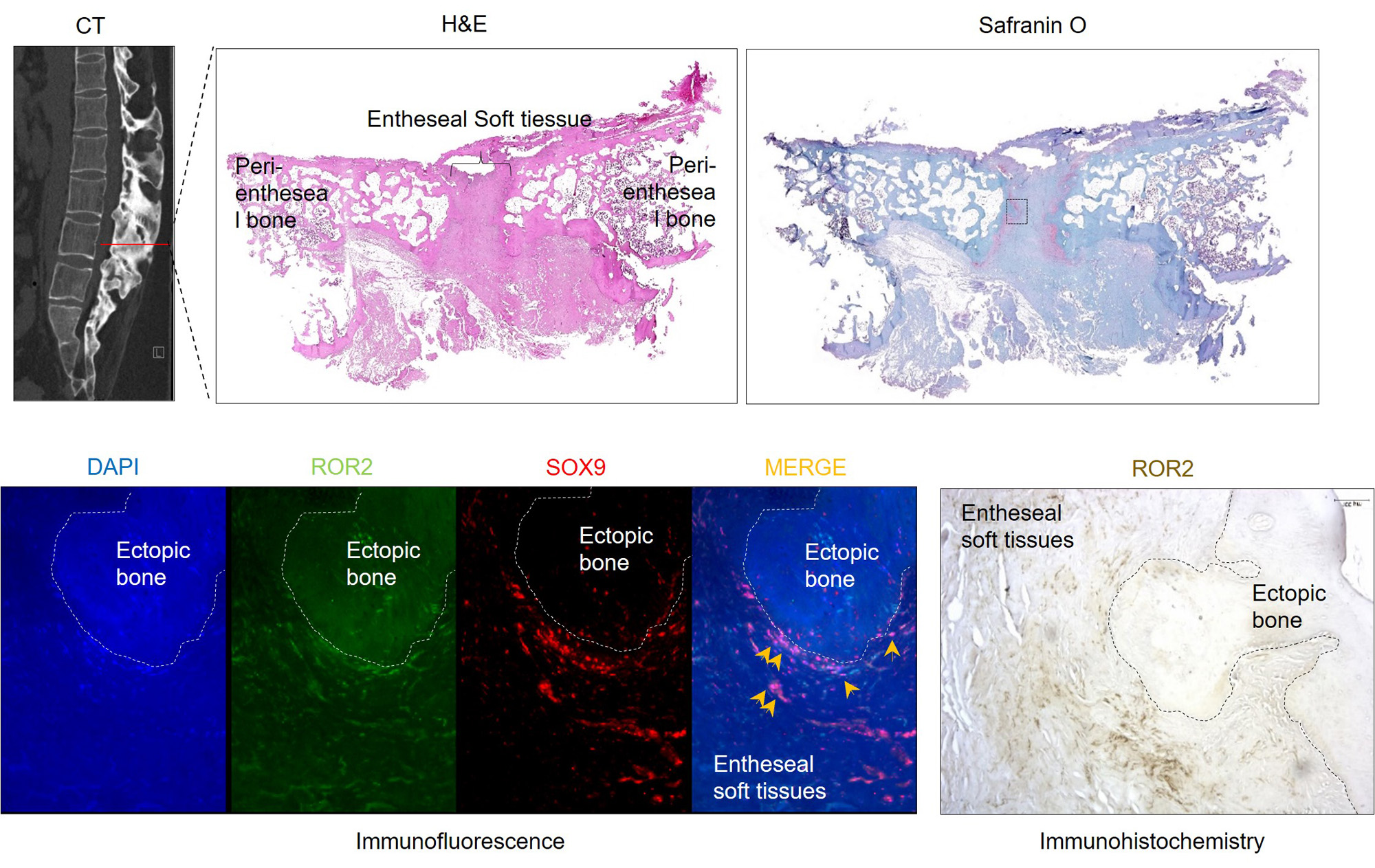
Results: TNF, IL-17A and Wnt5a in AS sera were significantly increased and positively correlated with mSASSS. Co-treatment with TNF and IL-17A dramatically increased WNT5a expression in AS-enthesis cells, as evaluated by RNA-sequencing, RT-qPCR, immunoblotting, and ELISA. Also, co-treatment with TNF and IL-17A augmented the bone-forming activity, bone-related gene expressions (ALP, RUNX2, and OCN), and WNT5A in AS-enthesis cells accompanied as compared to diseases control. Moreover, WNT5A treatment not only upregulated RUNX2 and CTCF expression in AS-enthesis cells via ROR2, but also showed excessive bone-forming activity under osteogenic stimulation. Intriguingly, an increase ROR2 expression in AS enthesis was revealed by RNA sequencing and validated at ectopic bone in spinal enthesis tissues from AS patients. Overexpression of ROR2 in enthesis had an accelerating bone-forming effect in Wnt5a treatment, whereas the knockdown of ROR2 in enthesis had shown the delaying bone-forming activity of AS enthesis in WNT5a treatment. Finally, treatment of Ror2 mouse shRNA lentiviral particle in curdlan-injected SKG mice exhibited a significant decrease in enthesitis and ectopic bone formation at the ankle.
Conclusion: We found that synergism of TNF and IL-17A triggers acceleration of bone mineralization and new bone formation in enthesis via WNT5/ROR2 axis. TNF&IL-17A/WNT5a/ROR2 axis may play a crucial role in pathological new bone formation in AS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jo S, Lee S, Jeon C, Choi S, Park Y, Kim T. The Emerging Mechanism of TNF&IL-17A/WNT5a/ROR2 Axis in Pathological Bone Formation of Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-emerging-mechanism-of-tnfil-17a-wnt5a-ror2-axis-in-pathological-bone-formation-of-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-emerging-mechanism-of-tnfil-17a-wnt5a-ror2-axis-in-pathological-bone-formation-of-ankylosing-spondylitis/