Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: B-cell hyperactivity (1) is a hallmark of the disordered immunity of SLE, arising in the context of a complex array of innate and adaptive mediators. A phase 2 study (NCT03978520) in SLE of upadacitinib (UPA, Janus kinase inhibitor) administered alone or in combination (ABBV-599) with elsubrutinib (a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor). found significant improvement in disease activity, as measured by SLE Responder Index-4 (SRI-4) and BILAG-Based Combined Lupus Assessment, (BICLA) at weeks 24 and 48.
This analysis evaluates response to UPA and ABBV-599 of immunologic pathways associated with SLE pathogenesis.
Methods: Patients with SLE (n = 205) were randomized to placebo (PBO; n = 75), UPA 30 mg once daily (n = 62), or ABBV-599 (n = 68). At screening, patients were stratified by immunosuppressant use (Yes/No), corticosteroid dose ( > 10-mg prednisone or not), IFN score (High/Low), and SLE Disease Activity Index 2000 score. Changes in biomarkers between treatment vs PBO were evaluated with a repeated mixed-linear model, with the Benjamini–Hochberg method used to correct for multiple testing. Total IgG and IgM and anti-dsDNA IgG were measured from serum using a commercially available immunoturbidimetric assay and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. B-cell subsets and immune cell counts were identified using flow cytometry. Plasma samples were collected for proteomic analyses and assessed with a proximity-extension immunoassay.
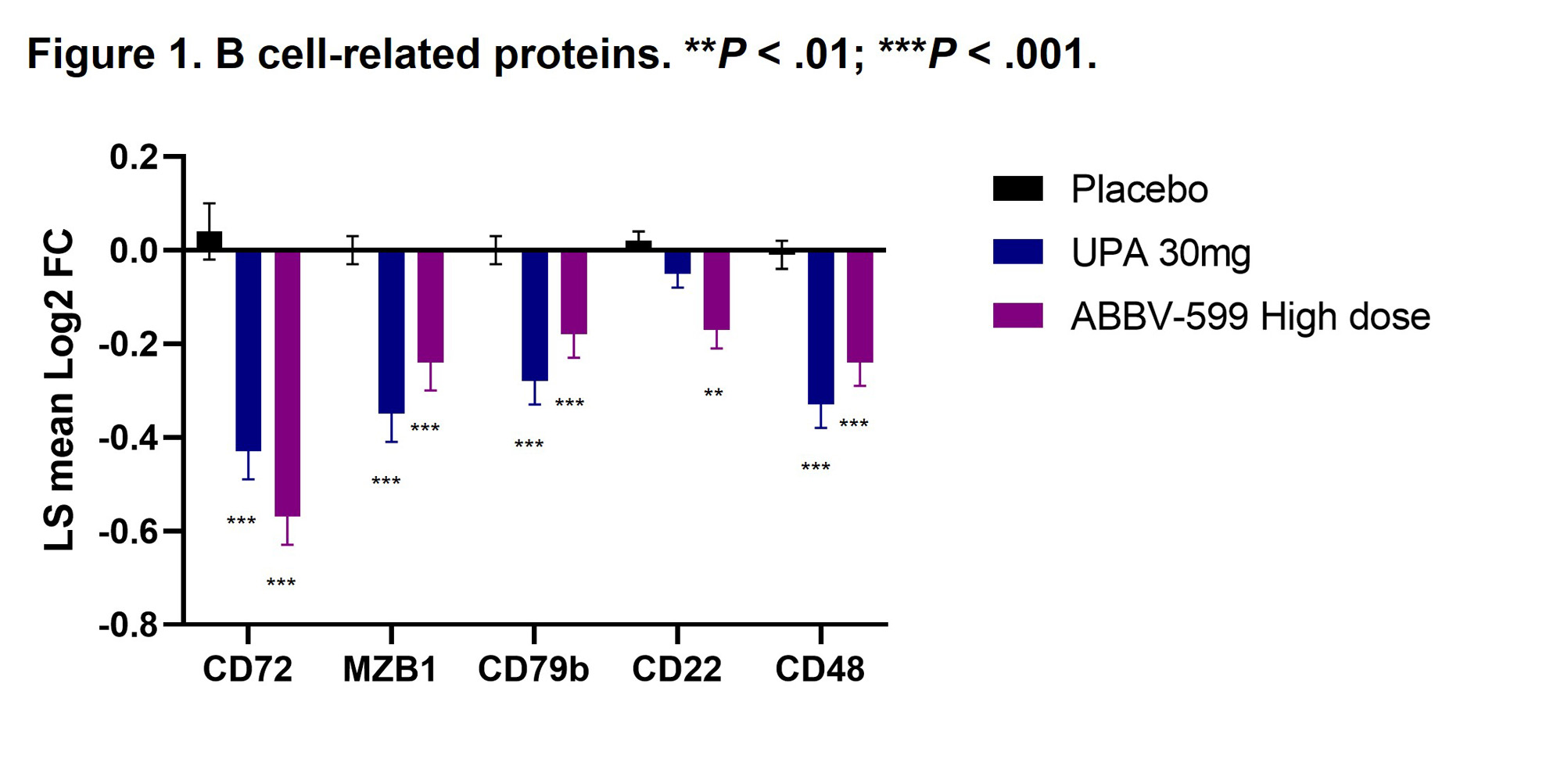
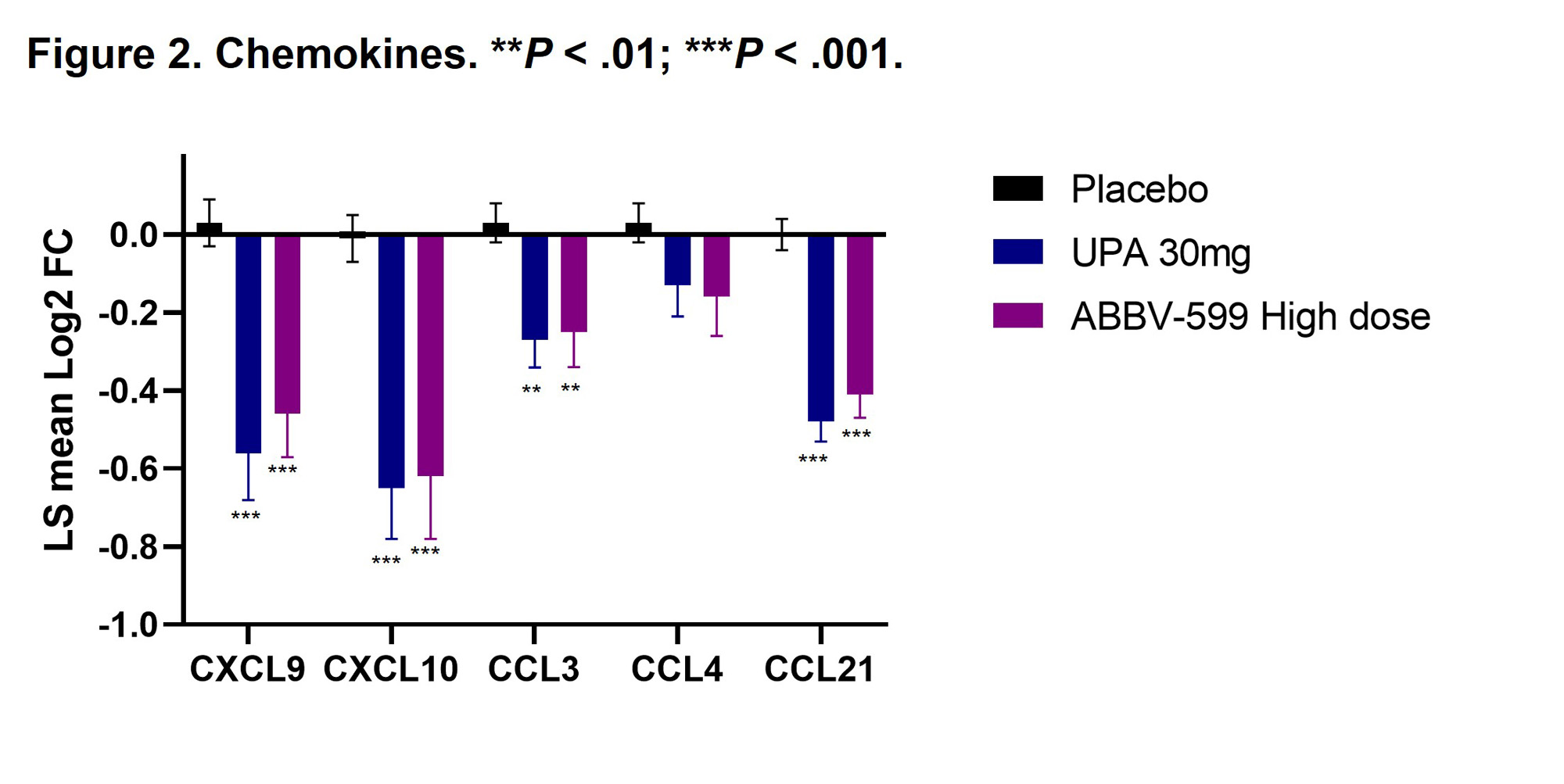
Results: Flow cytometry analyses revealed an increase in absolute number of B cells in the peripheral blood of patients treated with UPA or ABBV-599, while the percentage of plasmablasts and plasma cells were reduced, corresponding to a decrease in total IgG and anti-dsDNA antibodies. Reduction in B-cell activation proteins in plasma such as CD72, CD22 and CD79b suggests a direct impact of UPA and ABBV-599 on B cells (Figure 1). The observed increase in total peripheral B cells could be explained by the marked reduction in chemokines induced by UPA or ABBV-599 including CXCL9, CXCL10, CCL3 and CCL21 (Figure 2). These effects were similar with UPA and ABBV-599, suggesting that the main impact on B cell and plasma cell activating pathways was due to activity of UPA.
Conclusion: These results suggest an association between clinical benefit seen with UPA and an impact on pathogenic B cells involved in SLE, with biomarker effects of both UPA and ABBV-599 apparently driven by UPA. These findings are consistent with our previous analysis in this population that showed treatment with UPA or ABBV-599 significantly reduced the IFN gene scores compared with PBO at weeks 4 and 24. (2)
- Szelinski F, et al. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2022;34(2):125-132. DOI: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000865
- Gaudreau M-C, et al. Abstract 4002. Presented at European Congress of Rheumatology (EULAR), 31 May–3 June 2023, Milan, Italy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gaudreau M, Fann J, Friedman A, Sornasse T, Merrill J. Treatment with Upadacitinib in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Results in the Inhibition of B-Cell–related Biomarkers: Analysis of the M19-130 (SLEek) Phase 2 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-in-the-inhibition-of-b-cell-related-biomarkers-analysis-of-the-m19-130-sleek-phase-2-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-in-the-inhibition-of-b-cell-related-biomarkers-analysis-of-the-m19-130-sleek-phase-2-study/